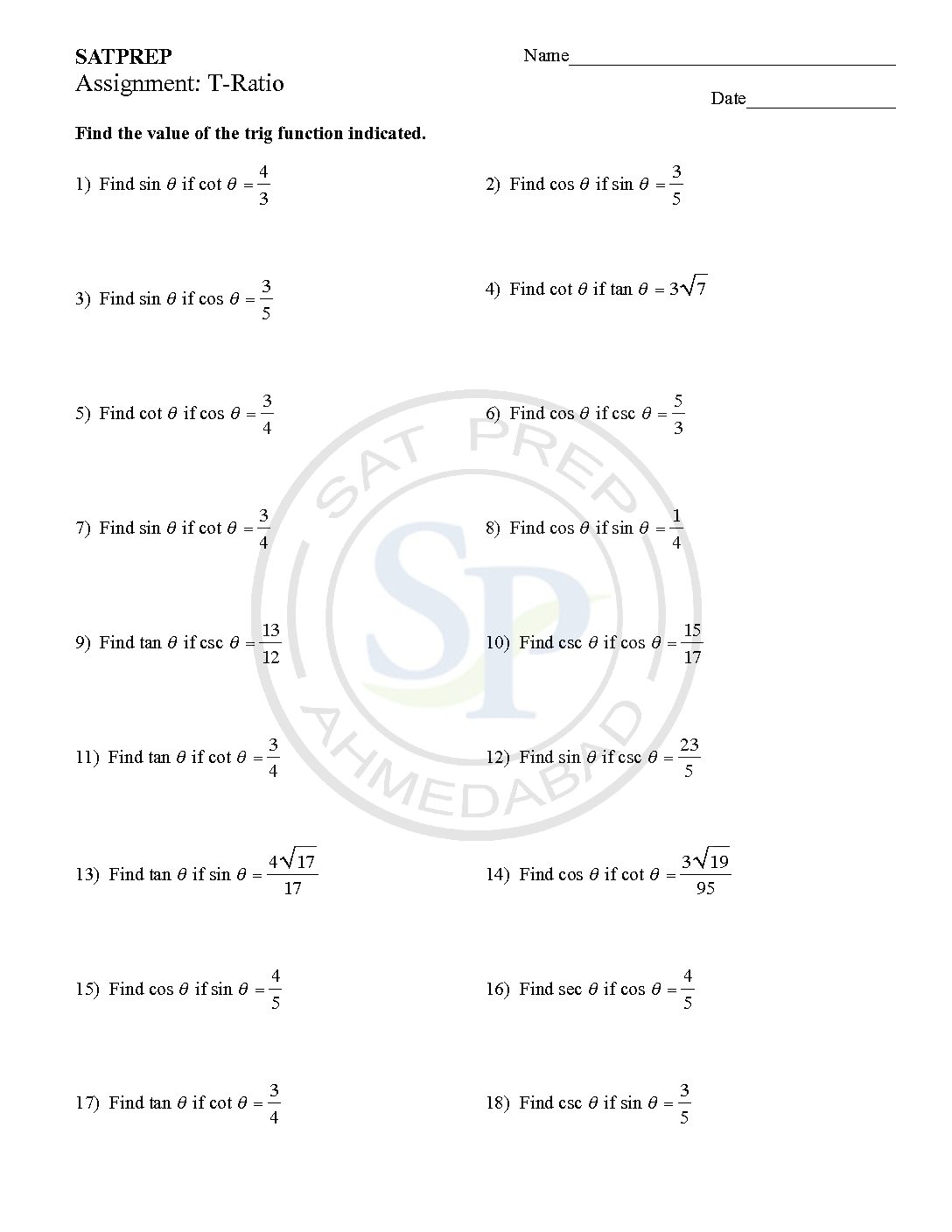
The ratios of the sides of a right triangle are called trigonometric ratios. Sine, Cosine and Tangent are main ratio while rest three reciprocal. Hence Sine and Cosine are the trigonometric ratios, whose values are less that 1 for an acute angle. Because they are periodic. www.kutasoftware.com
You are browsing archives for
Category: AP
Trigonometric ratio
The ratios of the sides of a right triangle are called trigonometric ratios. Sine, Cosine and