Polar systems is system which defined in term of magnitude and angle , coordinates are also defined in terms of magnitude and angle. Polar equation define in terms of magnitude and angle. Hence, graph of equation in polar system sketch by using magnitude and angle Polar system P P p
You are browsing archives for
Category: AP
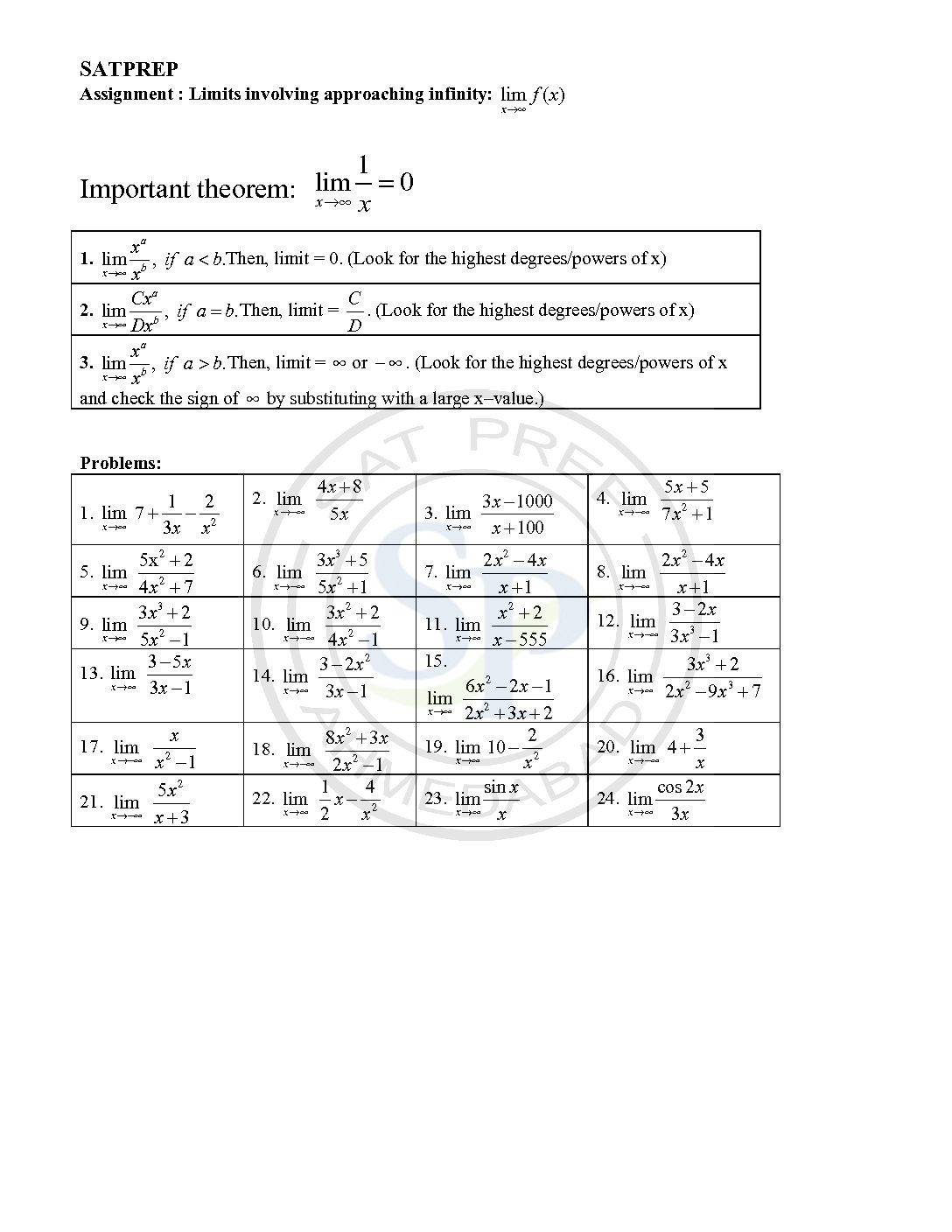
Limit
Limits are the concept of function. So, we have to solve function for given limits. Due to different type of limits , function cannot solve. limit
