Describes the motion of points, objects and systems of groups of objects, without reference to the causes of motion. The symbol a stands for the acceleration of the object. And the symbol v stands for the instantaneous velocity of the object. The derivative of displacement with time is velocity ( v = ds/dt ). The […]
You are browsing archives for
Category: Integration
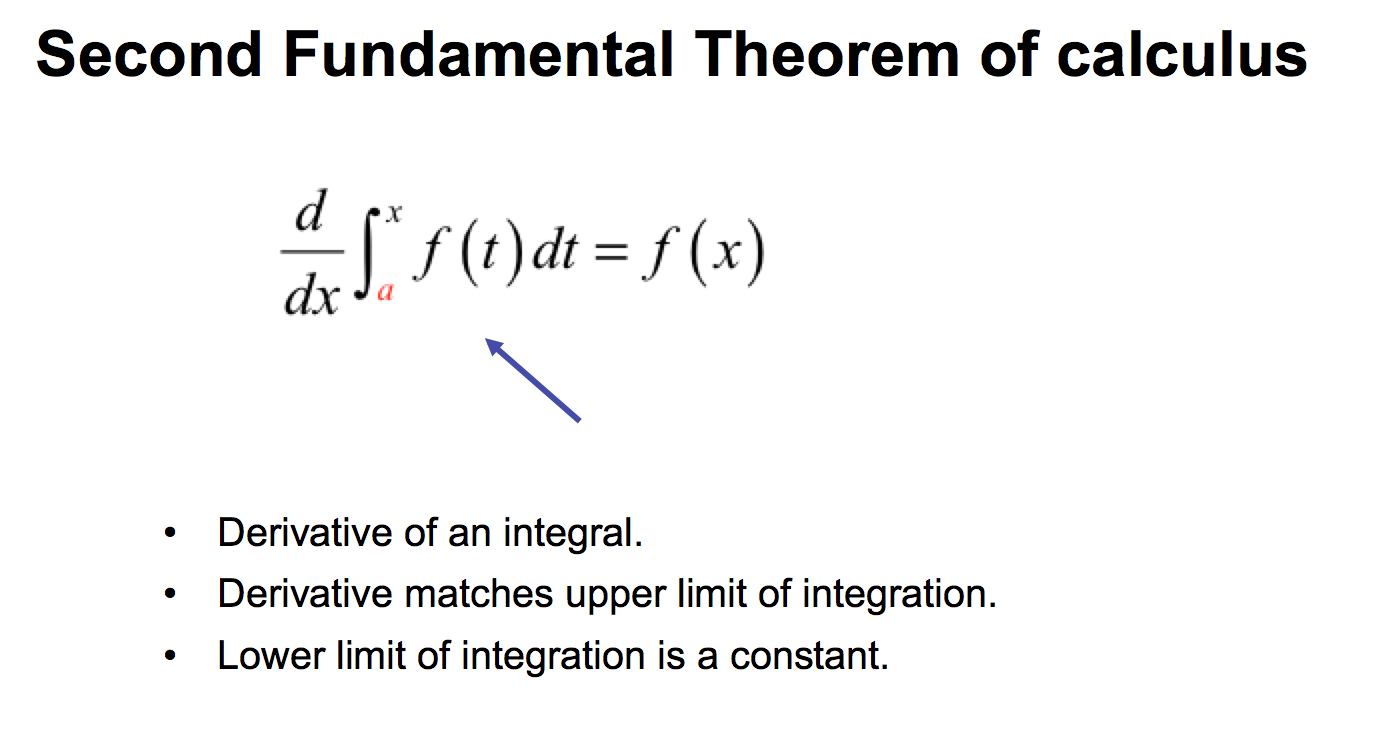
Second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
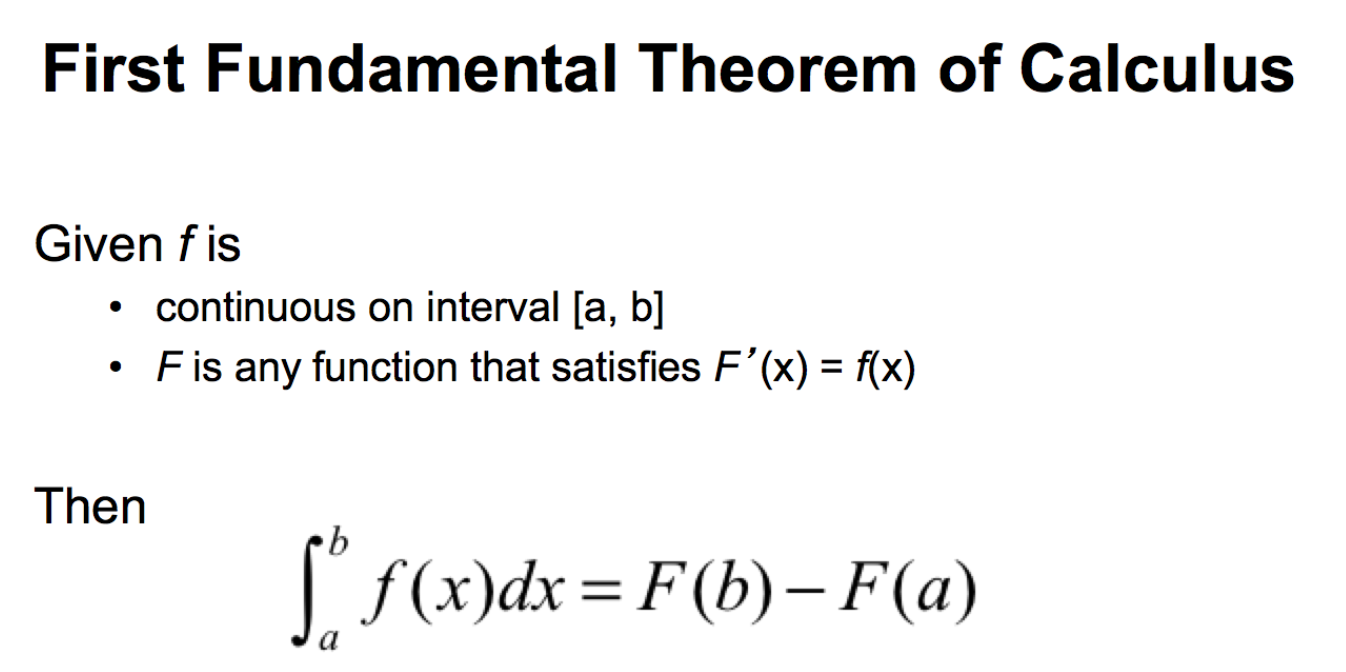
First fundamental theorem of calculus
First fundamental theorem of calculus If we define an area function, F (x), as the area under the curve y=f (t) from t=0 to t=x, then the area function in this case is F (x)=c∗x. The fundamental theorem of calculus shows how, in some sense, integration is the opposite of differentiation Theorem of Calculus of integration