This post about practice worksheet of questions of function and equation. The type of questions in this worksheet are non calc. IB
You are browsing archives for
Tag: domain
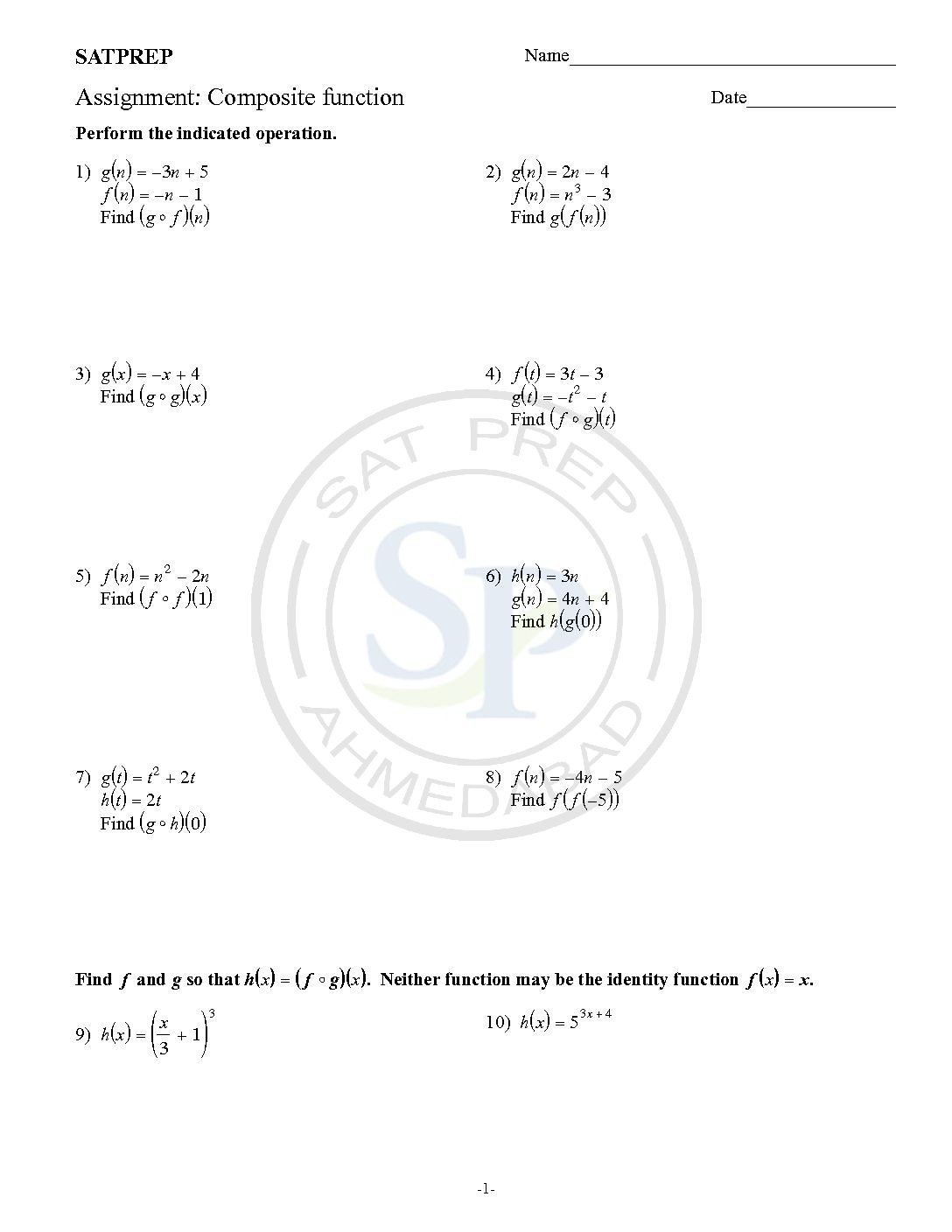
Function – Composite and Inverse
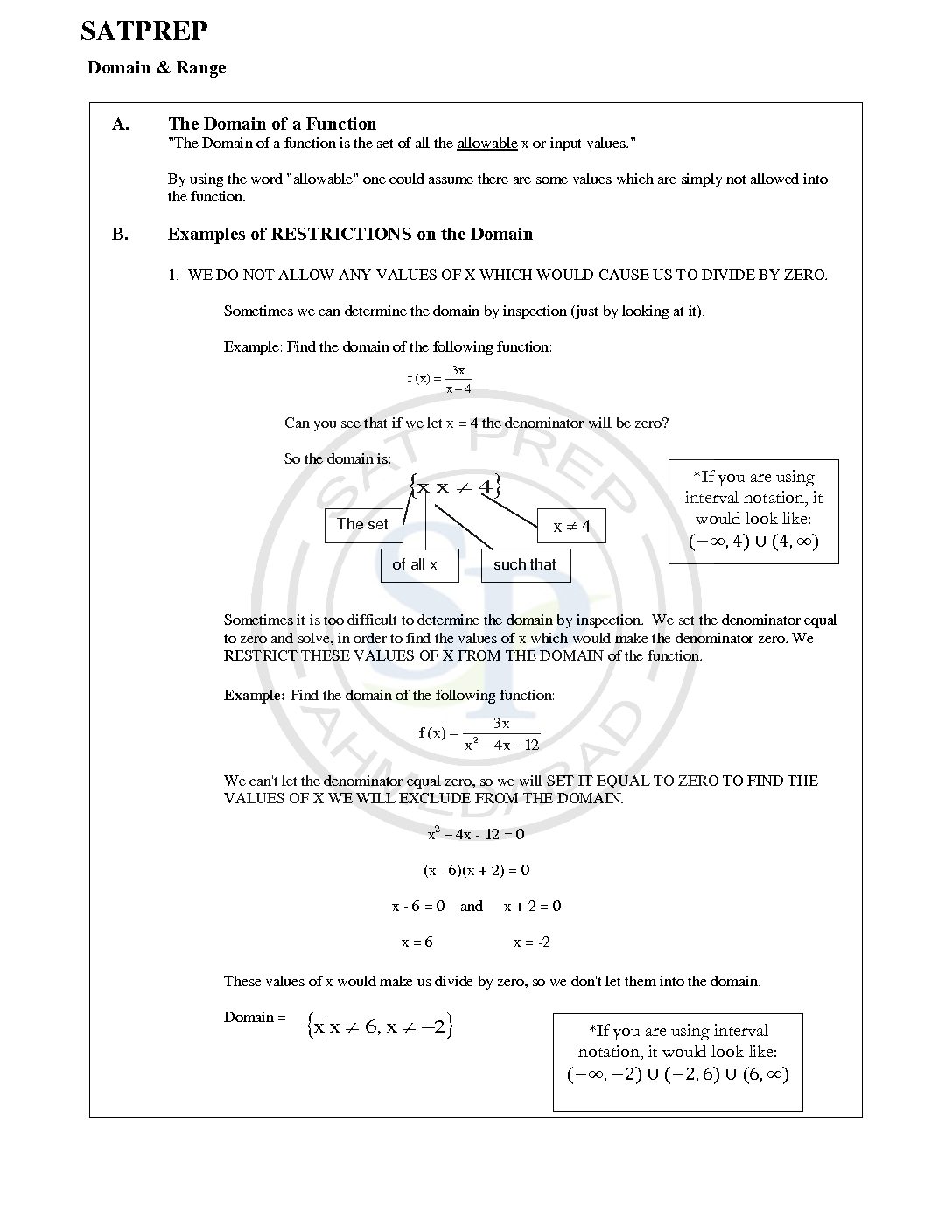
Function -Domain Range
In this post questions are, to find domain and range function. Also have to find domain and range of composite function. Domain and Range
Function-Exponent and logarithm