Tangent are main ratio while rest three reciprocal. Hence Sine and Cosine are the trigonometric ratios, whose values are less that 1 for an acute angle. Because they are periodic. Trigonometric ratio
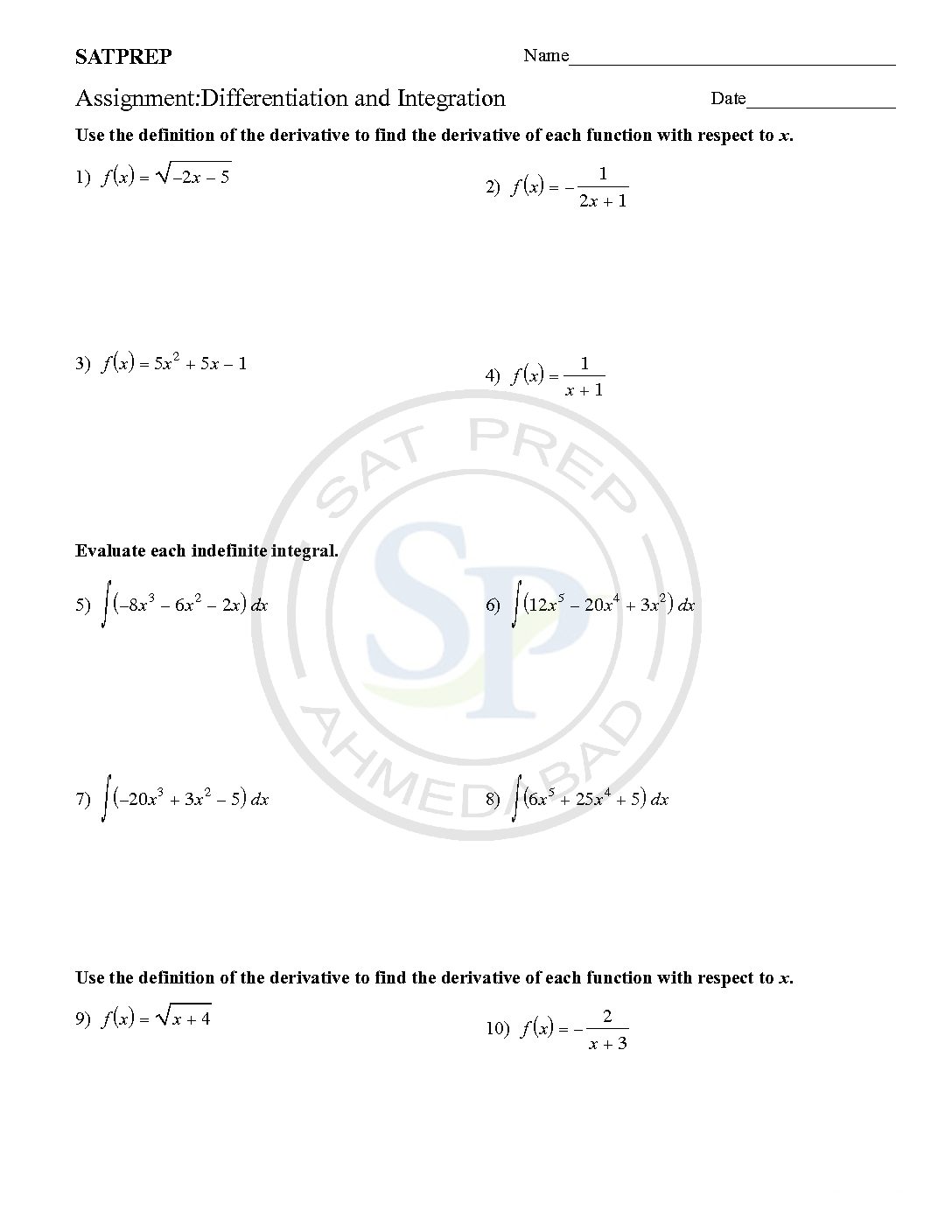
Differentiation and Integration
First of all differentiation and Integration are process of calculus. Due to differentiation we get derivative, while integration of derivative we get function back. Integration also called derivative. Differentiation and Integration
