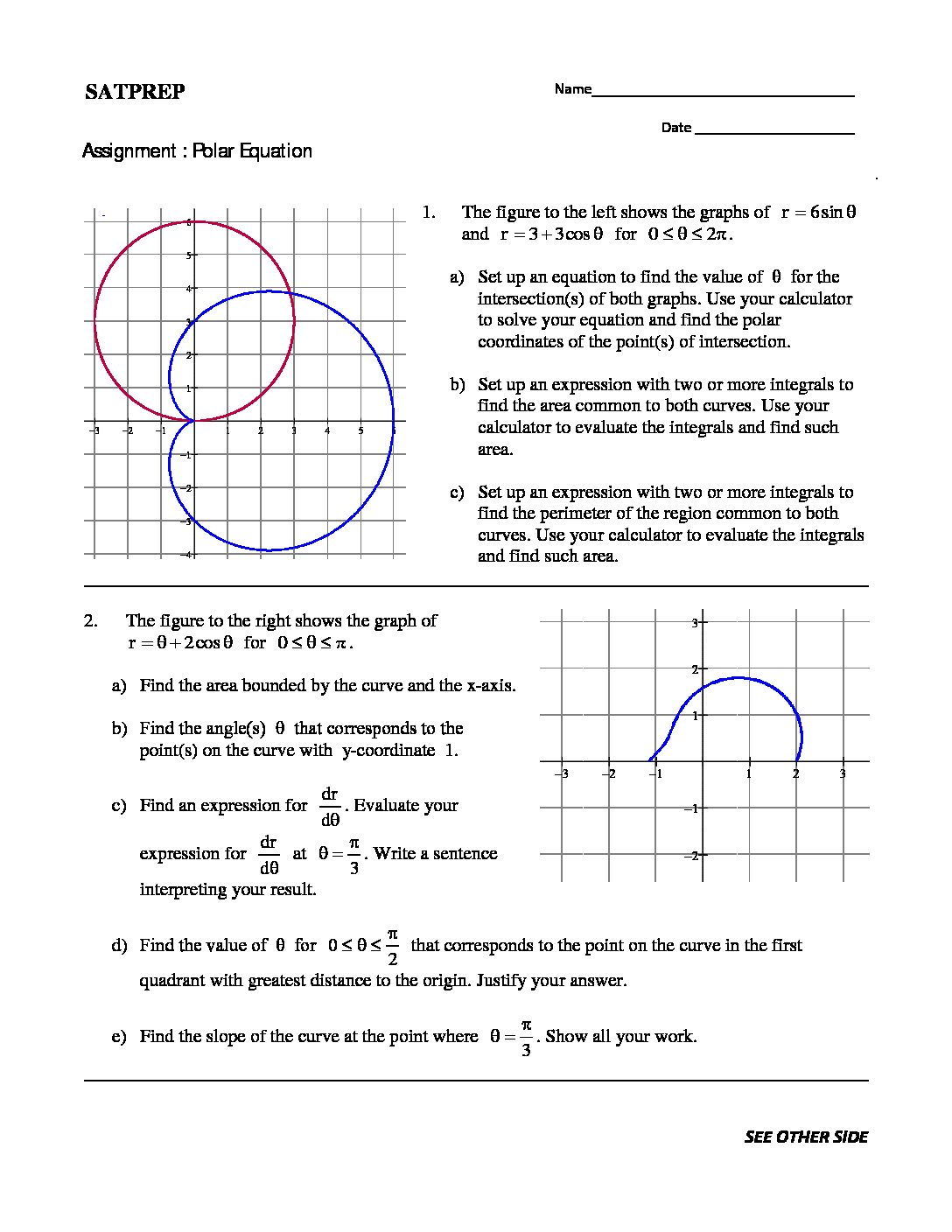
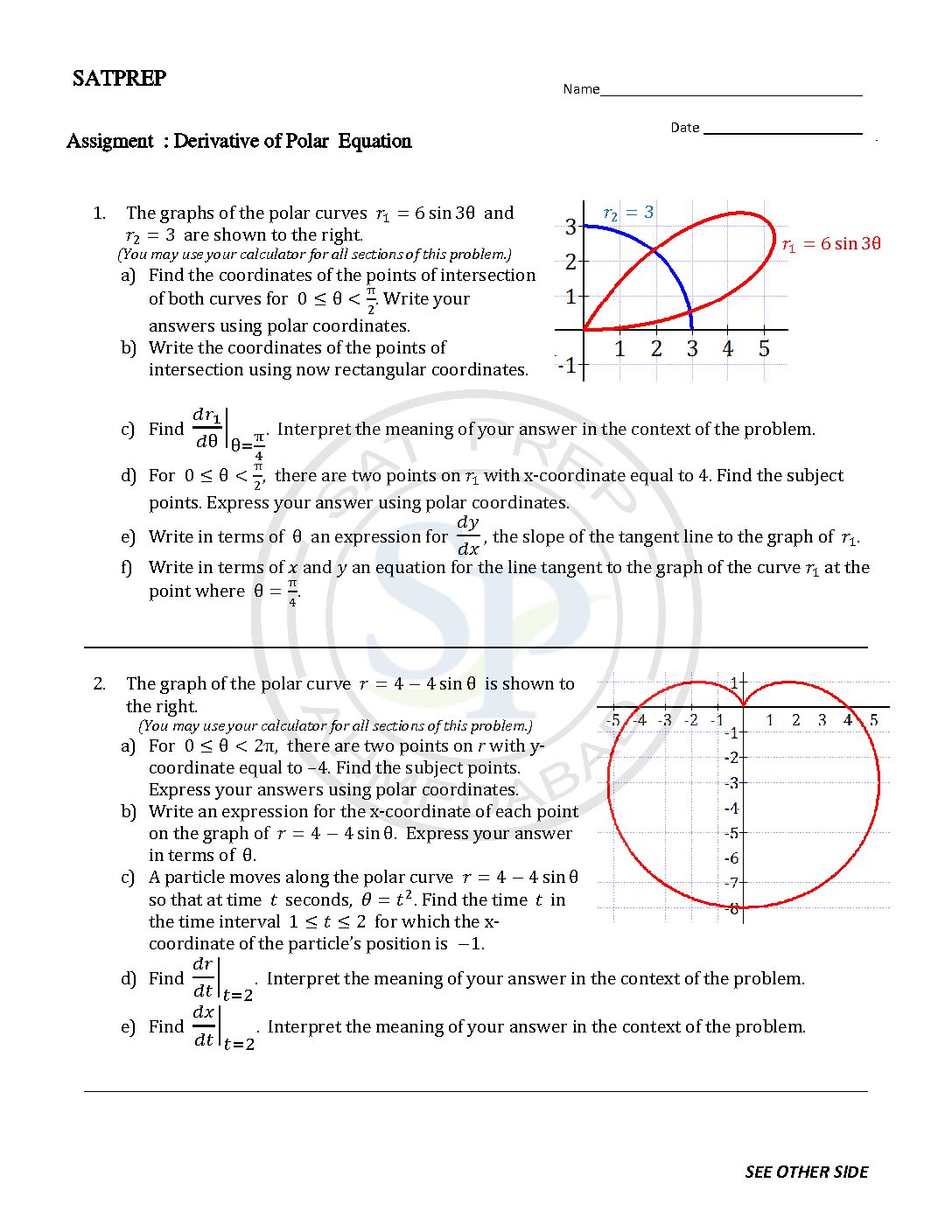
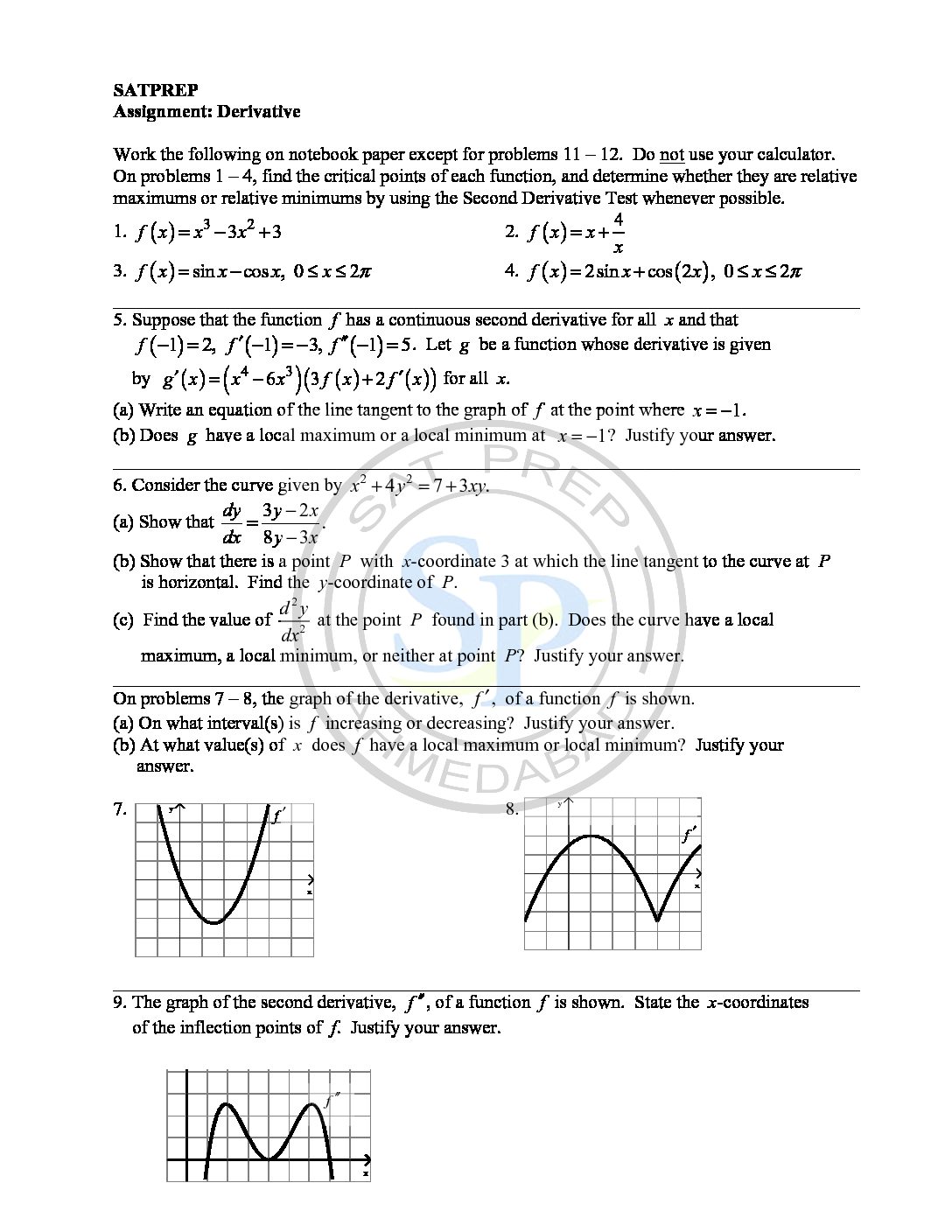
This post is about derivatives of Polar Equations. Because of polar equation, Polar equation like parametric equations of the curve where the angle θ is parameter. As well as equations have parameter (r,θ). For this polar equation, the parametric equations are x ( θ) = cos θ and y ( θ) = sin θ. Therefore, the derivative is which […]
You are browsing archives for
Category: Derivative at a point
Derivative of Polar Equation
This post is about derivatives of Polar Equations. Because of polar equation, Polar equation like parametric equations of the curve where the angle θ is parameter. As well as equations have parameter (r,θ). For this polar equation, the parametric equations are x ( θ) = cos θ and y ( θ) = sin θ. Therefore, the derivative is which […]
Rules of derivative
