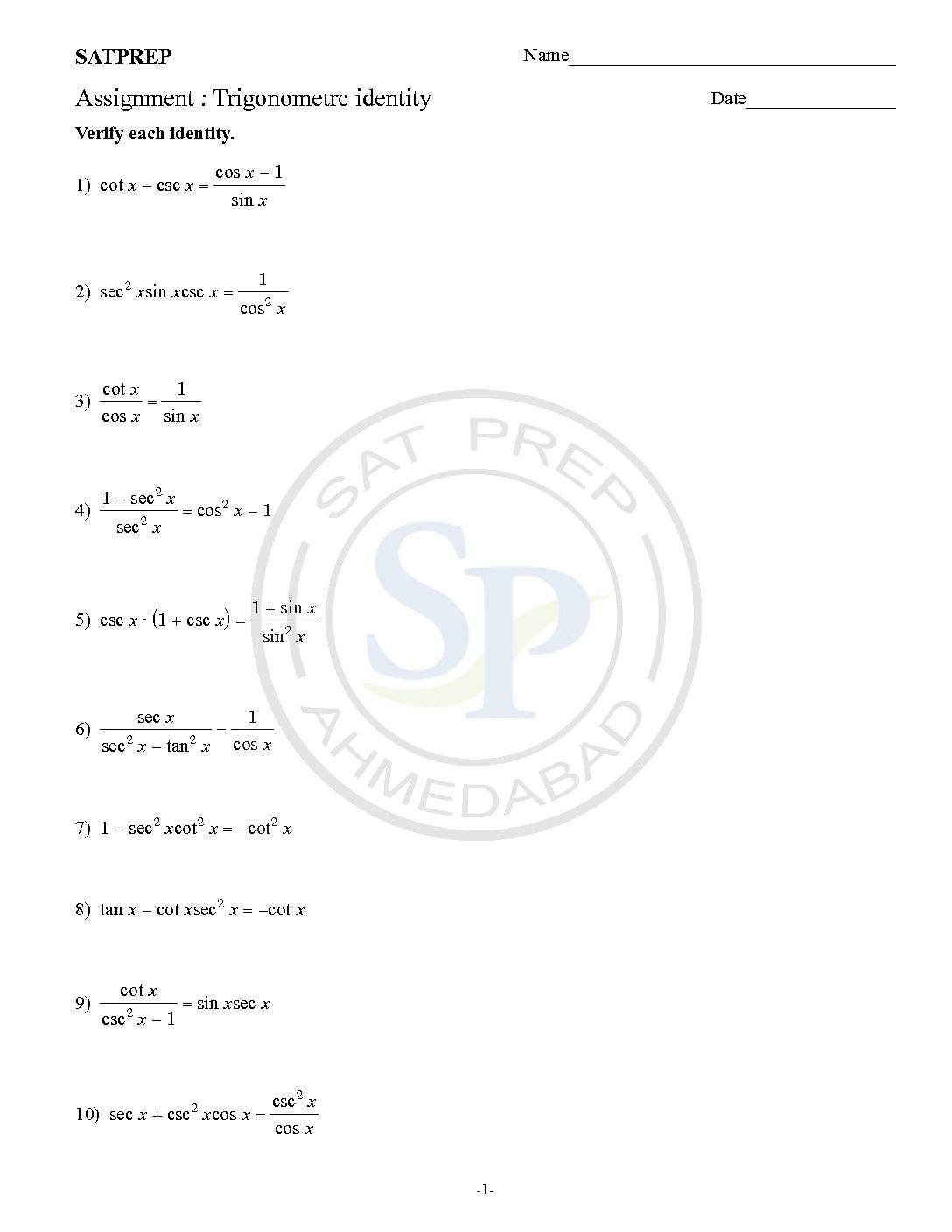
trigonometry identities showing that the identity is always true, no matter what value of x or θ is used. Because it has to hold true for all values of x, we cannot simply substitute in a few values of x to “show” that they are equal. We have to use logical steps to show that one […]
You are browsing archives for
Category: Graphs
Product to Sum
Product‐Sum and Sum‐Product Identities. The process of converting products into sums can make a difference . Integrate \( \int \! \sin 3x \cos 4x \, \mathrm{d}x.