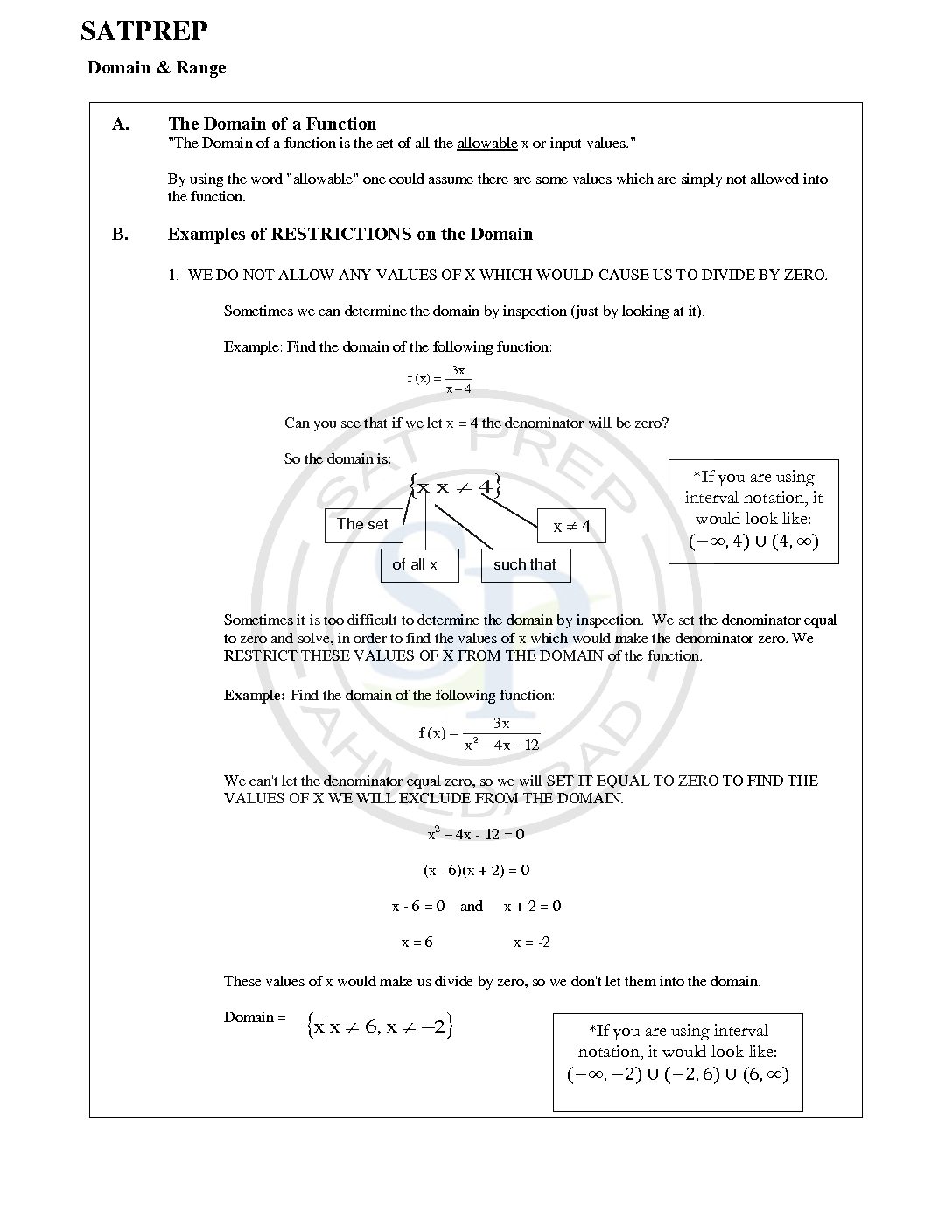
Domain and range of functions are an important concept . Domain values define on x – axis and Range is values on y- axis in the graph. Due to these values of functions, continuity of function defined. Another use of domain to show function defined. While range defined minimum and maximum value of function. […]
You are browsing archives for
Category: Additional Maths
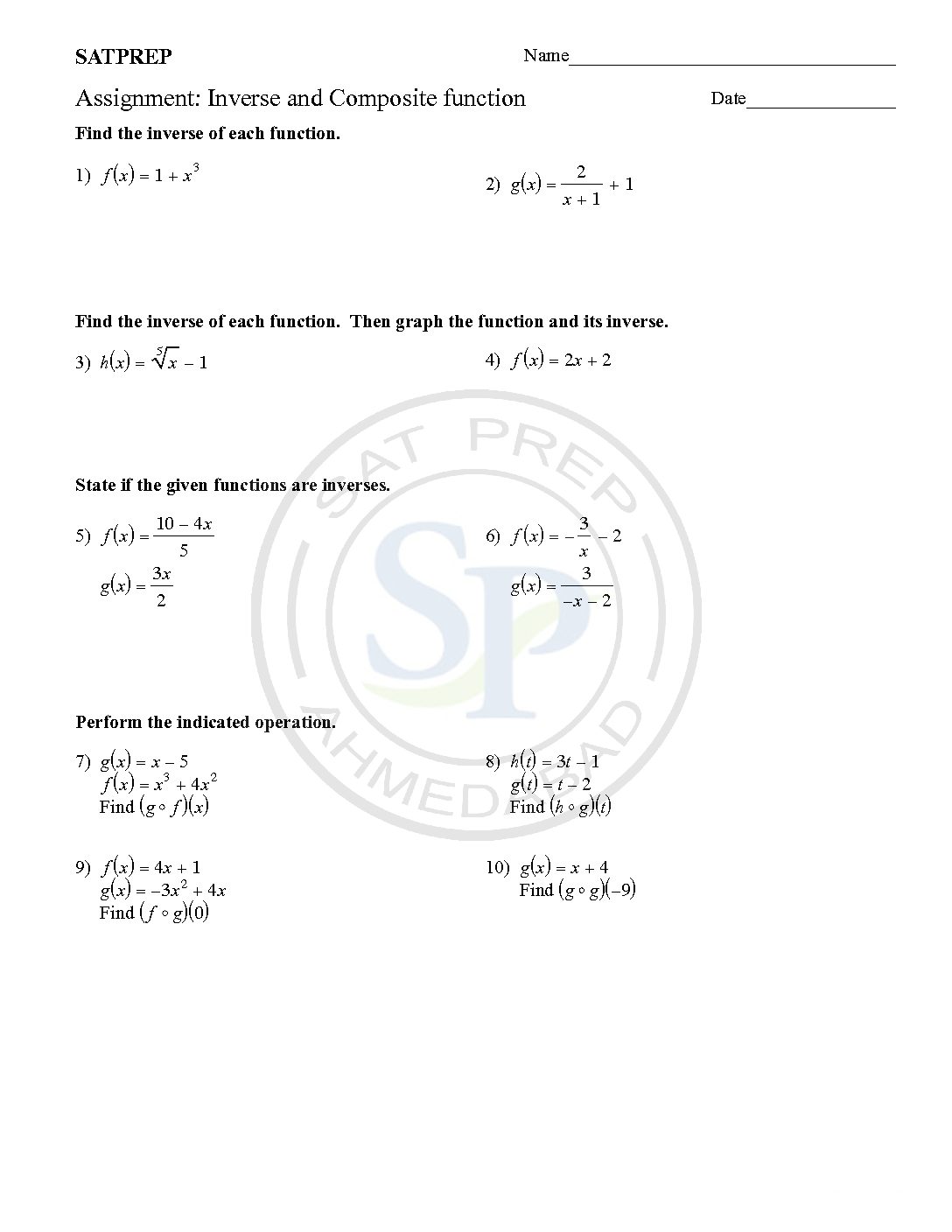