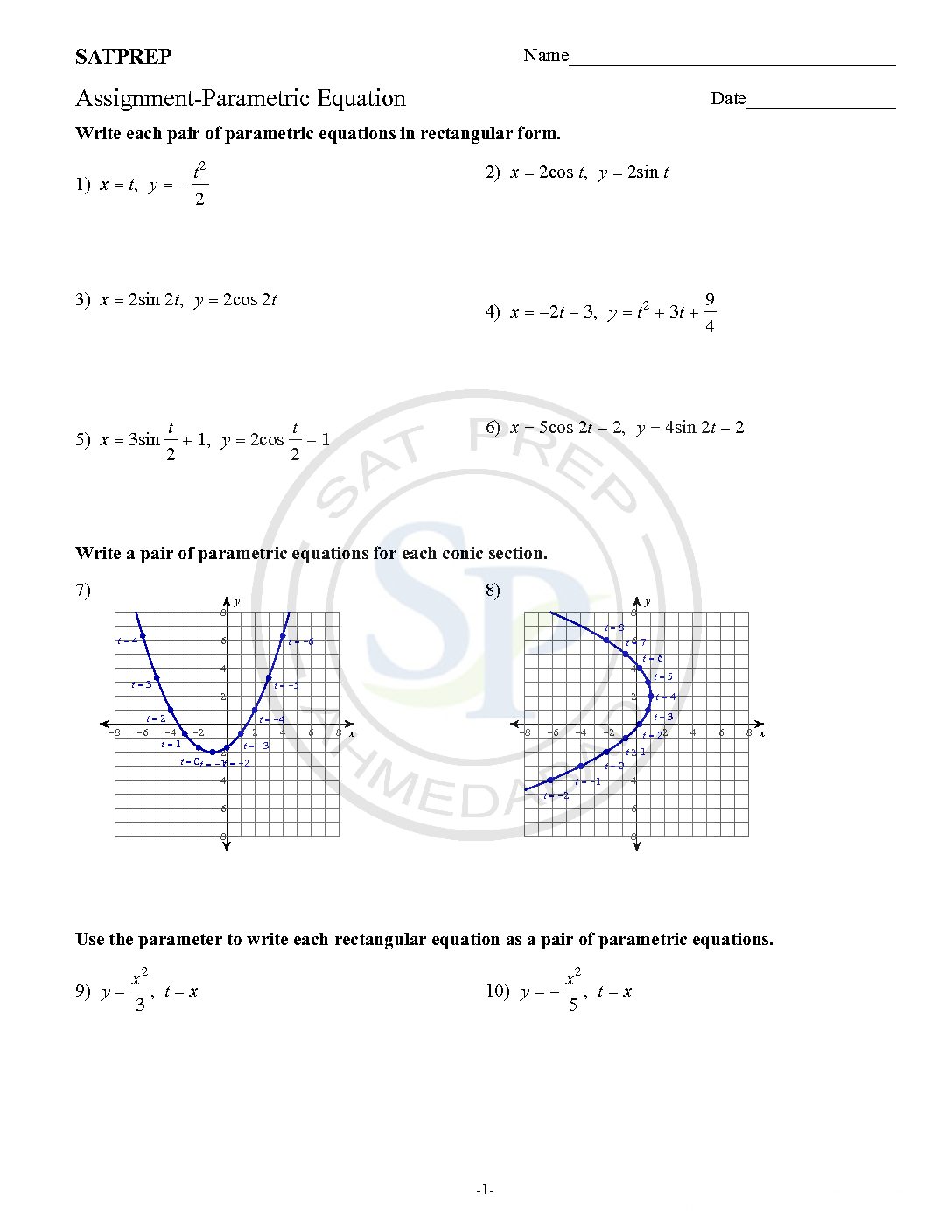
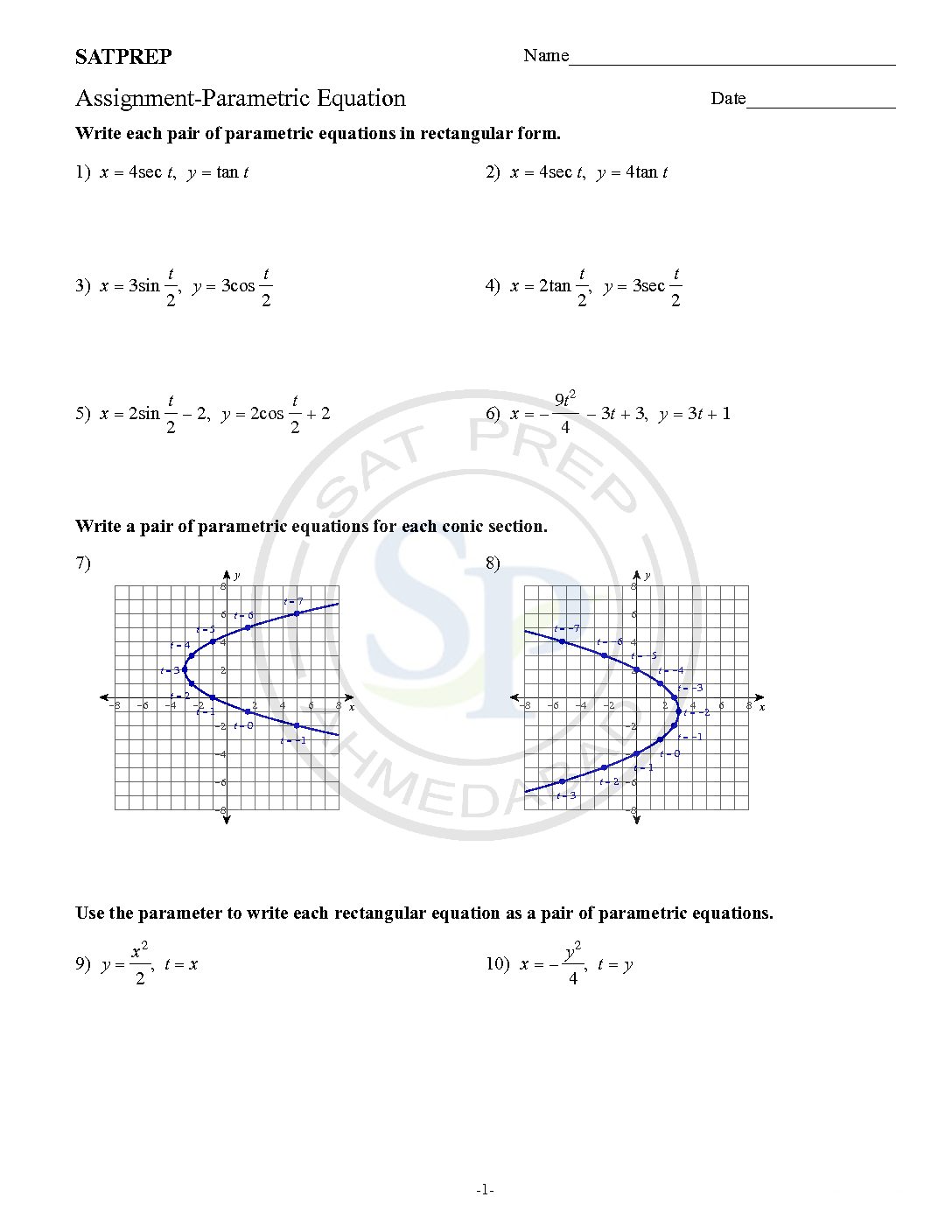
Parametric Equation
Parametric equations are three variable equations. It is in form x = f(t) and y = g(t), where t is parameter. Example: x= cos(t) and y = sin(t) , because t is present in both equation so t is parameter Parametric Eq
Parametric Equation
Parametric equations are three variable equation. In this type of equation two variable defines in terms of third variable to form two