\) This problem may seem tough at first, but after using the product-to-sum trigonometric formula, this integral very quickly changes into a standard form . Converting a sum of trig functions into a product. Write as and then […]
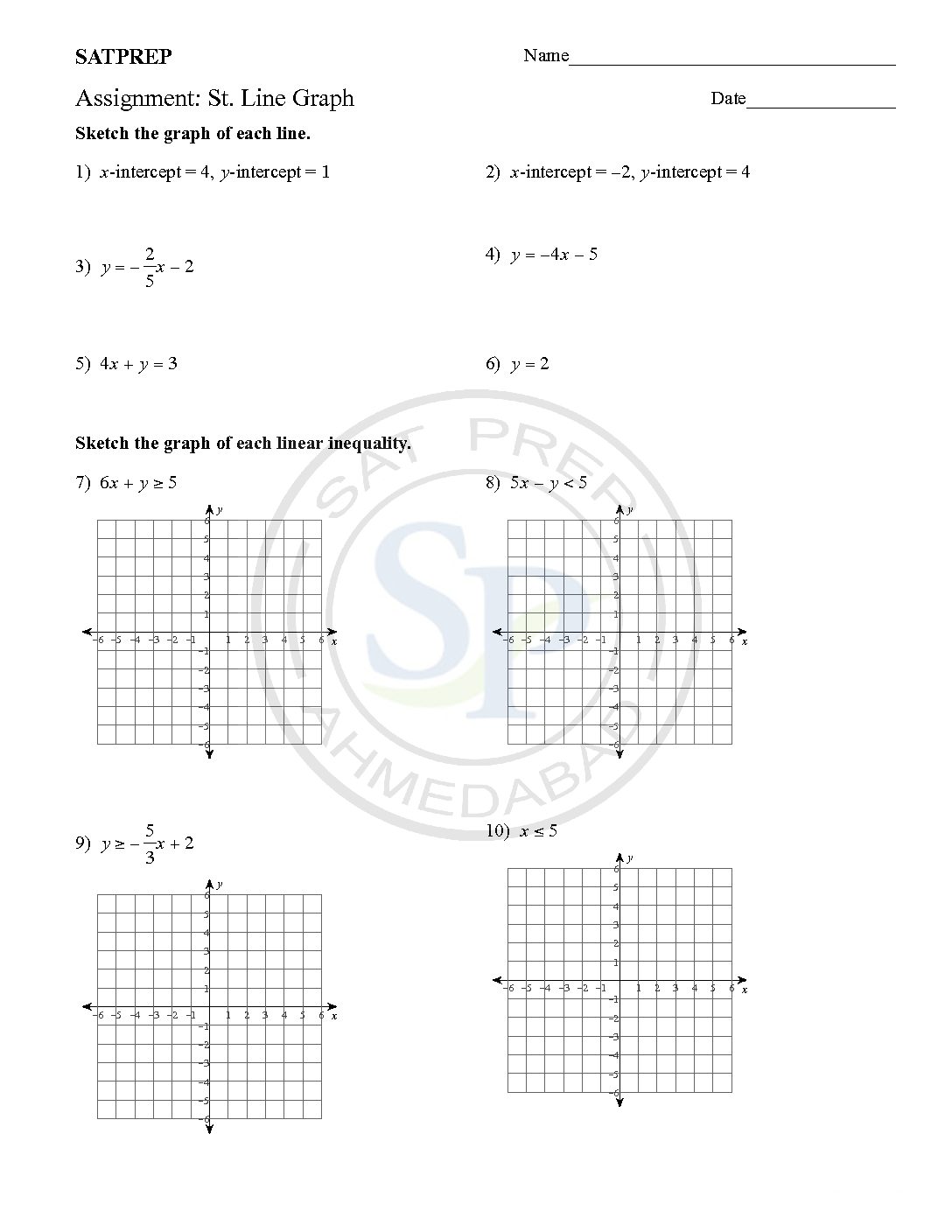
Straight line
Simultaneous Equation
The simultaneous equations are solve by the elimination. These equations are also solve by substitution