Binomial theorems is another ways of expansion of two terms. Another way it is generalised form of expansion. Due to expansion of two term it is binomial. “What are the binomial coefficients?” . It shows how to calculate the coefficients in the expansion of (a + b) n. The symbol for a binomial coefficient nCr. As well as pascal […]
You are browsing archives for
Category: Pure Maths
This is pure maths category under cambridge as level
Double angle trigonometric equation
Double angle equations are allowing the expression of trigonometric functions of angles equal to 2u in terms of u. The double angle formulas can simplify the functions and gives ease to perform more complex calculations. The double angle formulas are useful for finding the values of unknown trigonometric functions. Therefore in double angle equation we need to consider two rotation. […]
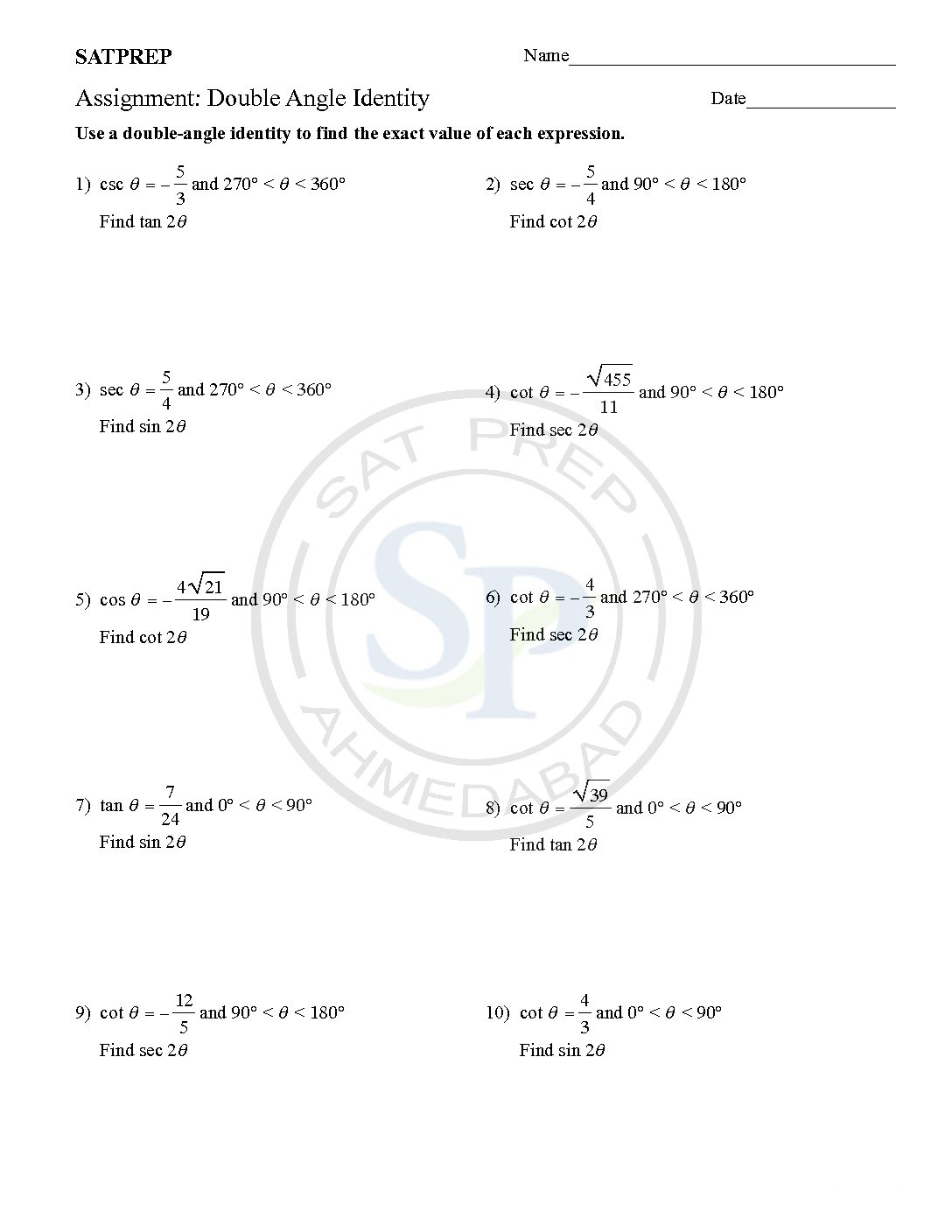
A Double angles identity
A Double angles identity is written2θ, for example, as sin 2θ, cos 2α, or tan 2x, where 2θ, 2α, and 2x. The angle measures and the assumption is that you mean sin(2θ), cos(2α), or tan(2x). Because tangent is equal to the ratio of sine and cosine . Therefor its identity comes from their double-angle identities. double angle identity
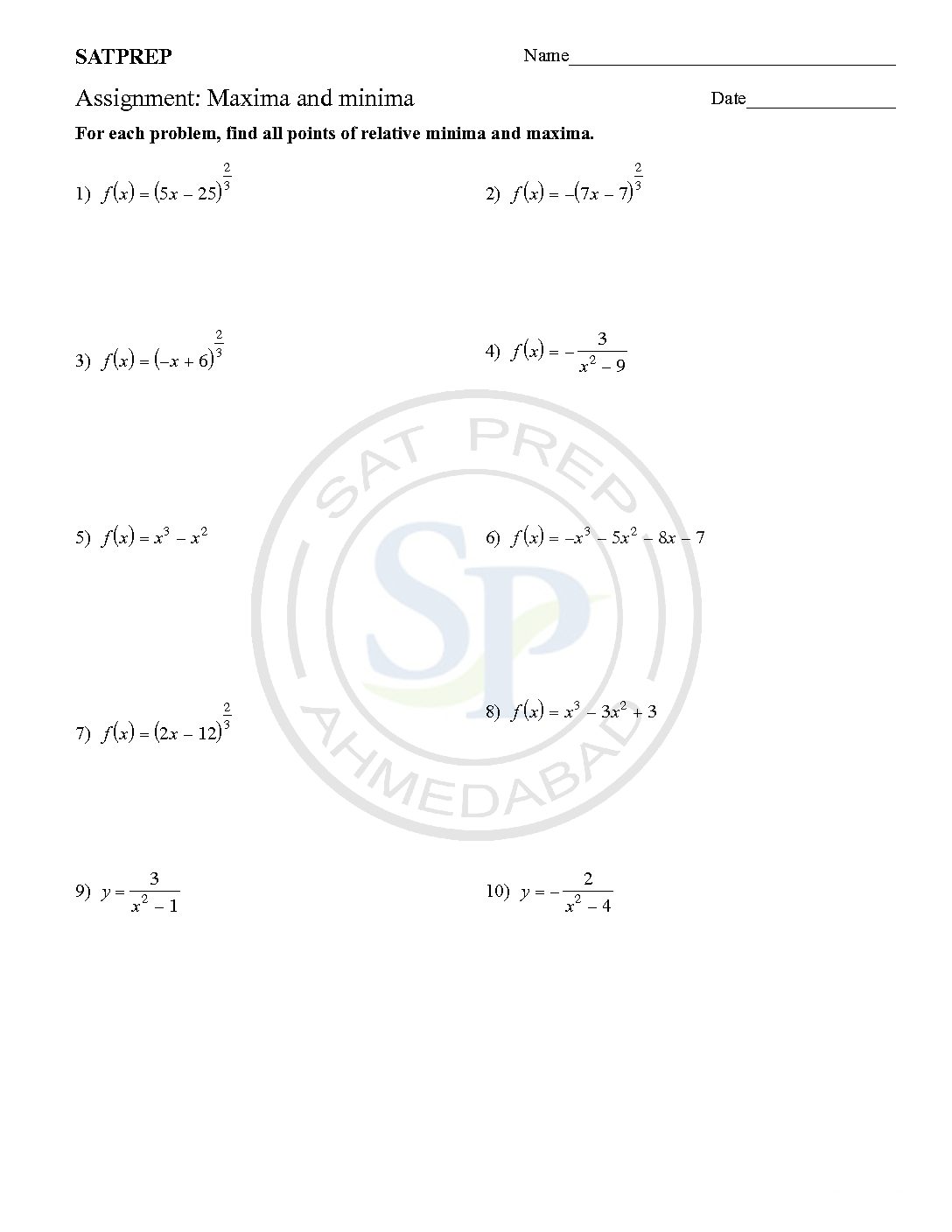
Maxima and Minima
Maximum and minimum of Points of Inflection. The value f ‘(x) is the gradient at any point but often we want to find the Turning or Stationary Point (Maximum and Minimum points) or Point of Inflection These happen where the gradient is zero, f ‘(x) = 0. Critical Points include Turning points and Points where f ‘ (x) does […]
Equation of Tangent and Normal