Inverse and Composite function
Inverses and Composites are two important concept of functions. Composite function is defined as one function defined inside another function. Like ff(x)) or f(g(x)) etc. Concept of inverse is interchange of variables . Inverse notations are f-1(x),g-1(x) etc. Hence interchange is inverse. Therefore function and its inverse is reflection about y = x. Inverse and composite
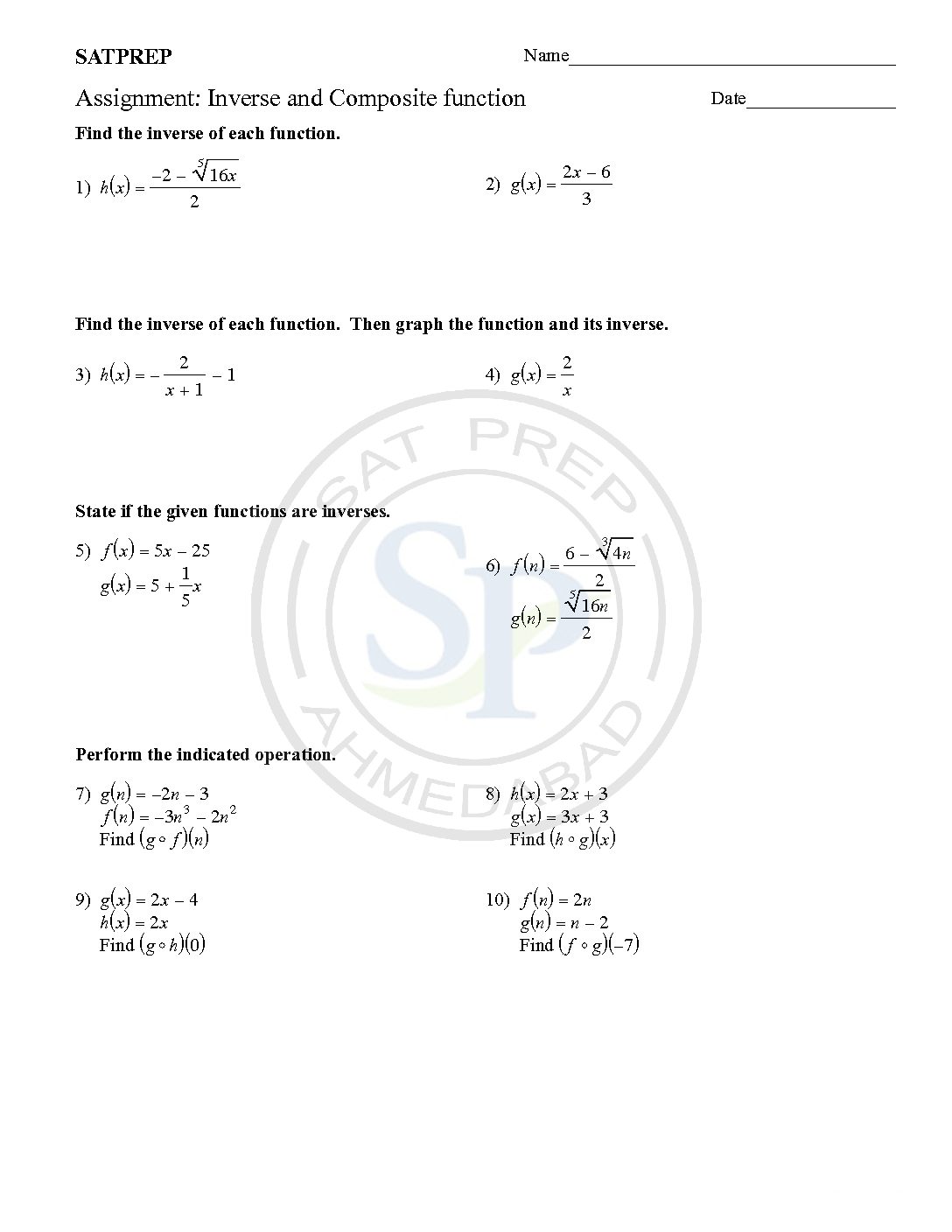
Inverse and composite function