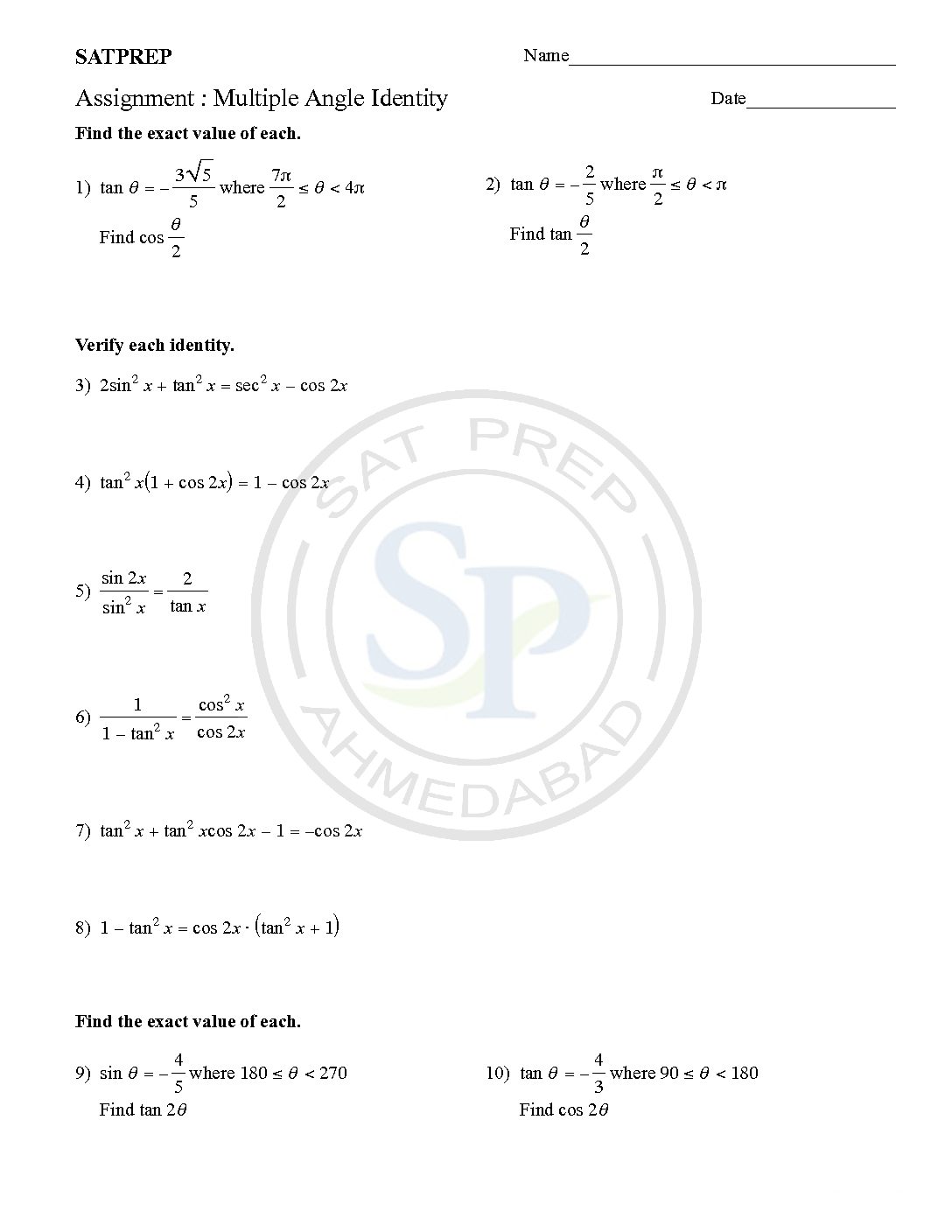
Multiple angle identity
Multiple angles identity are nothing but the trigonometric identity of multiple angles. Use for Proof of the double-angle and half-angle formulas. Solving Trigonometric Equations and Identities using Double–Angle and Half- Angle Formulas, examples and step by step solutions. Hence double angle formulae for sin 2A, cos 2A and tan 2A use for solving identity. Also to solve […]
Derivative of implicit and inverse trigo...