as well as graphic method. Due to variable solution give coordinate. Simultaneous eq
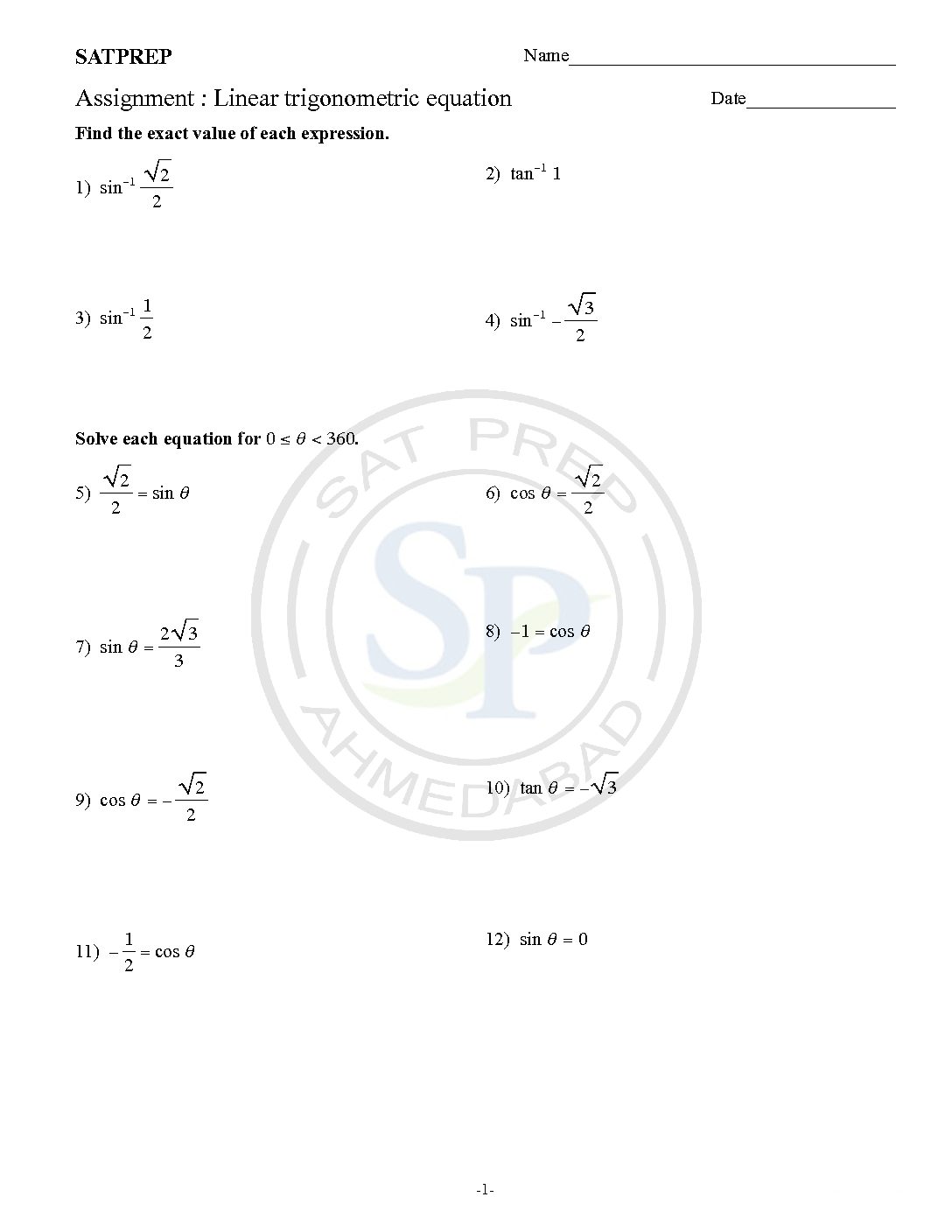
Linear trigonometric equation
Linear Trigonometric equations are either linear or quadratic in nature. To find the angle value(s) that satisfy the given equation. Because it is linear trigonometric eq. hence it has two roots. Linear trigonometric eq
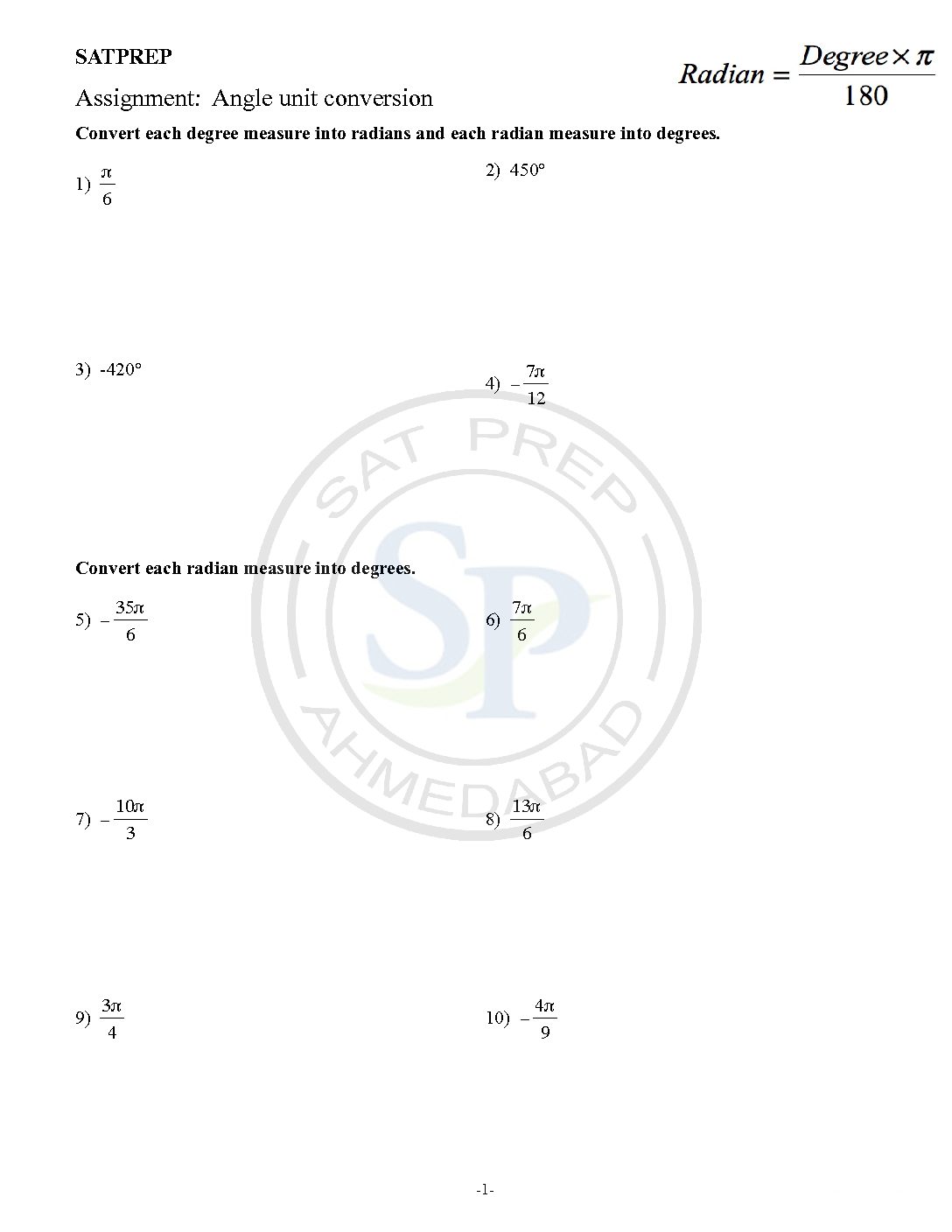
Angle unit conversion