Inverses and Composite are two important concept of functions. Composite function is defined as one function defined inside another function. Like ff(x)) or f(g(x)) etc. Concept of inverse is interchange of variables . Inverse notations are f-1(x),g-1(x) etc. Hence interchange is inverse. Therefore function and its inverse is reflection about y = x. inverse and […]
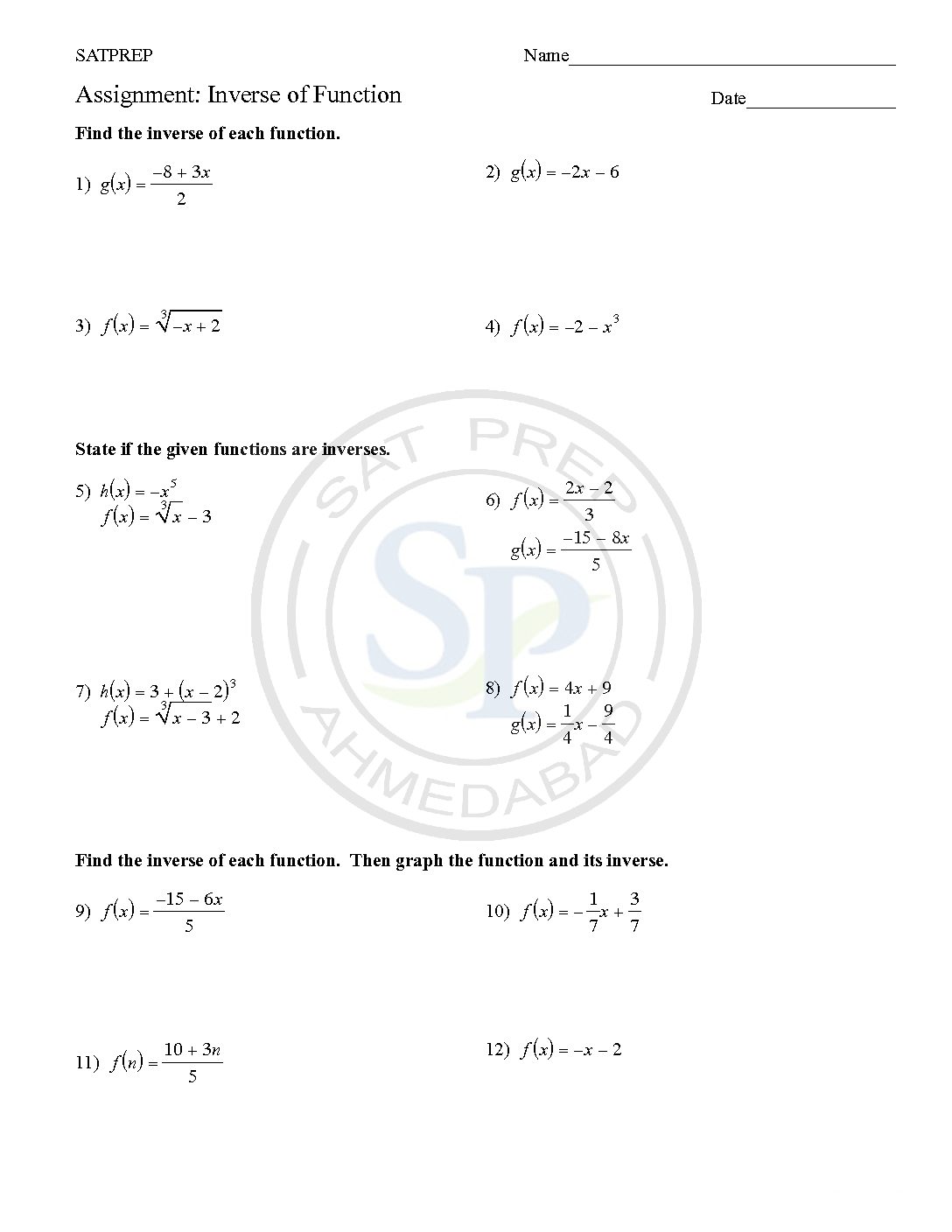
Inverse of function