This post is about Exponential and Logarithm function . These function are inverse to each other. Therefore graph function are reflection about line y = x . The questions are to change exponent to log and reverse. Exponential and Logarithm P P
Domain and Range of Function
Domain and range of functions are an important concept . Domain values define on x – axis and Range is values on y- axis in the graph. Due to these values of functions, continuity of function defined. Another use of domain to show function defined. While range defined minimum and maximum value of function. […]
Domain and Range of Function
Domain and range of functions are an important concept . Domain values define on x – axis and Range is values on y- axis in the graph. Due to these values of functions, continuity of function defined. Another use of domain to show function defined. While range defined minimum and maximum value of function. […]
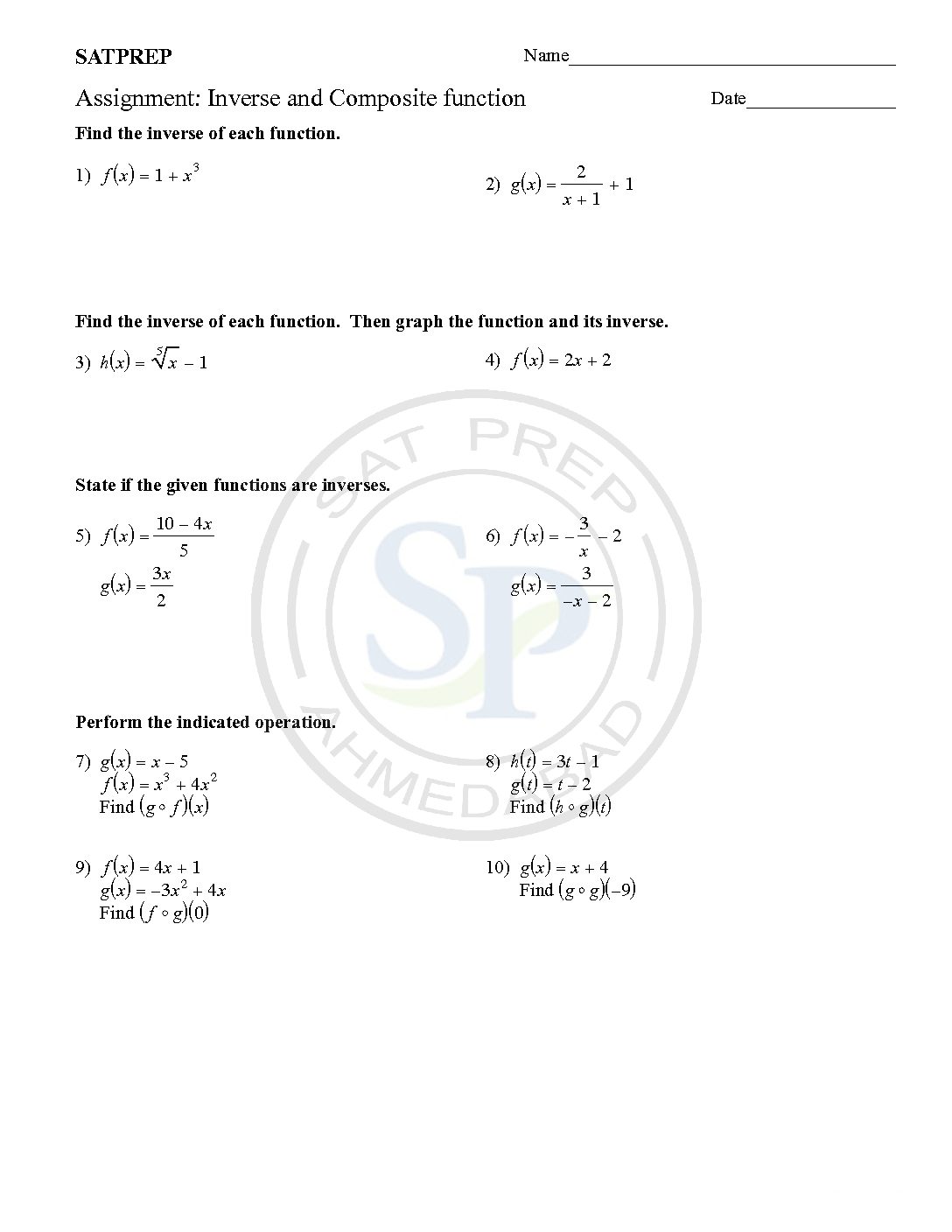
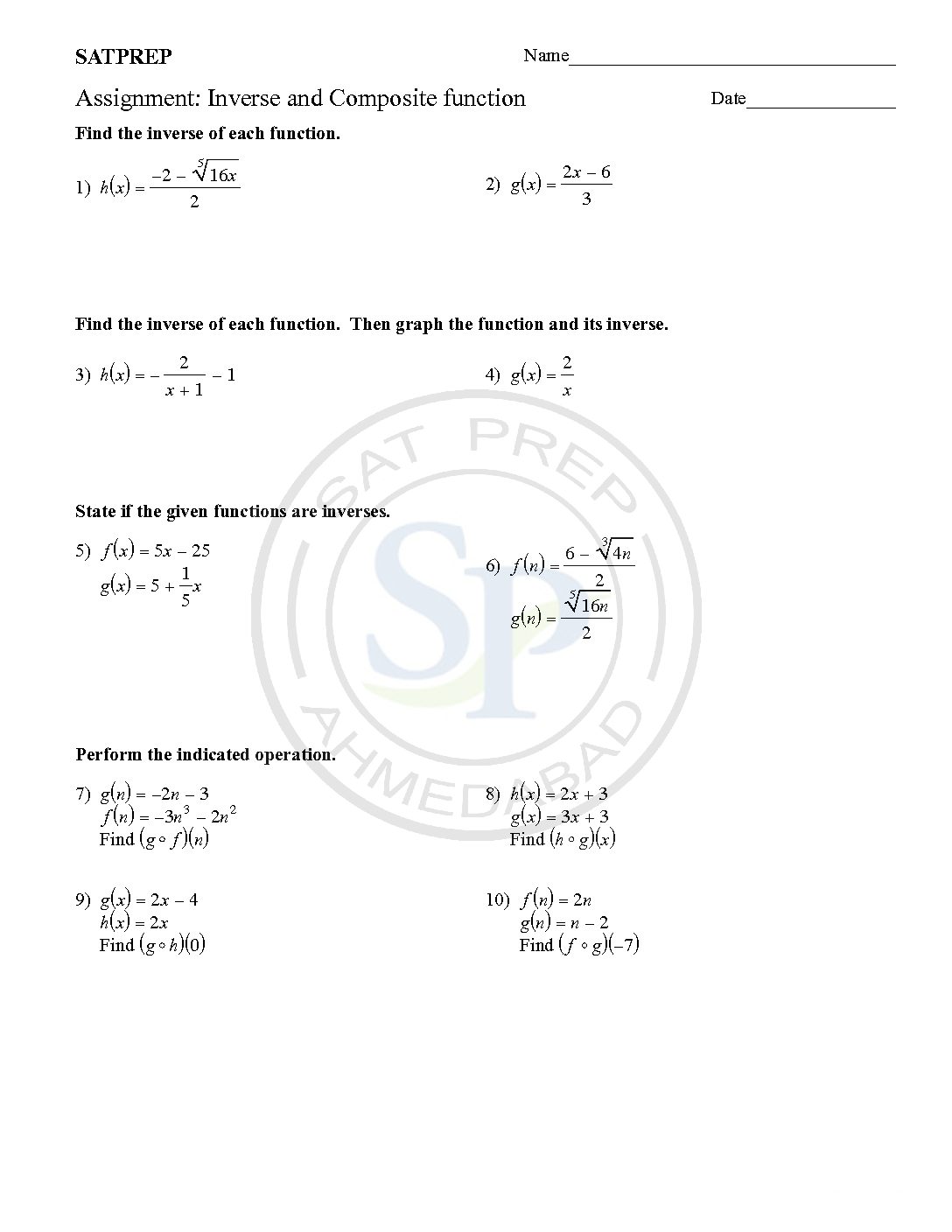