Rules for derivatives. Rules for derivatives. Sum rule: The derivative of the sum or difference of two functions is the sum or difference of their derivatives. (u + v)’ = u’ + v’ Constant multiple: The derivative of a constant times a function is the constant times the derivative of the function. (ku)’ = ku’ Rules for derivative
Equation of Tangent and Normal
Tangents to a curve are a line that touches the curve at one point and has the same slope as the curve at that point. A normal to a curve is a line perpendicular to a tangent to the curve. Tangent and Normal
Derivative of implicit and inverse trigo...
In calculus, a methods of implicit differentiation, Makes use of the chain rule to differentiate implicitly defined functions. To differentiate an implicit function y ( x ), defined by an equation R ( x, y) = 0, it is not generally possible to solve it explicitly for y and then differentiate. The derivatives of inverse trig functions we’ll need the formula from the last section […]
Point of inflection
Inflection Point. An inflection point is a point on a curve at which the sign of the curvature (i.e., the concavity) changes. Inflection points may be stationary points, but are not local maxima or local minima. For example, for the curve plotted above, the point is an inflection point. Point of infection
Derivative
The derivative of a function of a single variable at a chosen input value. Derivative is the slope of the tangent line to the graph of the function at that point. Hence derivative of a function y = f(x) of a variable x is a measure of the rate at which the value y of the function changes with respect to the change […]
Derivative test
First Derivative Test for Local Extrema. If the derivative changes from positive (increasing function) to negative (decreasing function), the function has a local (relative) maximum at the critical point. Second Derivative Test. 1. If , then has a local minimum at . 2. If , then has a local maximum at . The extremum test gives slightly more general conditions under which […]