Combination and permutation are a very important topic of mathematics as well as the quantitative aptitude section. In permutation we arrange object while in combination we select items. Combinations and permutations
You are browsing archives for
Category: Algebra
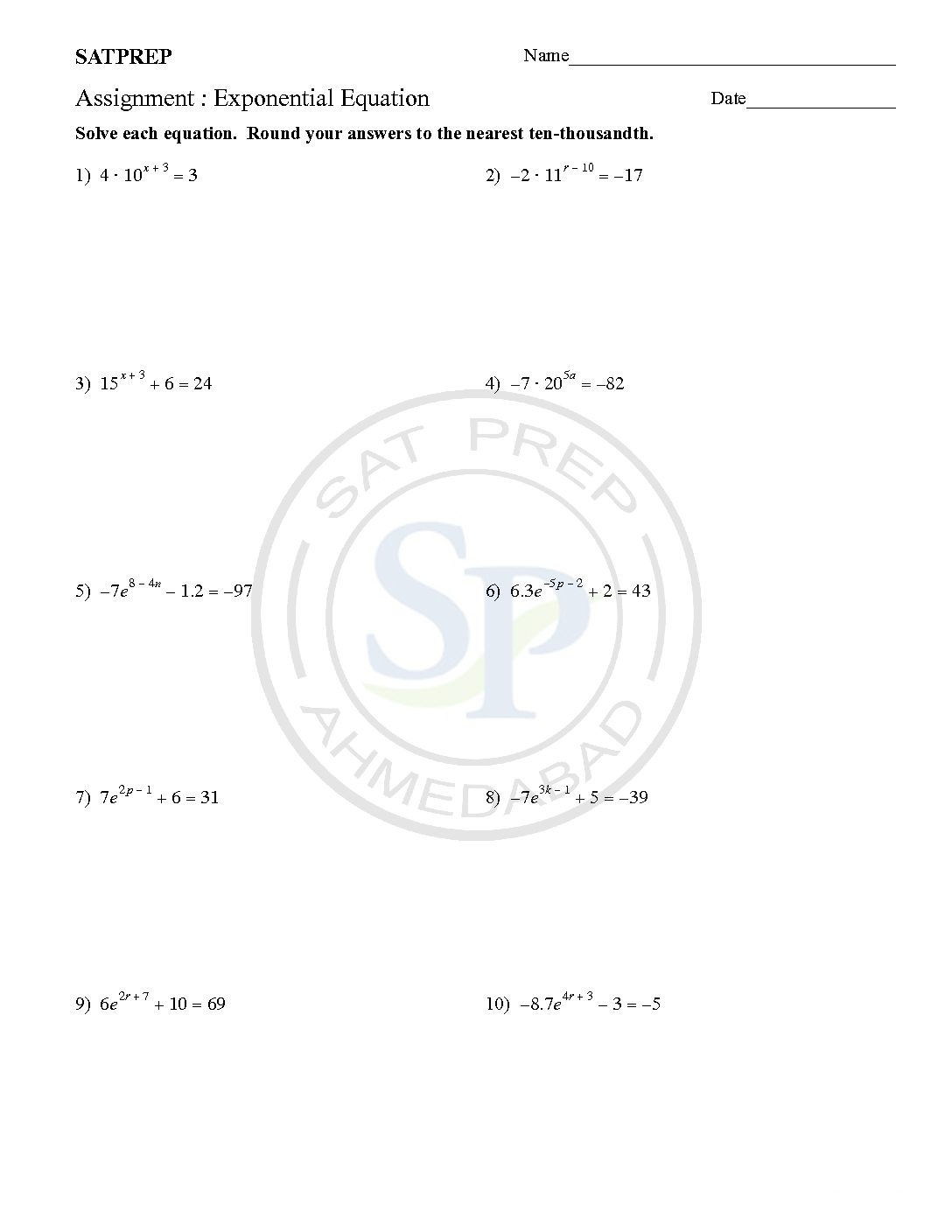
Exponential Equation