Inverse of functions is an important concept . Domain values and Range values gets interchange . Due to these values of functions, continuity of function also change. Graph of inverse function also change and become y-axis oriented. Therefore graph of inverse is reflection of function graph about y = x. Inverse of Function
Function
A function f(x) tells you what to do with the input, but, to be completely defined, function also need to know what type of input is permitted to go into the function. Function
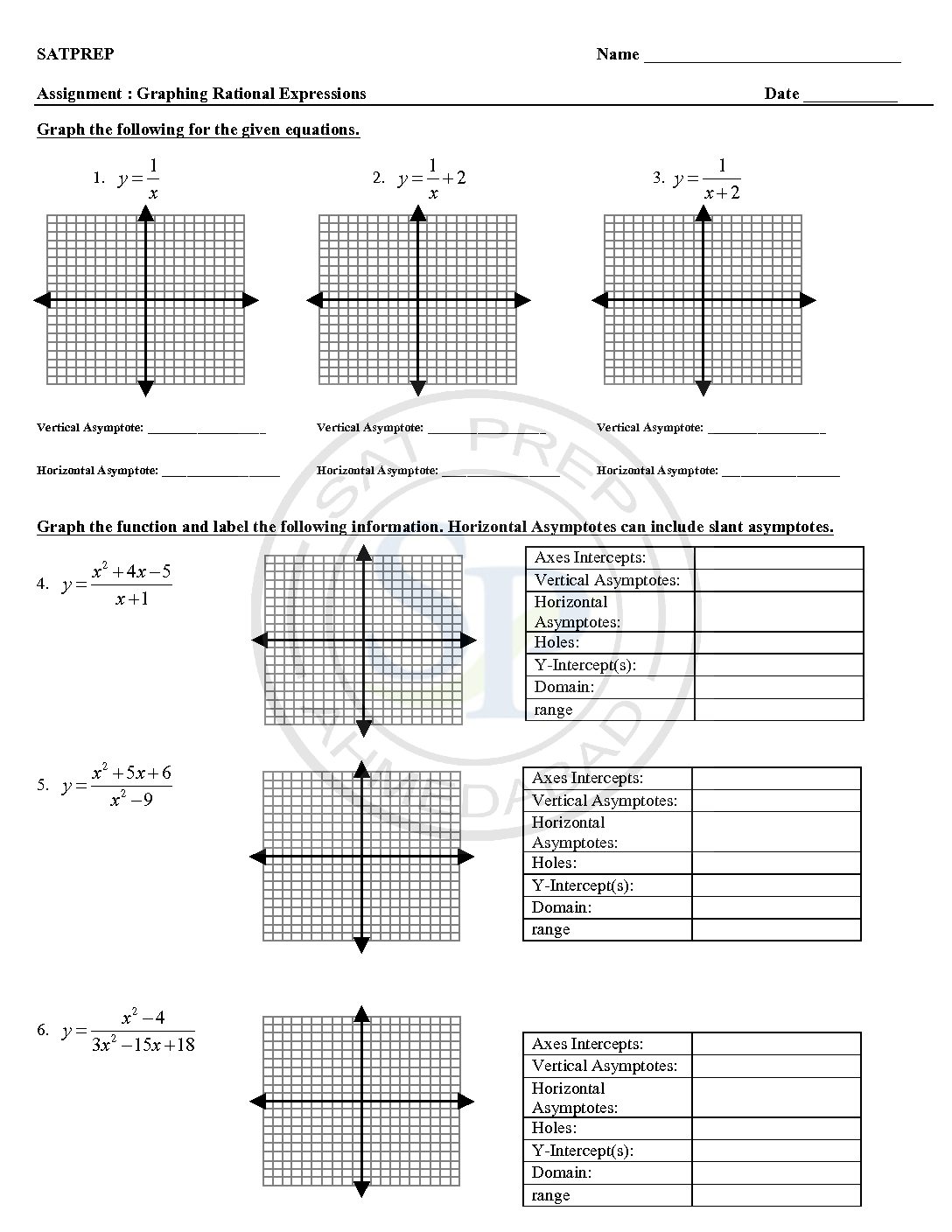
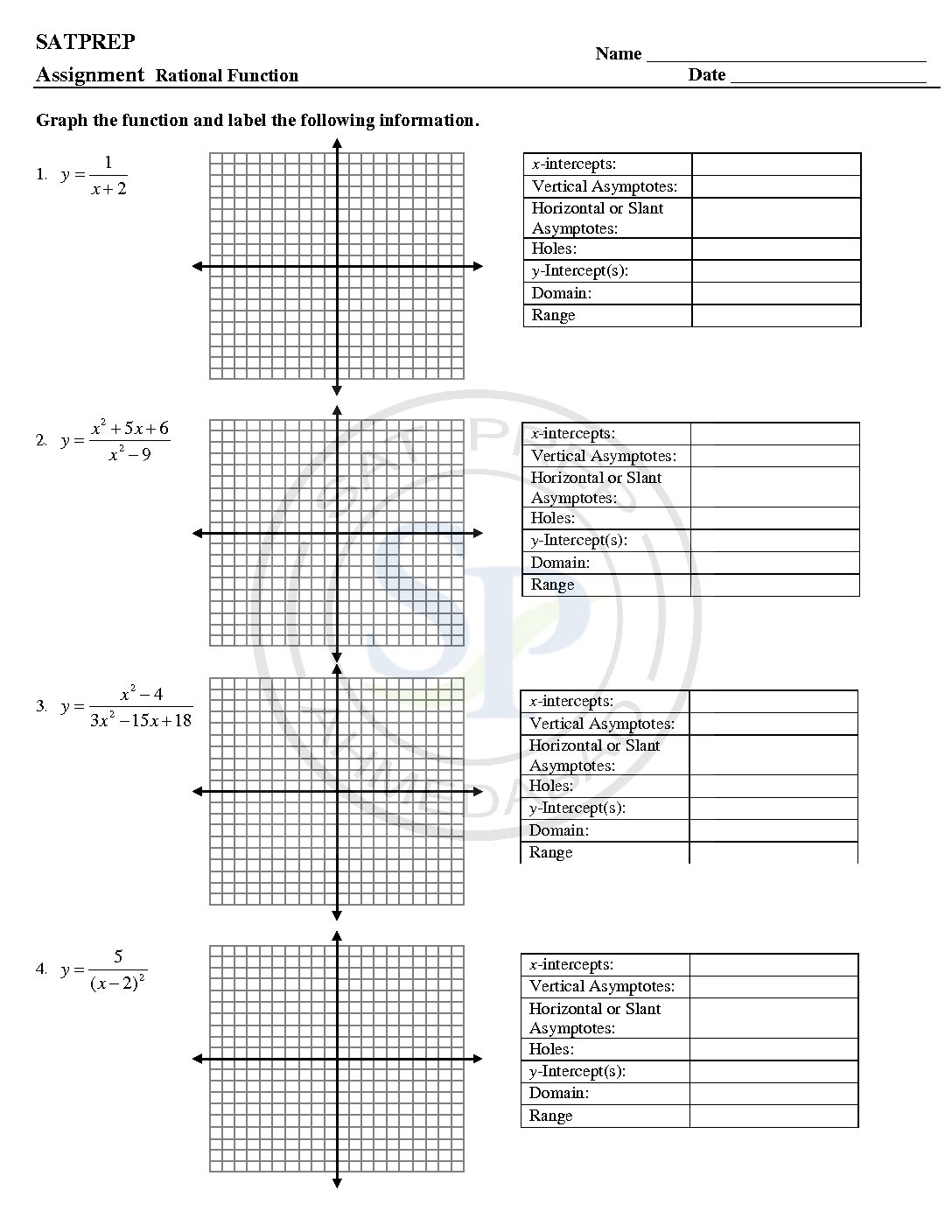
Rational Function
Rational functions is a function that is the quotient of two polynomials. Also polynomial a function that is the quotient of two polynomials. Rational functions and the properties of their graphs such as domain, vertical and horizontal asymptotes, x and y intercepts . Rational function graph is discontinuous graph at asymptotes. Rational function
