Tangents to a curve are a line that touches the curve at one point and has the same slope as the curve at that point. A normal to a curve is a line perpendicular to a tangent to the curve. Tangent and Normal
You are browsing archives for
Category: Differentiation
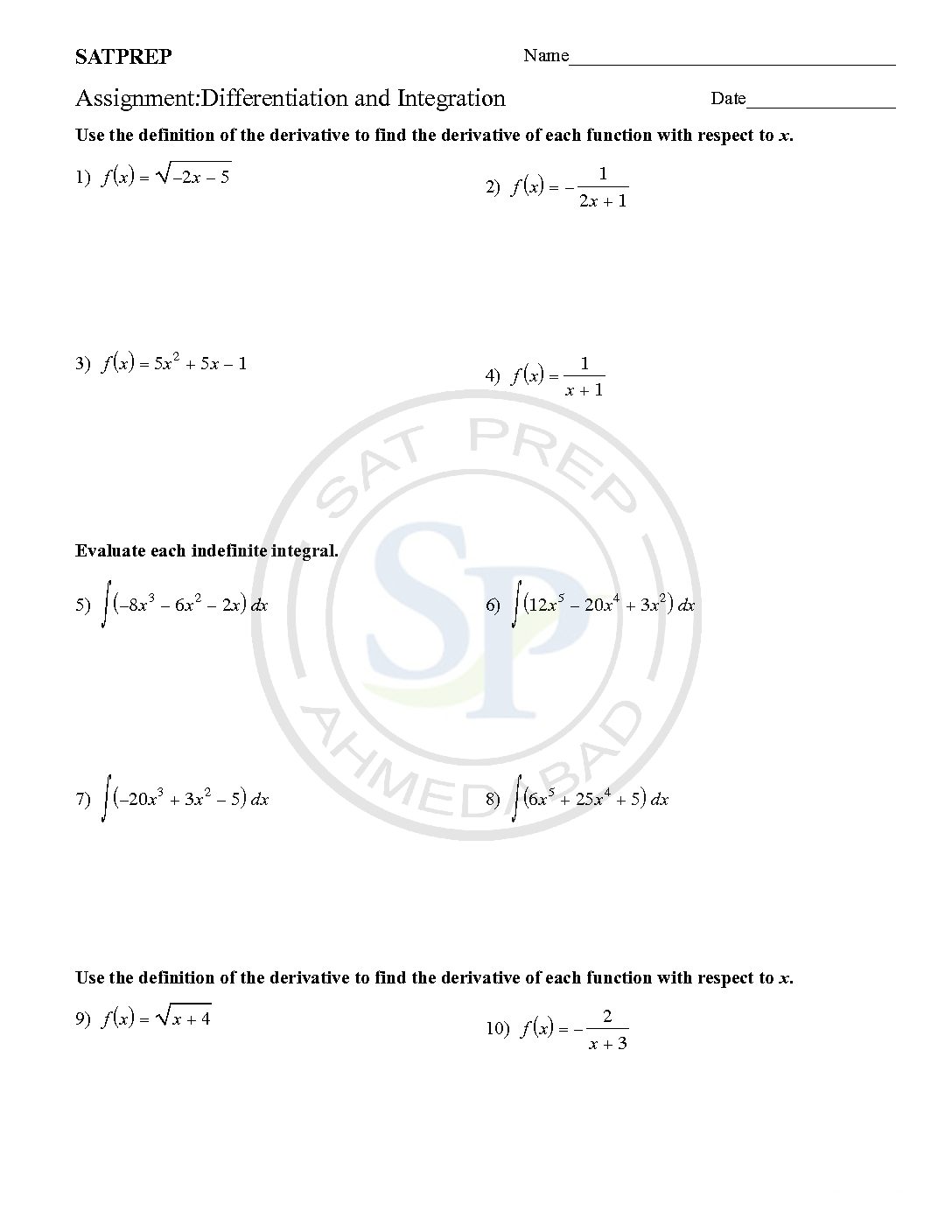
Differentiation and Integration
First of all differentiation and Integration are process of calculus. Due to differentiation we get derivative, while integration of derivative we get function back. Integration also called derivative. Differentiation and Integration
Differentiation of polynomial
Differentiation is process of getting derivative. Differentiation has applications to nearly all quantitative disciplines. For example, in physics, the derivative of the displacement of a moving body with respect to time is the velocity of the body, and the derivative of velocity with respect to time is acceleration. Similarly in chemistry as well as Economics also derivative
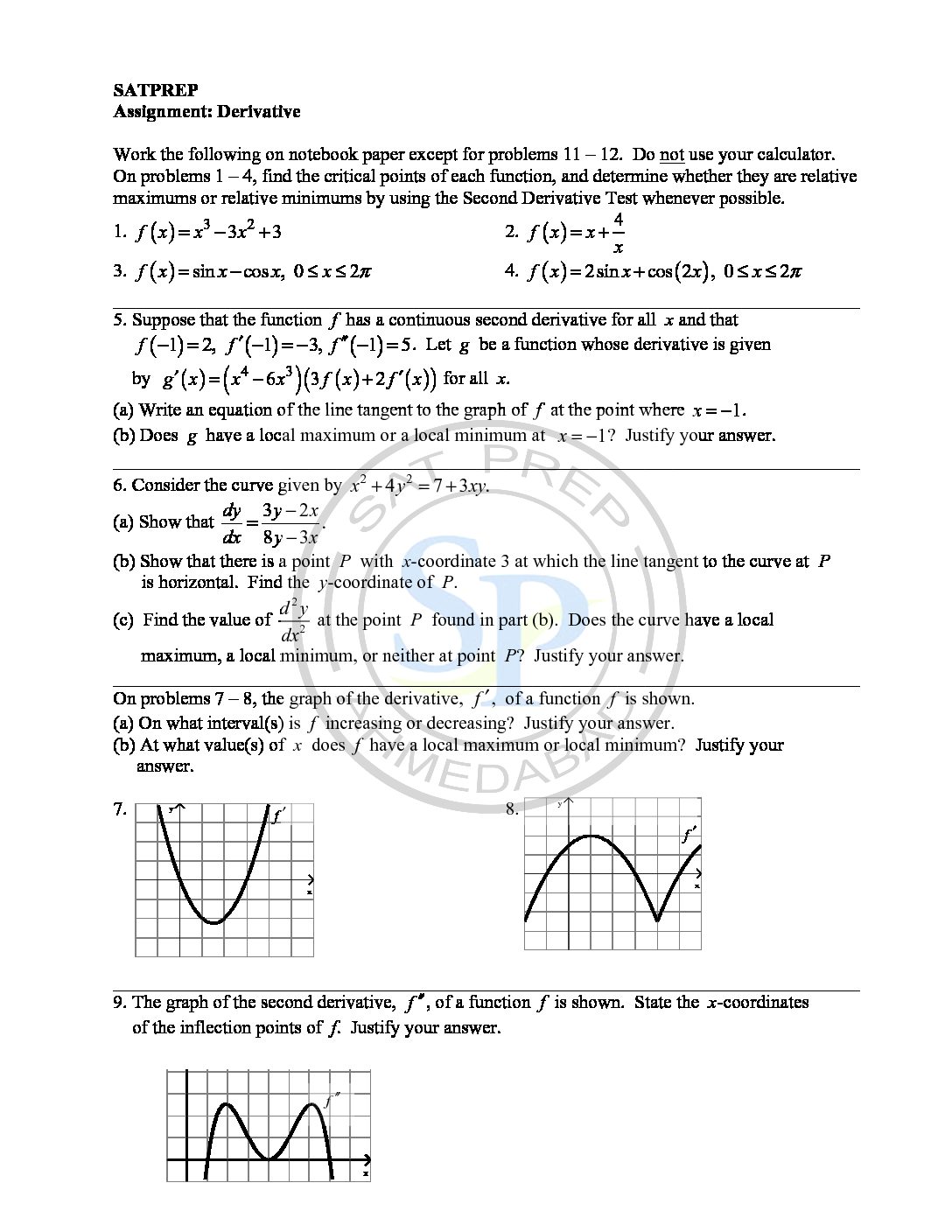
Derivative
The derivative of a function of a single variable at a chosen input value. Derivative is the slope of the tangent line to the graph of the function at that point. Hence derivative of a function y = f(x) of a variable x is a measure of the rate at which the value y of the function changes with respect to the change […]
Curve Sketching -2
the sketching of curve though coordinate of turning and axes intercepts . So equation of the curve is given. Curve sketching
Curve sketching
Coordinate of turning point and axes intercepts for the sketching of curves though . So equation of the curve is given. Curve sketching
Derivative of polynomials
Derivative is product of differentiation. Differentiation has applications to nearly all quantitative disciplines. For example, in physics, the derivative of the displacement of a moving body with respect to time is the velocity of the body, and the derivative of velocity with respect to time is acceleration. Therefore differentiation is process Derivative
Optimization-2
Process of optimisation means optimal value of function at turning point (maximum or minimum ) value of the curve. Therefore second derivative use to find greatest or least value . Also it show greatest value. Optimization
Related Rates -2
First of all related rate problems are applications of derivative . One of the hardest calculus problems that students have trouble . Because each application question has a different approach in solving the problem. Hence called rate of change. Related rates
Kinematics
Describes the motion of points, objects and systems of groups of objects, without reference to the causes of motion. The symbol a stands for the acceleration of the object. And the symbol v stands for the instantaneous velocity of the object. The derivative of displacement with time is velocity ( v = ds/dt ). The […]