Exponential equations are one in which a variable occurs in the exponent, for example, . When both sides of the equation have the same base, the exponents on either side are equal by the property Exponential Equation
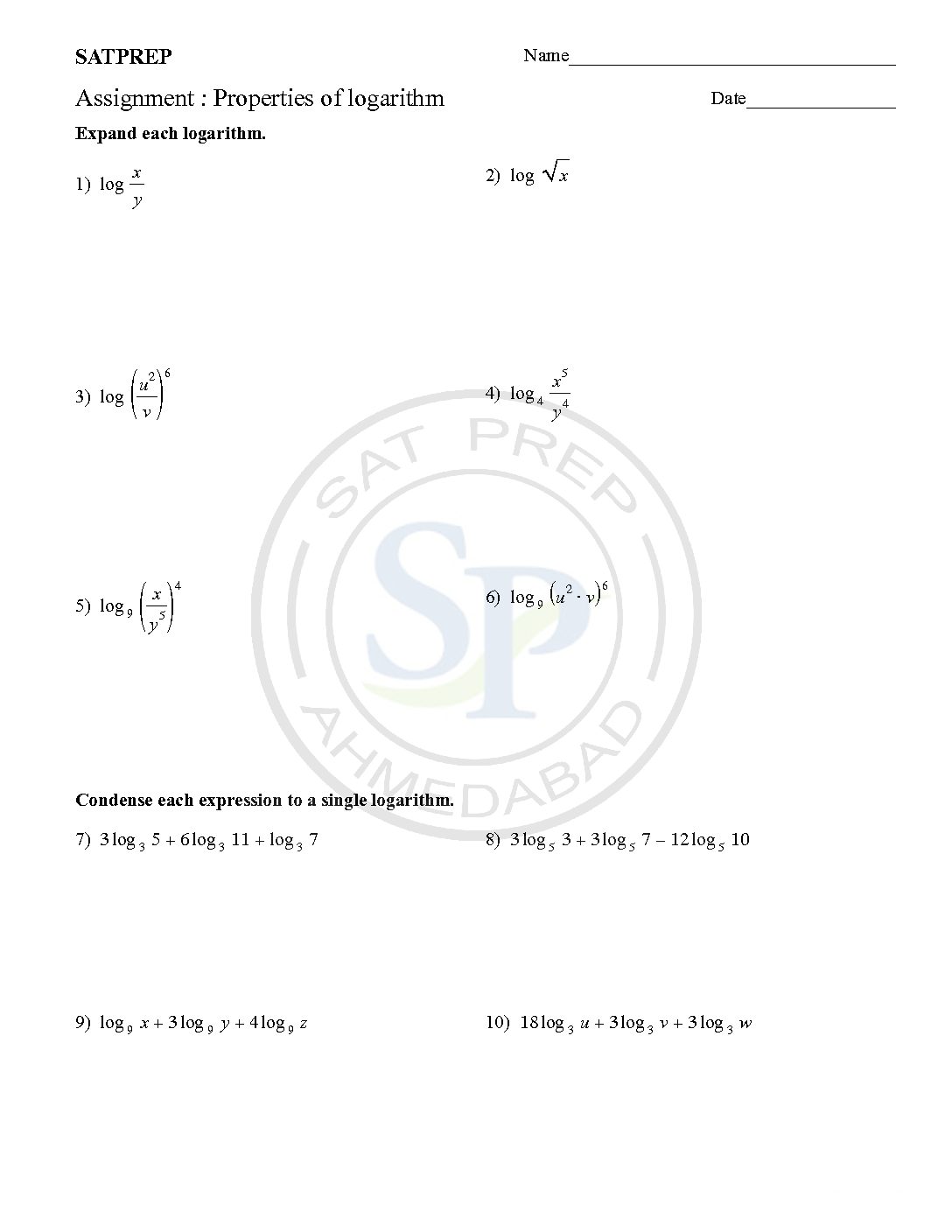
Properties of logarithm
Properties of logarithms are use to evaluate or