In calculus, a methods of implicit differentiation, Makes use of the chain rule to differentiate implicitly defined functions. To differentiate an implicit function y ( x ), defined by an equation R ( x, y) = 0, it is not generally possible to solve it explicitly for y and then differentiate. The derivatives of inverse trig functions we’ll need the formula from the last section […]
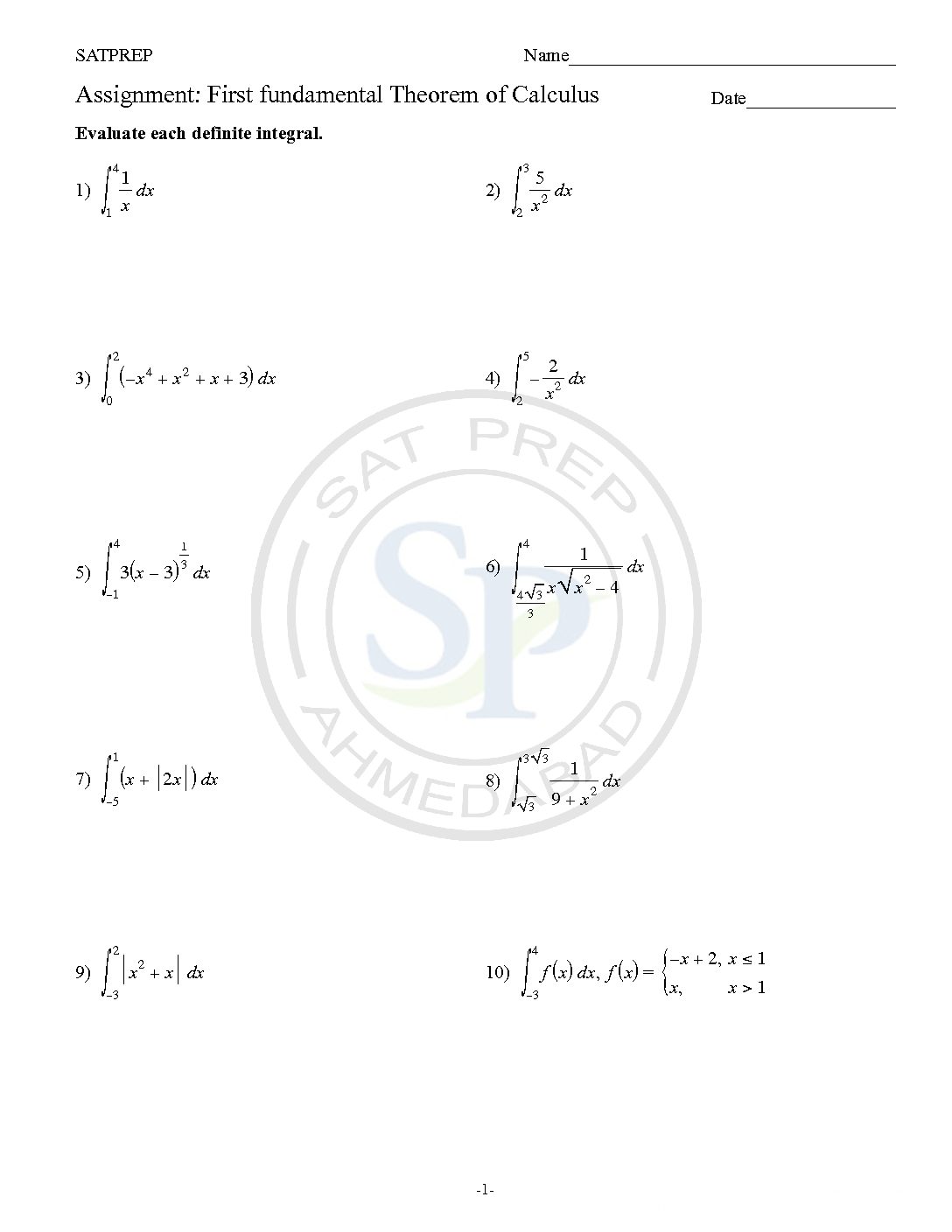
First fundamental Theorem of Calculus
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus. If we define an area function, F (x), as the area under the curve y=f (t) from t=0 to t=x, then the area function in this case is F (x)=c∗x. We would like to be able to evaluate more integrals with a process like this, The fundamental theorem of calculus tells us that if f […]
Second fundamental Theorem of Calculus