Tangents to a curve are a line that touches the curve at one point and has the same slope as the curve at that point. A normal to a curve is a line perpendicular to a tangent to the curve. Tangent and Normal
Trigonometric equations
Trigonometric equations use both the reference angles and trigonometric identities The general method of solving an equation is to convert it into the form of one ratio only. Hence, we can obtain solutions. Trigonometric Equation
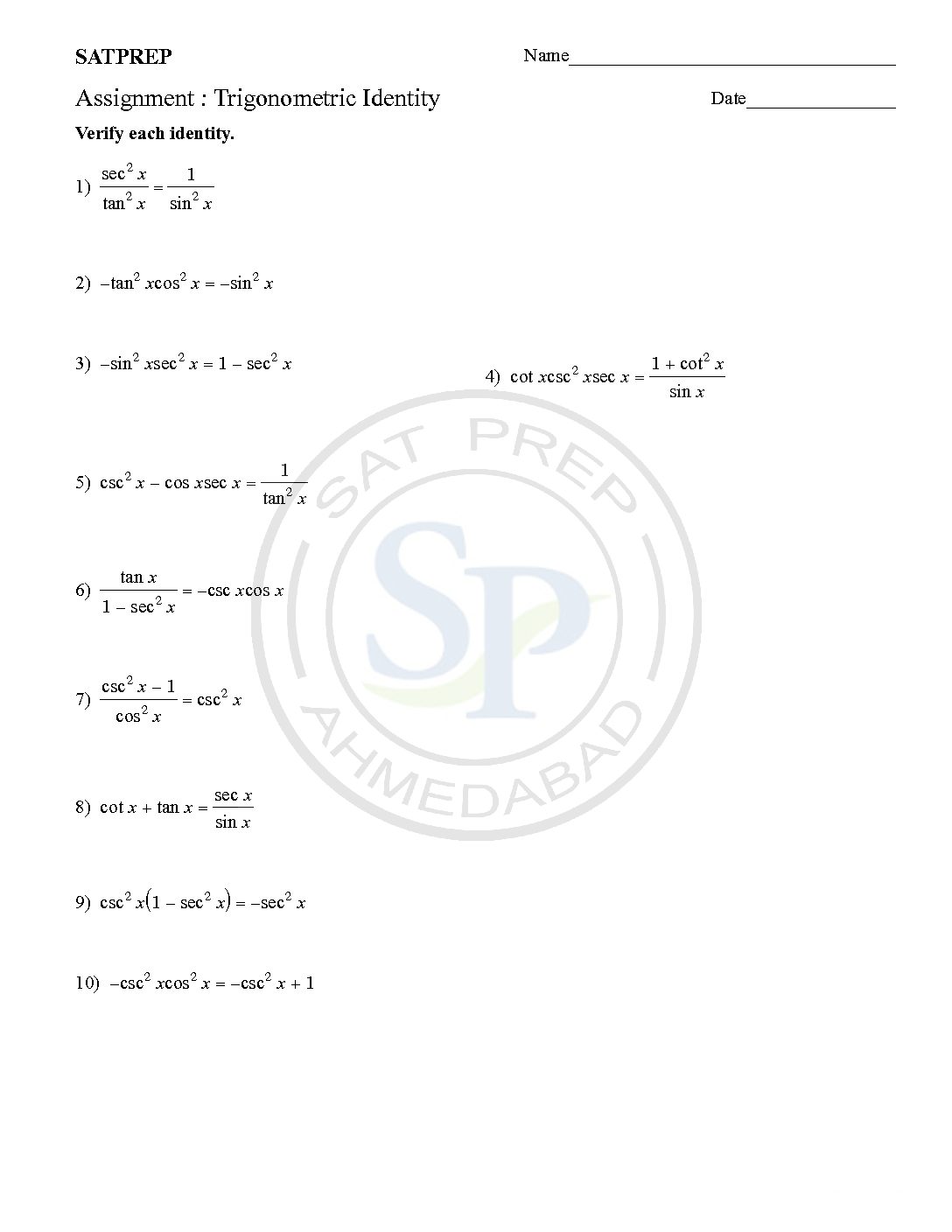
Trigonometric Identity
The trigonometric identity showing that the identity is always true, no matter what value of x or θ is used. Because it has to hold true for all values of x, we cannot simply substitute in a few values of x to “show” that they are equal. We have to use logical steps to show […]
Trigonometric Identity
