Rules for derivatives. Rules for derivatives. Sum rule: The derivative of the sum or difference of two functions is the sum or difference of their derivatives. (u + v)’ = u’ + v’ Constant multiple: The derivative of a constant times a function is the constant times the derivative of the function. (ku)’ = ku’ Rules for derivative
You are browsing archives for
Category: Differentiation
Rules of derivative
Rule for derivatives. Rules for derivatives. Sum rule: The derivative of the sum or difference of two functions is the sum or difference of their derivatives. (u + v)’ = u’ + v’ Constant multiple: The derivative of a constant times a function is the constant times the derivative of the function. (ku)’ = ku’ Rules of derivative
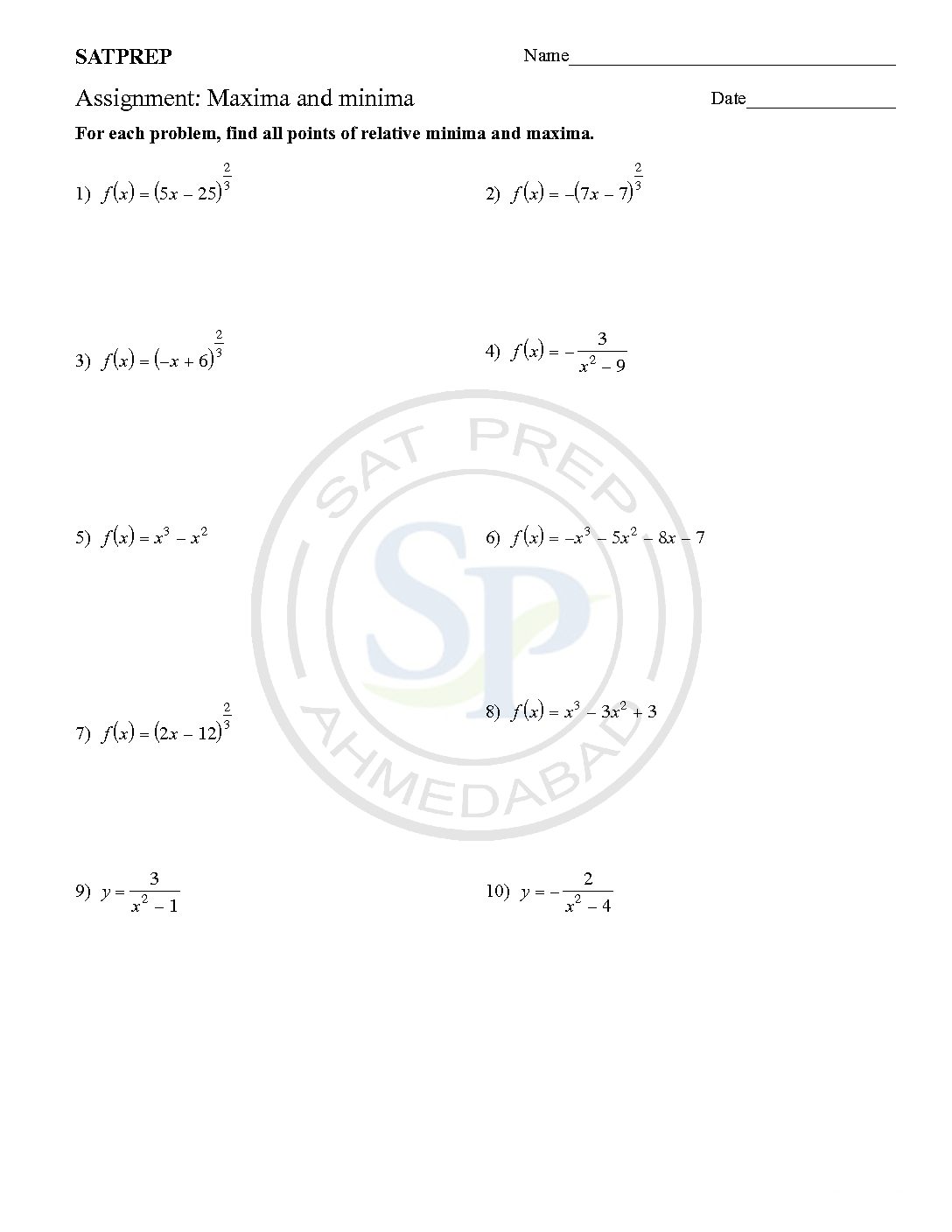
Maxima and Minima
Maximum and minimum of Points of Inflection. The value f ‘(x) is the gradient at any point but often we want to find the Turning or Stationary Point (Maximum and Minimum points) or Point of Inflection These happen where the gradient is zero, f ‘(x) = 0. Critical Points include Turning points and Points where f ‘ (x) does […]
Equation of Tangent and Normal
Tangents to a curve are a line that touches the curve at one point and has the same slope as the curve at that point. A normal to a curve is a line perpendicular to a tangent to the curve. Tangent and Normal
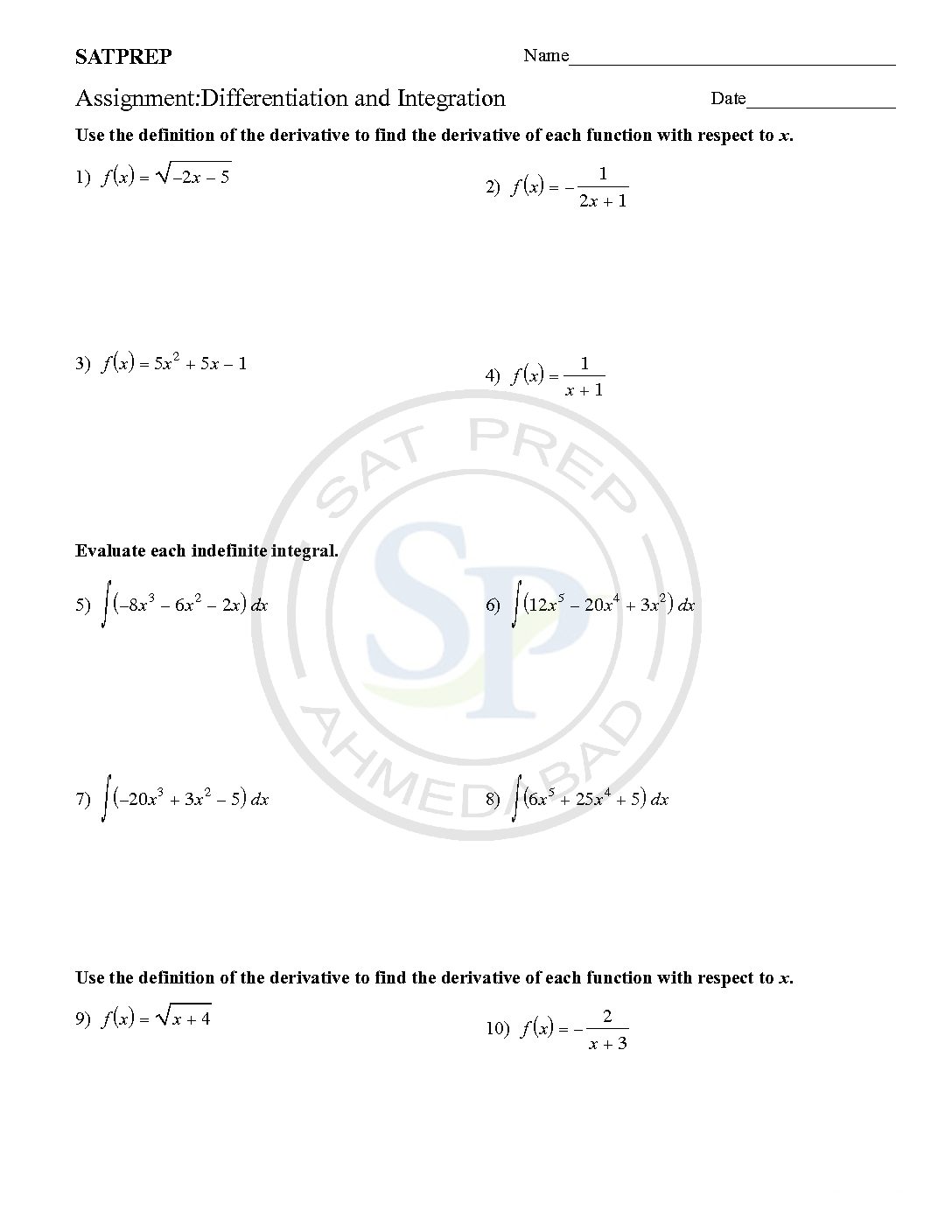
Differentiation and Integration
First of all differentiation and Integration are process of calculus. Due to differentiation we get derivative, while integration of derivative we get function back. Integration also called derivative. Differentiation and Integration
Tangent and normal : Implicit