Rational and Reciprocal functions
A rational functions is a function of the form f(x)=p(x)/q(x), where p(x) and q(x) are polynomials and q(x)≠0 ,q(x)≠0 . The domain of a rational function consists of all the real numbers x=0 except those for which the denominator is x= 0 . reciprocal for a number x, denoted by 1/x or x −1, is a number which when multiplied by x yields the multiplicative identity, 1.. The […]
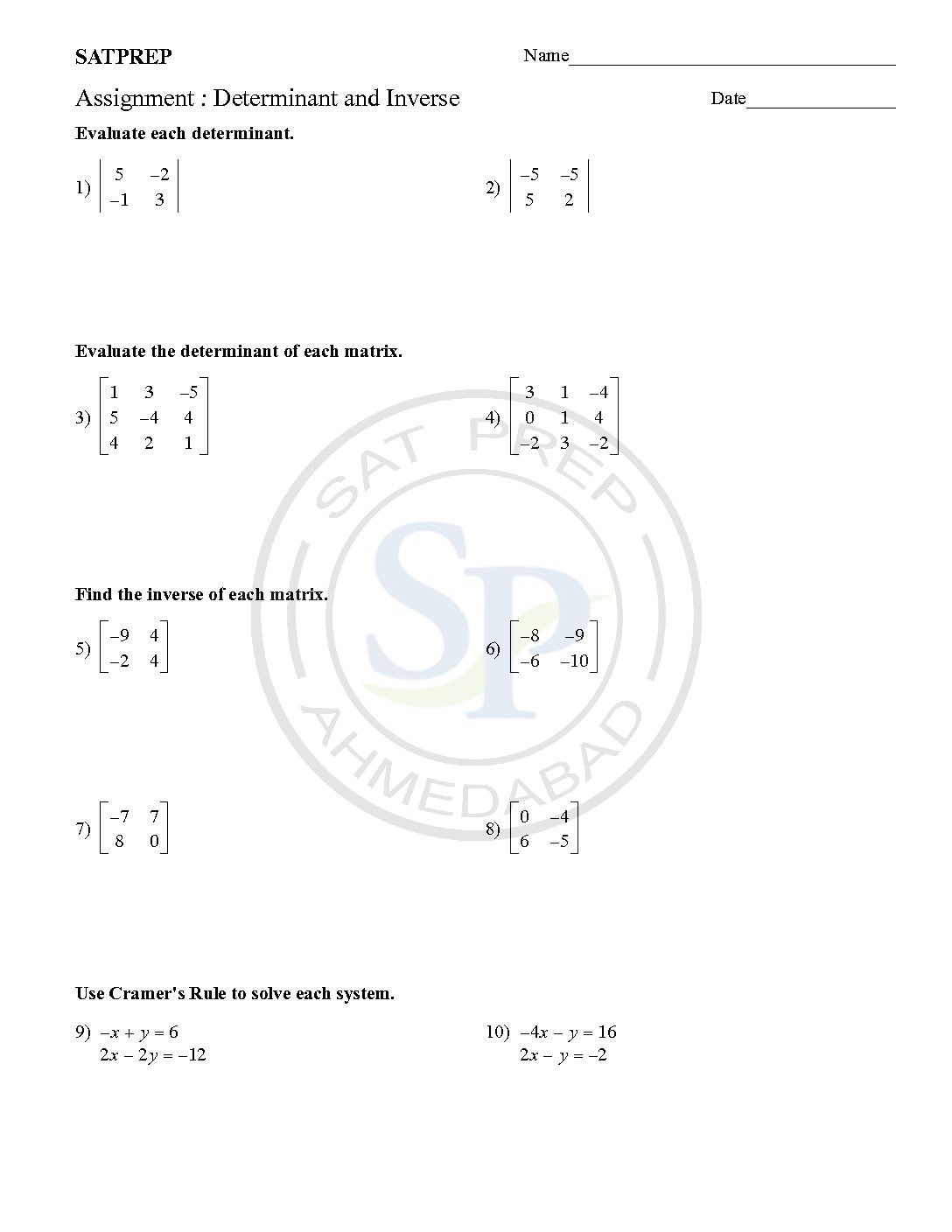