Radians and degrees are two different units for angle. The radian is the SI unit for measuring angles. Because it is continuous therefore it is use in trigonometric function. Hence it represent in multiple of π. Angle unit conversion
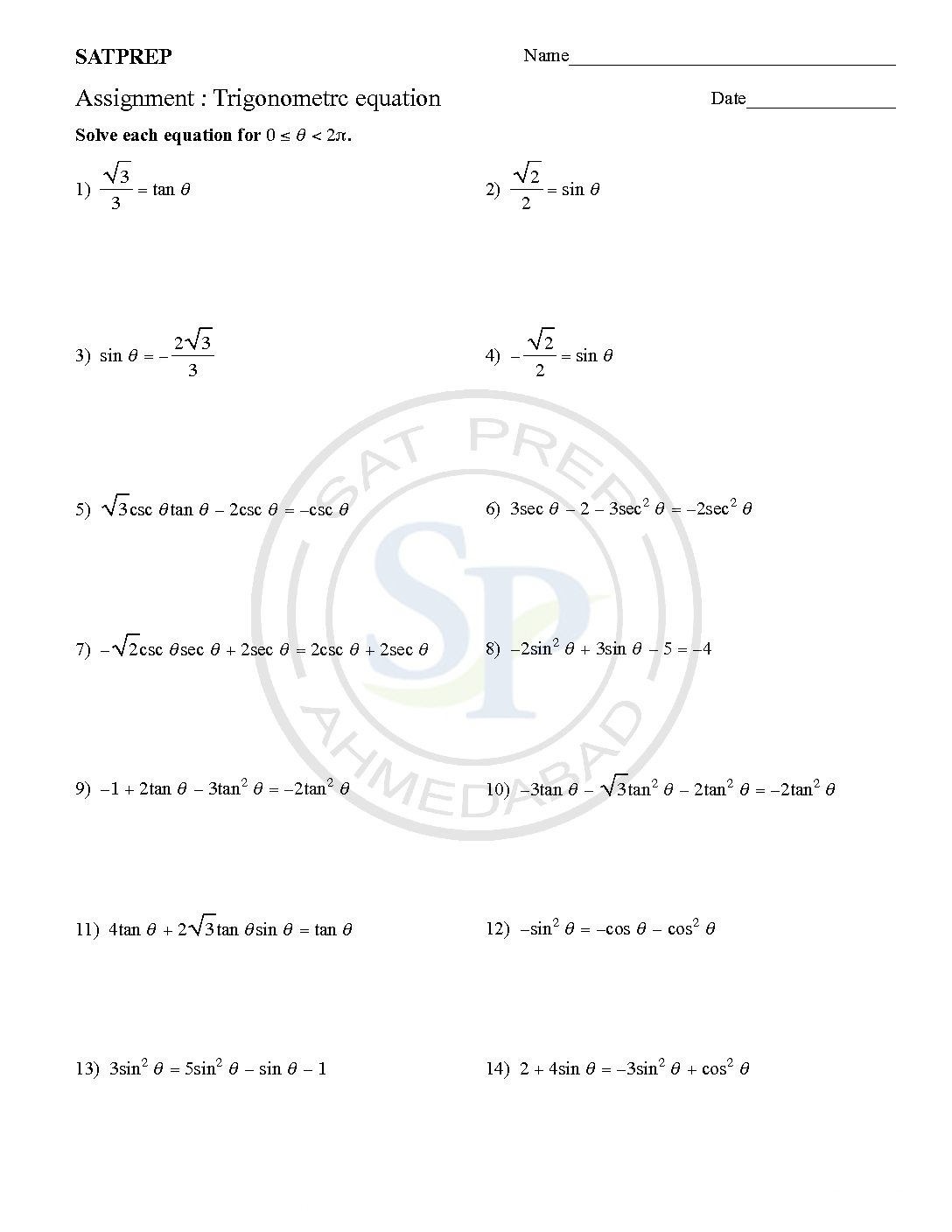
Trigonometric Equation (Radian)
Trigonometric Equation involve one or more trigonometric ratios of unknown angles. Due to difference unit of angle , hence it gives angle in different form. Similarly it give value in radian. Trigonometric equation
