The binomial theorem describes the algebraic expansion of powers of a binomial. Hence, To expand the polynomial (x + y)n into a sum involving terms of the form axbyc. where the exponents b and c are nonnegative integers. also n is positive integer. Binomial_theorem
You are browsing archives for
Category: Expansions
Binomial Theorem
The coefficient of term in expansion of binomial terms. Therefore we use general term of binomial theorem. Also we can use collection of power of x . Binomial theorem
Binomial Theorem (Basic)
Binomial Theorem
This post is about binomial expansion of two terms expression. In this post questions are related with expansion of two terms. Find particular term and find coefficient of particular terms. The Binomial Theorem is a quick way of expanding a binomial expression that has been raised to some higher power. This topic in AS-level , […]
Co-ordinate geometry
A coordinate geometry is a branch of geometry. In this, the position of the points on the plane supported by an ordered pair of numbers also known as coordinates. Coordinate geometry deal about gradient , distance , mid point and equation of line. Also, condition of lines like parallel , perpendicular and inclined lines. In […]
Binomial Theorem
The binomial theorems are a result of expansion of powers of binomial term. It also give sums of two terms. The coefficients of the terms in the expansion are the binomial coefficients. Coefficient of terms are calculate through pascal triangle or combination method. The concept is also related with algebra and calculus. binomial theorem p p
Binomial Theorem
This post is about binomial expansion of two terms expression. Also in this post question, like first of all find particular term and also find coefficient of particular terms. Moreover topic is in AS-level , A-level , IBDP Math HL and SL. To find the coefficient of term we use pascal triangle Binomial Theorem
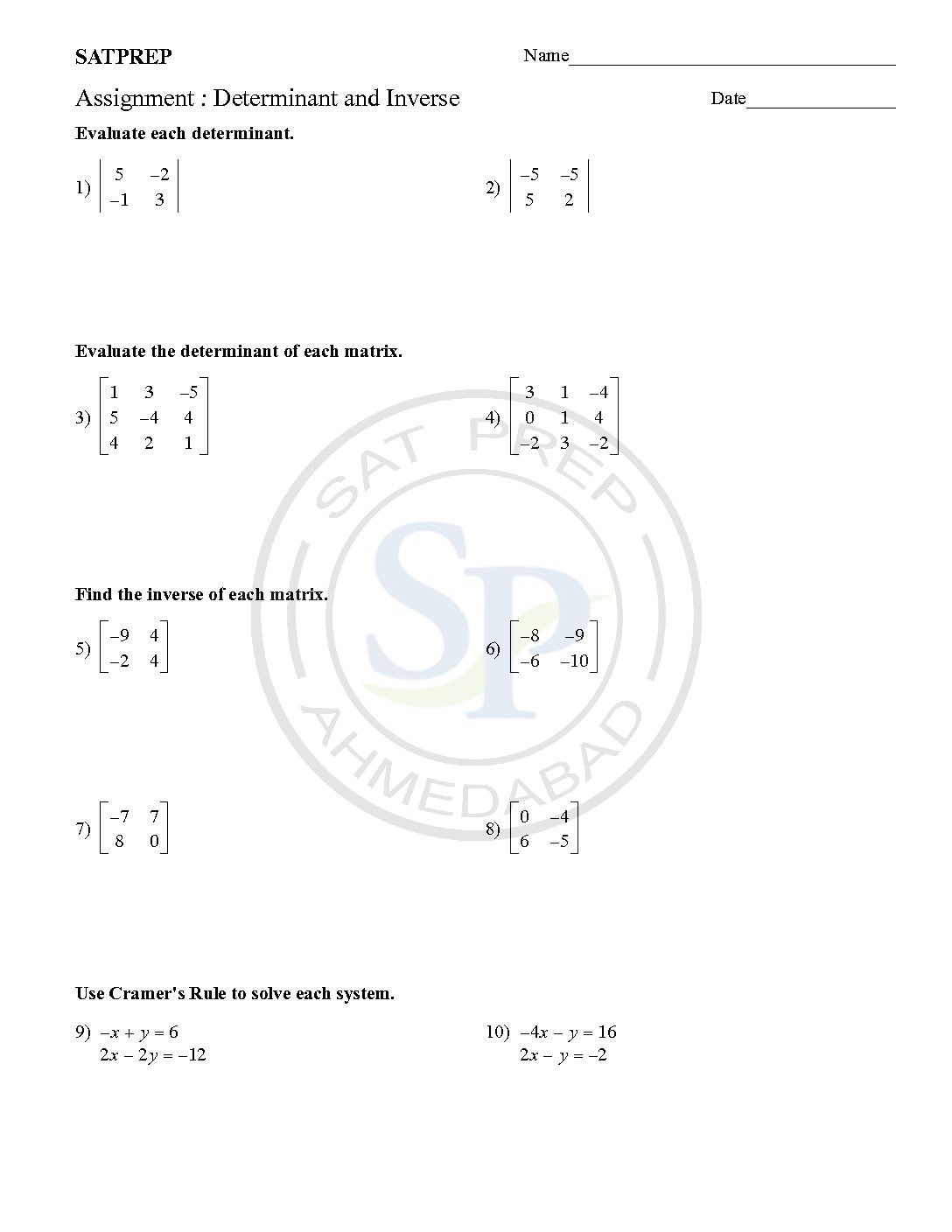
Matrix determinant and Inverse
Determinant det(A) of a matrix A is non-zero if and only if A is invertible or, yet another equivalent statement, if its rank equals the size of the matrix. If so, the determinant of the inverse matrix is given by (−) = (). Matrix
Binomial Theorem
When a binomial is raised to whole number powers, the coefficients of the terms in the expansion form a pattern. Each expansion has one more term than the power on the binomial. The sum of the exponents in each term in the expansion is the same as the power on the binomial. www.kutasoftware.com
Binomial Theorem
Binomial theorems is another ways of expansion of two terms. Another way it is generalised form of expansion. Due to expansion of two term it is binomial. “What are the binomial coefficients?” . It shows how to calculate the coefficients in the expansion of (a + b) n. The symbol for a binomial coefficient nCr. As well as pascal […]