Then F ( x) is an antiderivative of f ( x )—that is, F ‘( x) = f ( x) for all x in I. That business about the interval I is to make sure we only get limits of integration that are are reasonable for your function. Some things that wouldn’t be reasonable: Choosing […]
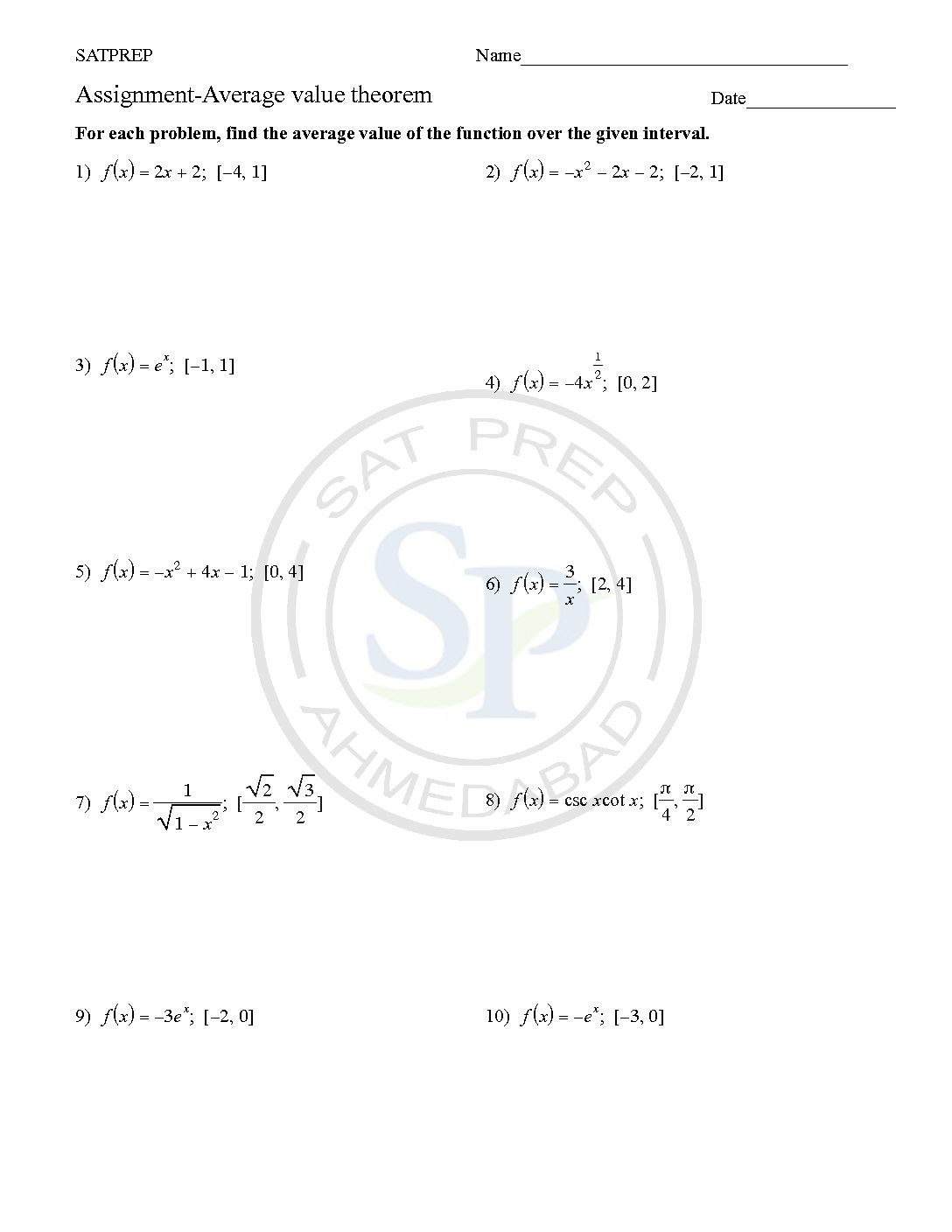
Average value theorem
Average values theorem of the function f(x) on the interval [a,b] is the integral of the function. Hence it give exact of a function on an interval. Also in decimal within interval. Average value
Trapezoidal Rule-2
trapezium rules is a way of estimating the area under a curve. so the trapezium rule gives a method of estimating integrals. Due to this we get approximate answer . Also we can get area using integration. trapezium rule
Trapezoidal Rule
The trapezium rules is a way of estimating the area under a curve. so the trapezium rule gives a method of estimating integrals. Due to this we get approximate answer . Also we can get area using integration. trapezium Rule