Trigonometric identity
Trig identity is equations that are true for Right Angled Triangles. D1: sin 2A+ cos 2A=1 D2: 1+ tan 2A= sec 2A D3: 1+ cot 2A= csc 2A Hence trigonometric identities are prove by above D1,D2 and D3. Similarly also using reciprocal identity. Trigonometric Identity
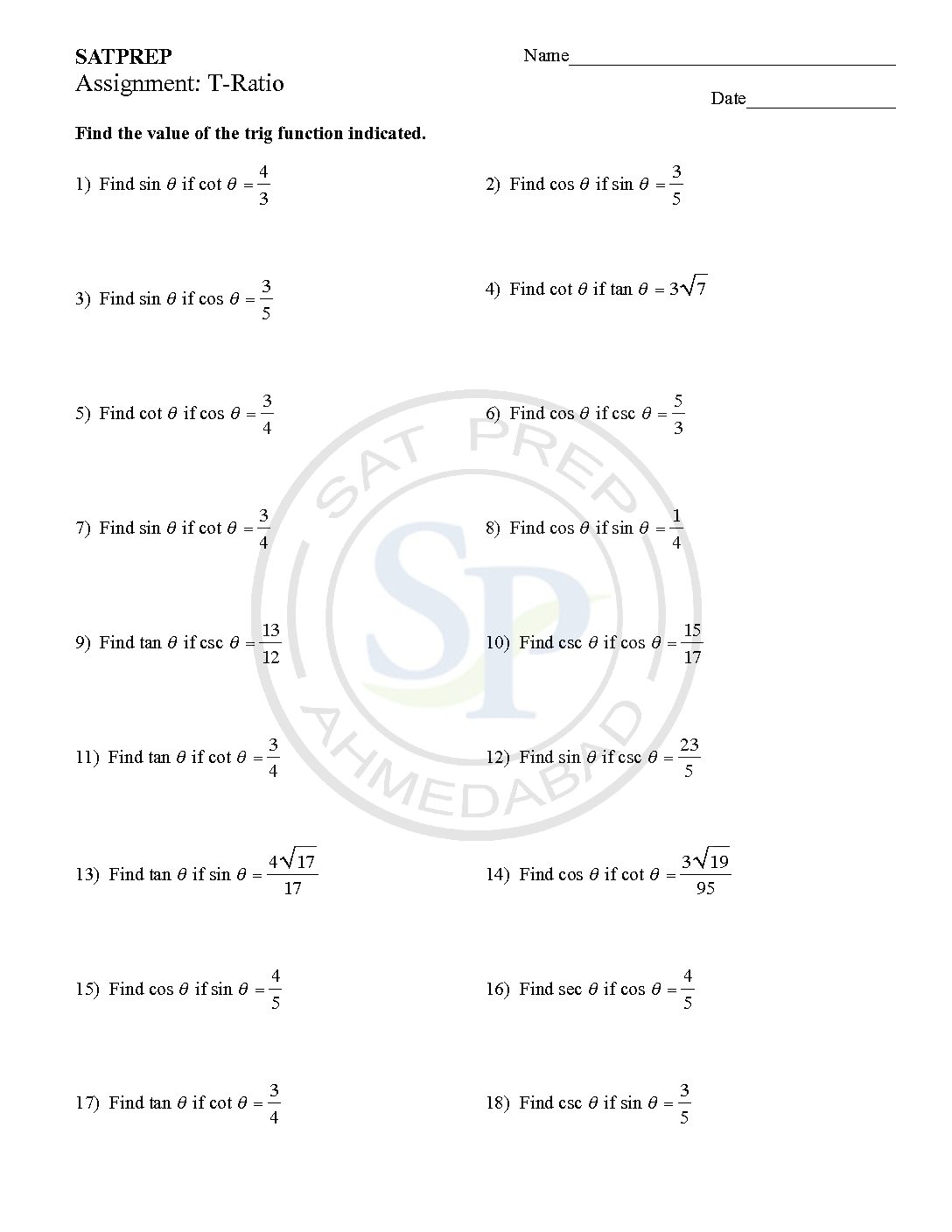
Trigonometric ratio-2
The ratios of the sides of a right triangle are called trigonometric ratios. Sine, Cosine and Tangent are main ratio while rest three reciprocal. Hence Sine and Cosine are the trigonometric ratios, whose values are less that 1 for an acute angle. Because they are periodic. www.kutasoftware.com
Trigonometric ratio
The ratios of the sides of a right triangle are called trigonometric ratios. Sine, Cosine and Tangent are main ratio while rest three reciprocal. Hence Sine and Cosine are the trigonometric ratios, whose values are less that 1 for an acute angle. Because they are periodic. Trigonometric ratio