equation. Third common variable is know as parameter. Due to parameter these equation call parametric equation. Likewise x = f(t) and y = g(t), where t is parameter. Also we can say x […]
Domain and Range of Function
Domain and range of functions are an important concept . Domain values define on x – axis and Range is values on y- axis in the graph. Due to these values of functions, continuity of function defined. Another use of domain to show function defined. While range defined minimum and maximum value of function. […]
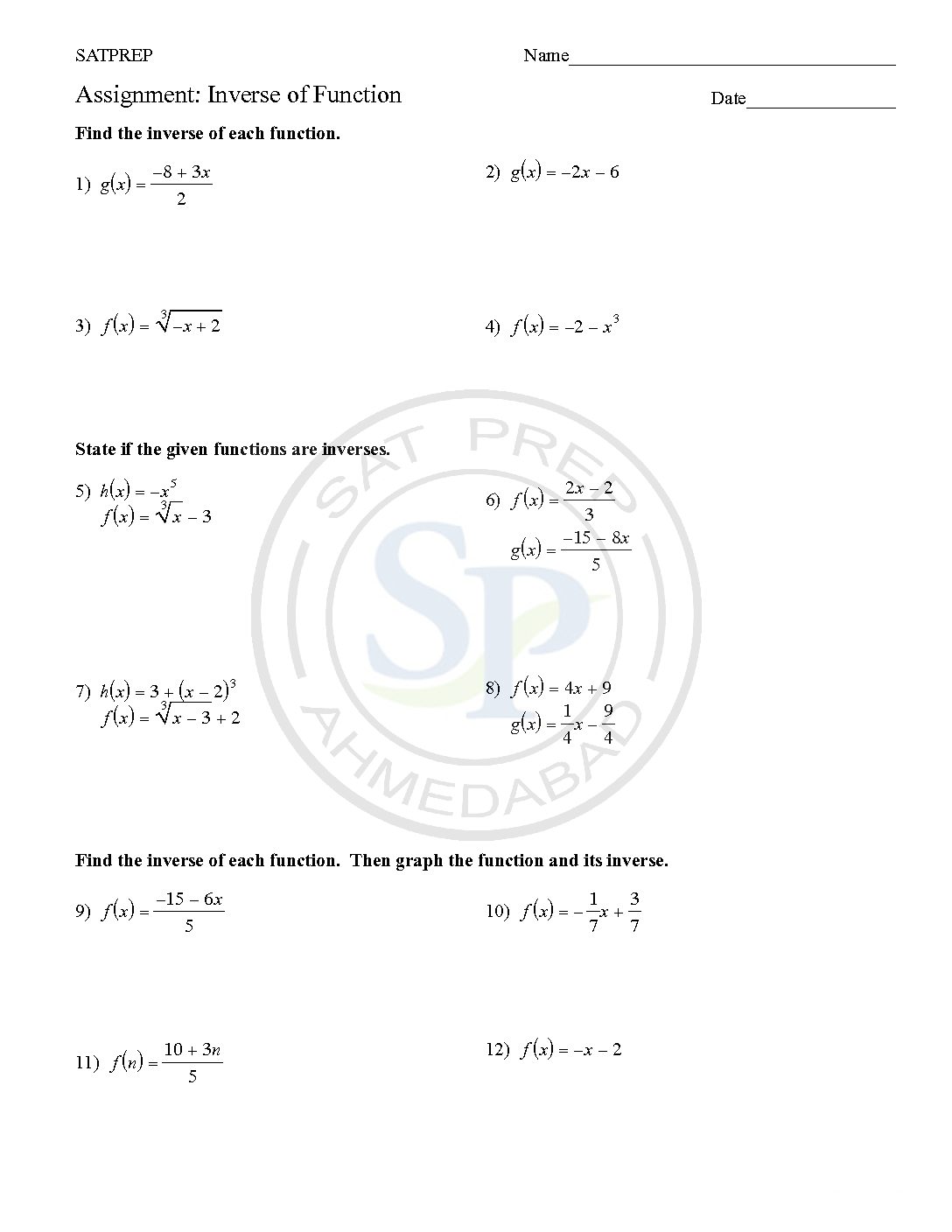
Inverse of function
Inverse of functions is an important concept . Domain values and Range values gets interchange . Due to these values of functions, continuity of function also change. Graph of inverse function also change and become y-axis oriented. Therefore graph of inverse is reflection of function graph about y = x. Inverse of Function
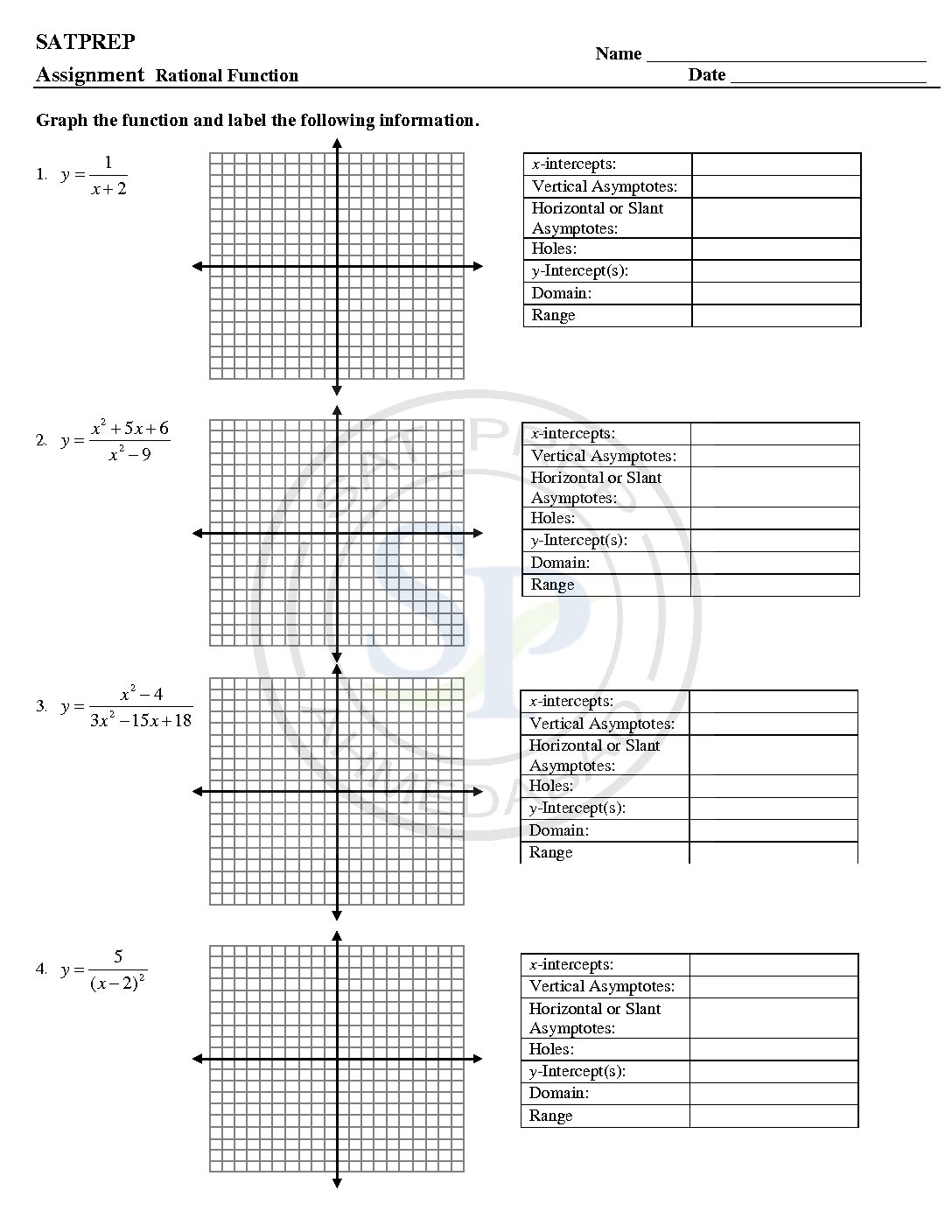
Rational and Reciprocal functions