trigonometry identities showing that the identity is always true, no matter what value of x or θ is used. Because it has to hold true for all values of x, we cannot simply substitute in a few values of x to “show” that they are equal. We have to use logical steps to show that one […]
Binomial Theorem
Binomial theorems is another ways of expansion of two terms. Another way it is generalised form of expansion. Due to expansion of two term it is binomial. “What are the binomial coefficients?” . It shows how to calculate the coefficients in the expansion of (a + b) n. The symbol for a binomial coefficient nCr. As well as pascal […]
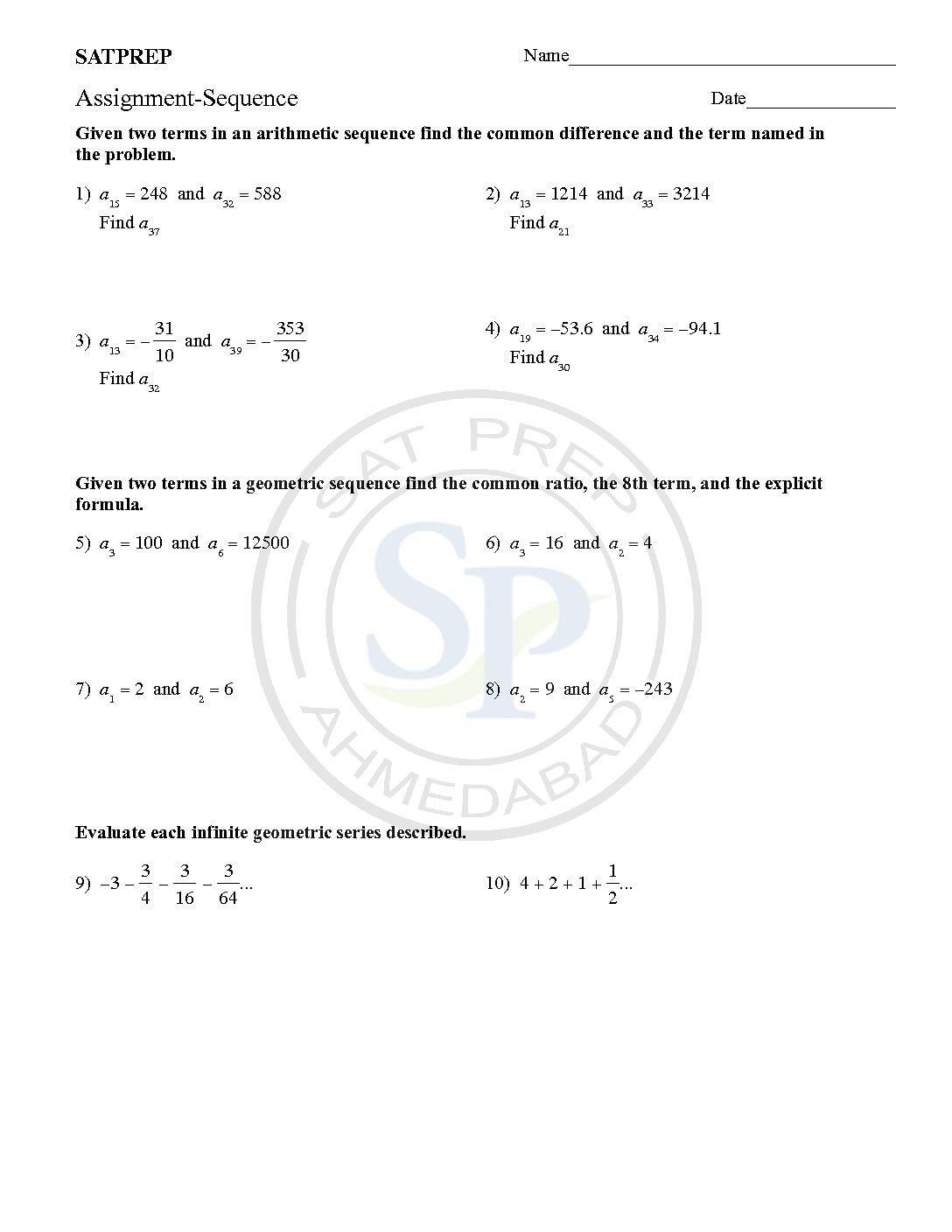
Sequence-2
Sequence and series is arrangement of term in particular pattern. Mathematical structures using the convergence properties of sequences. In particular, sequences are the basic for series Sequence and series