Inverse and Composite function
Inverses and Composites are two important concept of functions. Composite function is defined as one function defined inside another function. Like ff(x)) or f(g(x)) etc. Concept of inverse is interchange of variables . Inverse notations are f-1(x),g-1(x) etc. Hence interchange is inverse. Therefore function and its inverse is reflection about y = x. Inverse and composite
Inverse and composite function
Inverses and Composite are two important concept of functions. Composite function is defined as one function defined inside another function. Like ff(x)) or f(g(x)) etc. Concept of inverse is interchange of variables . Inverse notations are f-1(x),g-1(x) etc. Hence interchange is inverse. Therefore function and its inverse is reflection about y = x. inverse and […]
Function
A function f(x) tells you what to do with the input, but, to be completely defined, function also need to know what type of input is permitted to go into the function. Function
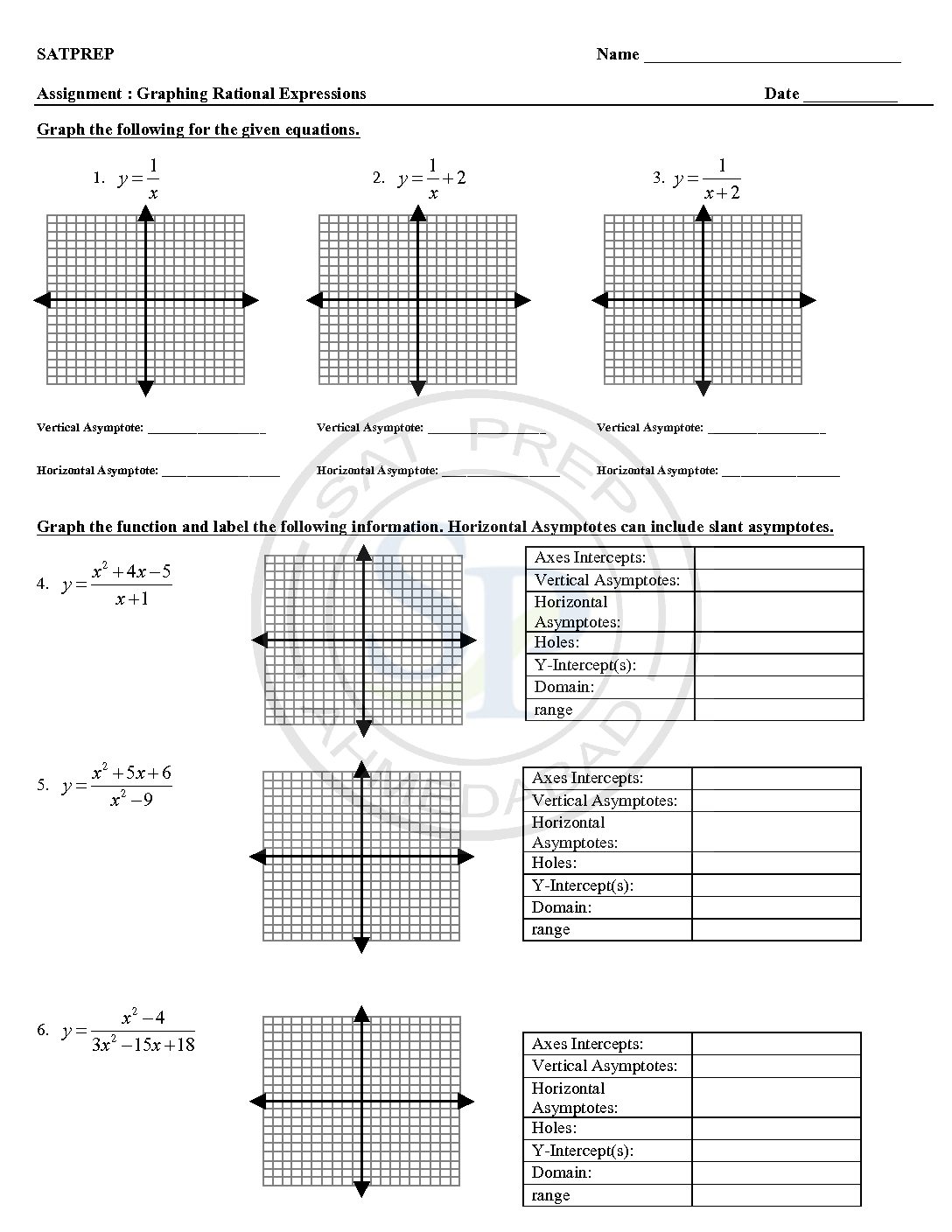
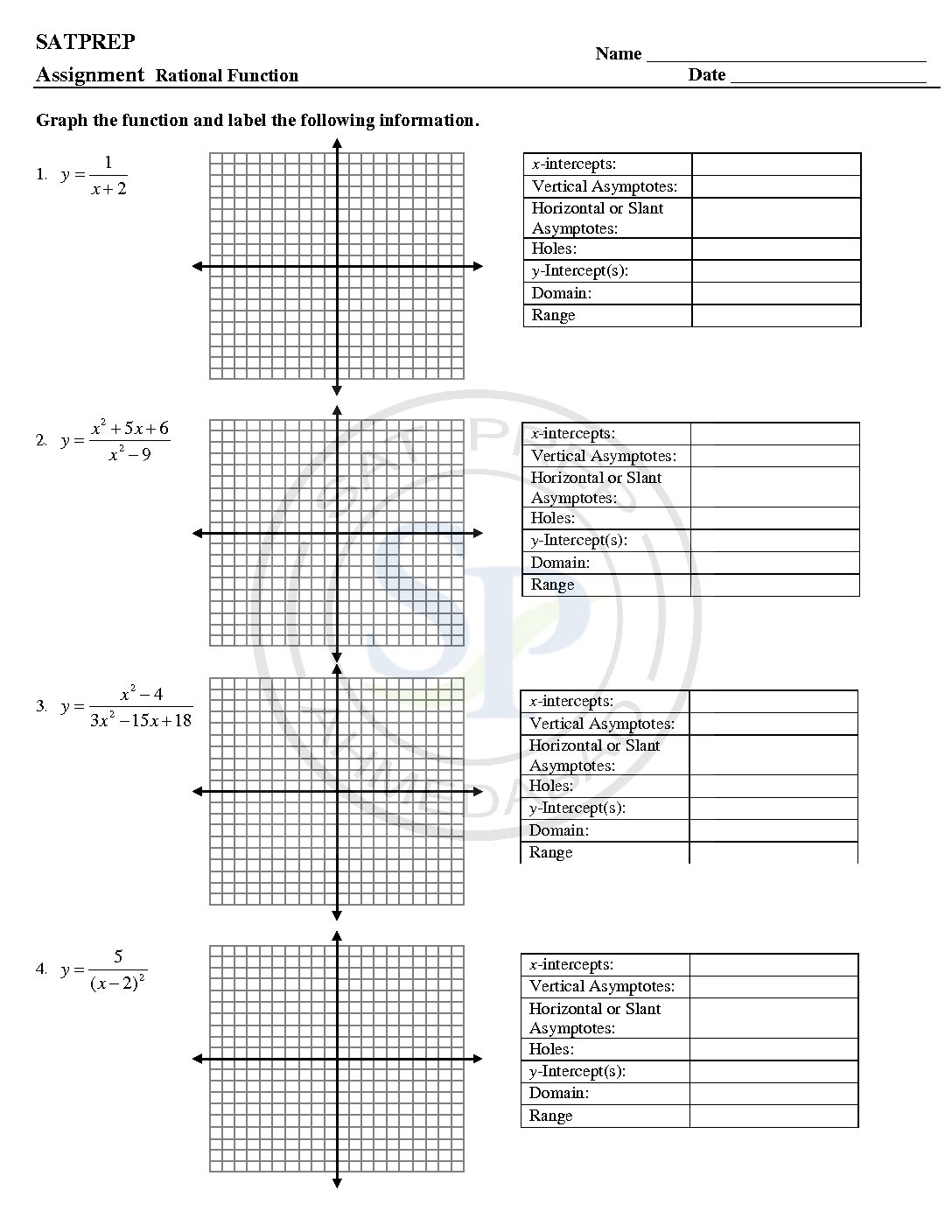
Rational and Reciprocal functions
A rational functions is a function of the form f(x)=p(x)/q(x), where p(x) and q(x) are polynomials and q(x)≠0 ,q(x)≠0 . The domain of a rational function consists of all the real numbers x=0 except those for which the denominator is x= 0 . reciprocal for a number x, denoted by 1/x or x −1, is a number which when multiplied by x yields the multiplicative identity, 1.. The […]