A rational functions is a function of the form f(x)=p(x)/q(x), where p(x) and q(x) are polynomials and q(x)≠0 ,q(x)≠0 . The domain of a rational function consists of all the real numbers x=0 except those for which the denominator is x= 0 . reciprocal for a number x, denoted by 1/x or x −1, is a number which when multiplied by x yields the multiplicative identity, 1.. The […]
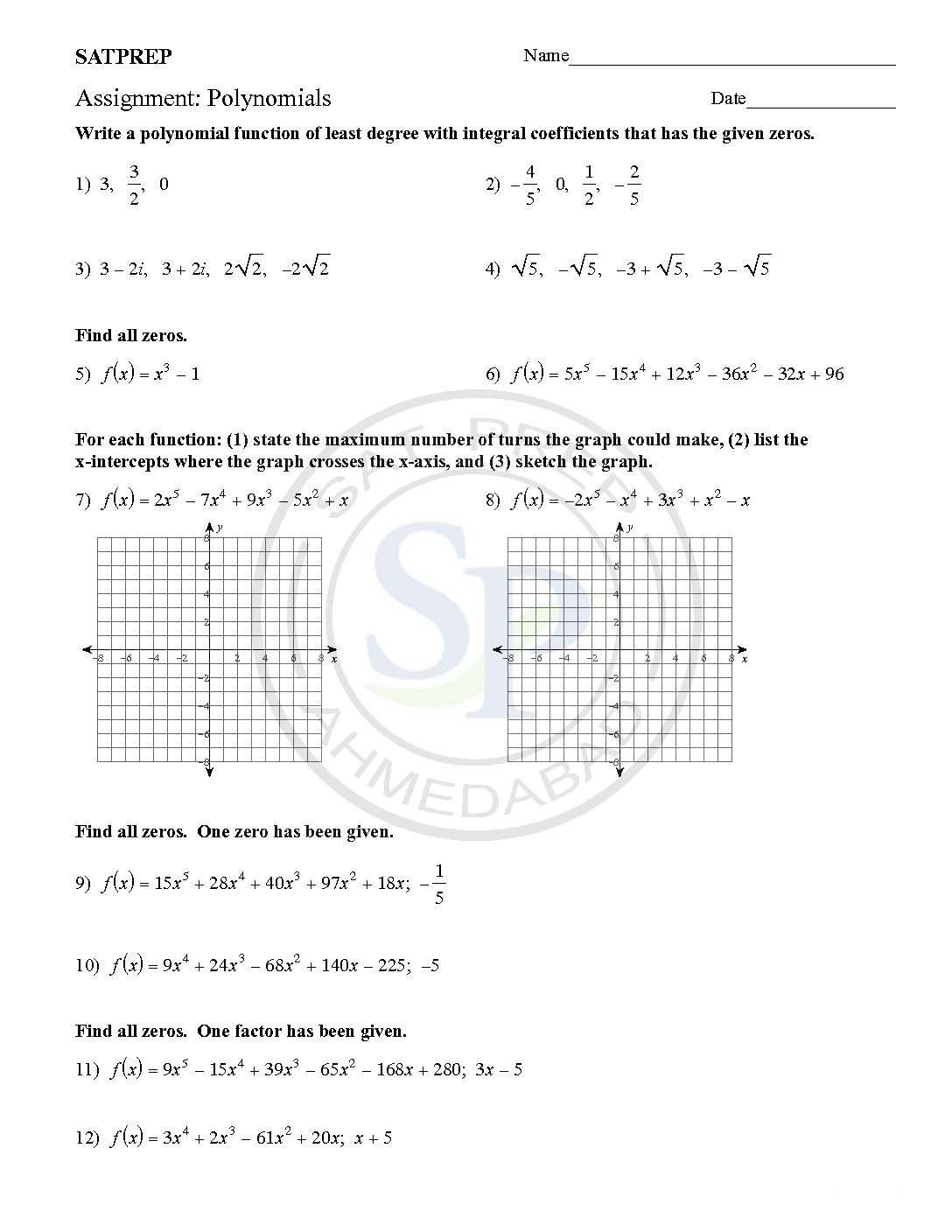
Polynomials