Matrix determinant and Inverse
Determinant det(A) of a matrix A is non-zero if and only if A is invertible or, yet another equivalent statement, if its rank equals the size of the matrix. If so, the determinant of the inverse matrix is given by (−) = (). Matrix
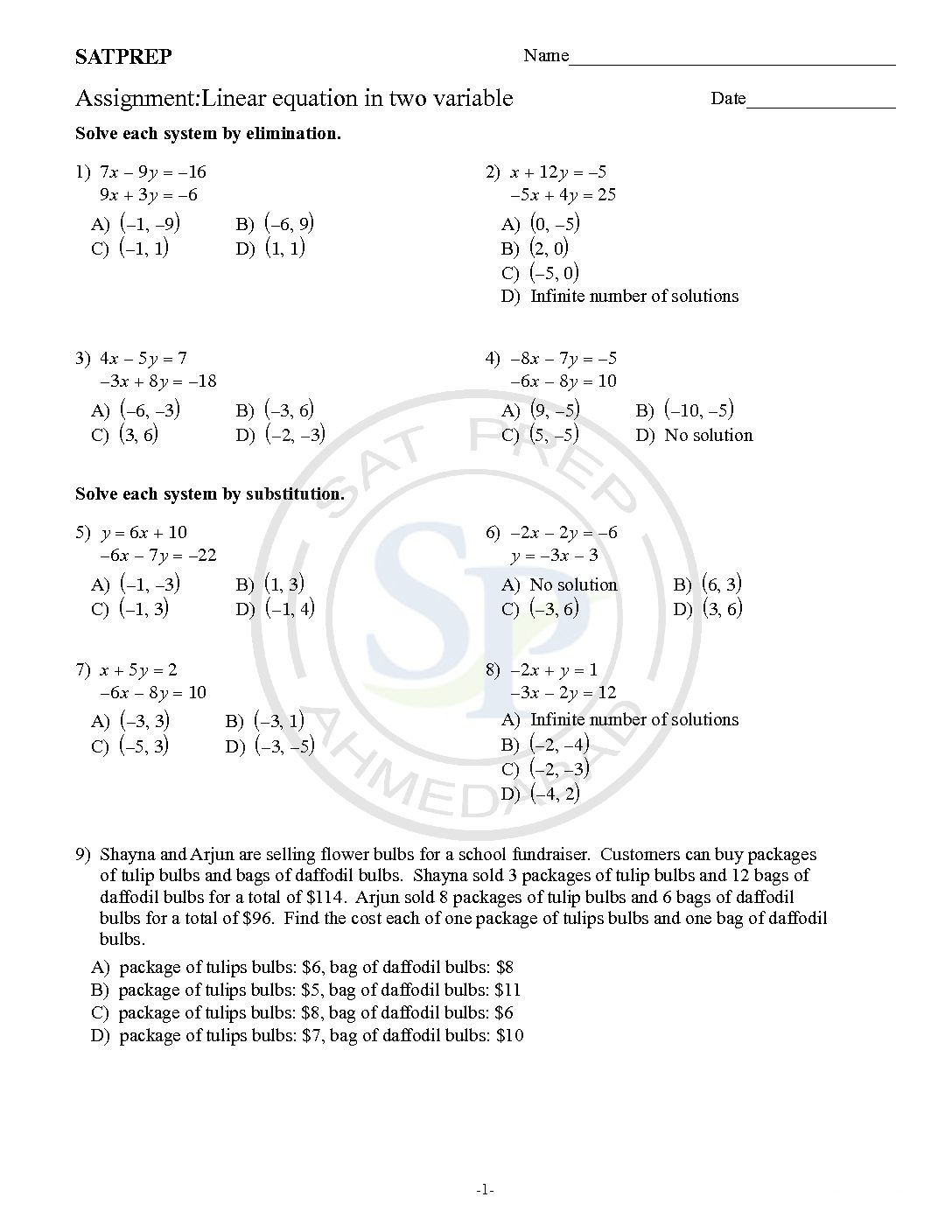
Linear equation in two variable
Two variable linear equation. The general form of Linear Equations are ax + by = c, where a is not equal to 0. Solution of a Linear Equation gives one value of x. Because line intersect axes at one point. Linear Eq.
Circular measure -2
The radian is a unit of measurement angle . Therefore, this unit is used in many topics likewise sector , angles . Parts of the mathematics area which include circular measure and more often, the branch of angle measurements where pi (Π) is used. Therefore, radian use to measure arc length, chord length, area of sectors of a circle and many others. […]