Tangent and Normal Lines for implicit curves are a line that touches the implicit curve at one point and has the same slope as the curve at that point. A normal to a curve is a line perpendicular to a tangent to the curve. tangent and normal
Co-ordinate geometry -2
Ordered pair of numbers also known as coordinates. Hence manipulation of coordinate such as Determine the distance between these points. Find the equation, midpoint, and slope of the line segment. Determine if the given lines are perpendicular or parallel. Also deal with graphic representation. Coordinate geometry
Differentiation of polynomial
Differentiation is process of getting derivative. Differentiation has applications to nearly all quantitative disciplines. For example, in physics, the derivative of the displacement of a moving body with respect to time is the velocity of the body, and the derivative of velocity with respect to time is acceleration. Similarly in chemistry as well as Economics also derivative
Formulae of Calculus
List of Calculus Formulas-basic Properties and Formulas of Integration : If f (x) and g(x) are differentiable functions . Another In basic calculus, we learn rules and formulas for differentiation, which is the method by which we calculate the derivative of a function, and integration, Differential Calculus that is concerning rates of change and slopes of curves, and Integral Calculus concerning […]
Derivative of polynomials
Derivative is product of differentiation. Differentiation has applications to nearly all quantitative disciplines. For example, in physics, the derivative of the displacement of a moving body with respect to time is the velocity of the body, and the derivative of velocity with respect to time is acceleration. Therefore differentiation is process Derivative