This post is about worksheet of polynomials . This worksheet consist question of finding roots of polynomial. There are two types of solution of polynomial , one algebraic and another graphic. Because of method two type of questions are there, one equation and another graph based. Due to graphic question calculator allowed. Polynomials
Sum and Product of Root of Polynomials
To find the zeros you have to equate polynomial with zero. This is easily factorable and you will get and . Next, set both of these equal to zero. and . Isolate the x’s and you will get and . The sum will be since you add the two together, and the product will be because you multiply the […]
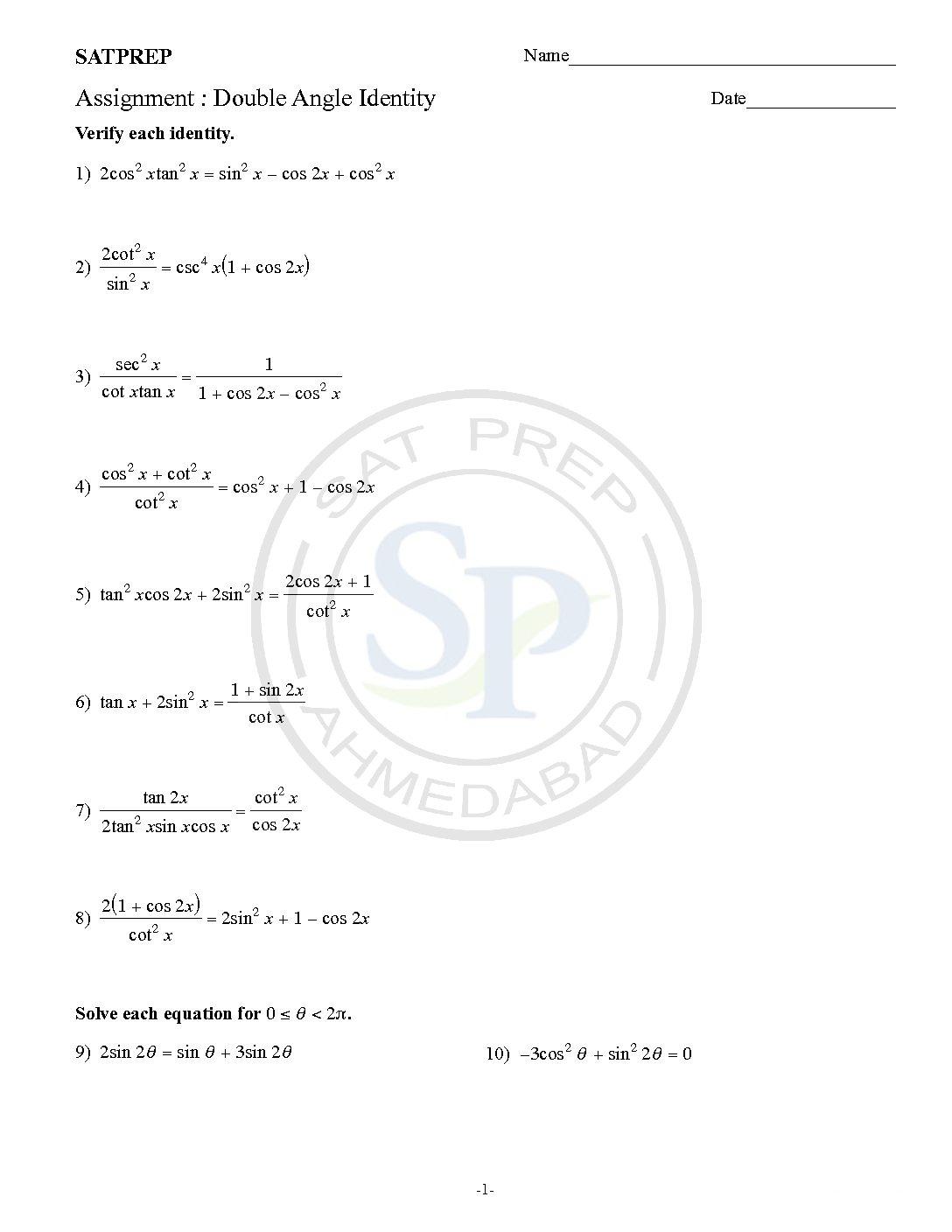
Double angle Identity
Double‐Angle and Half‐Angle Identities. Because sin x is positive, angle x must be in the first or second quadrant. The sign of cos 2 x will depend on the size of angle x. A double–angle function is written, for example, as sin 2θ, cos 2α, or tan 2x, where 2θ, 2α, and 2x are the angle measures and the assumption is that you […]