rewrite logarithmic expressions. Product Rule : ln x+ ln y = ln xy Quotient Rule : ln x – ln y = ln xy Power Rule : ln yx = x ln y Properties of logarithm
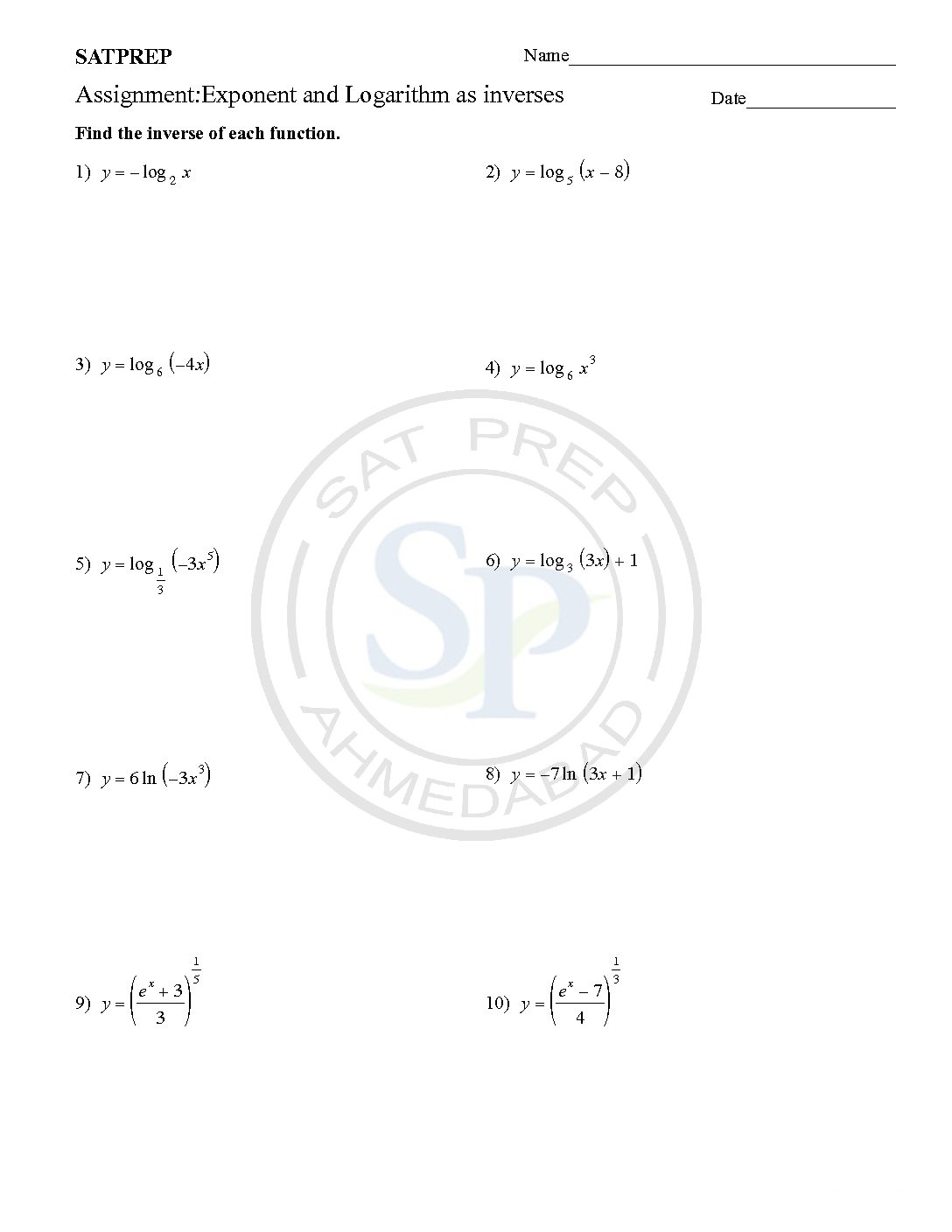
Exponent and Logarithm inverses
The inverse of the exponential function y = ax is x = ay. The logarithmic function y = logax is defined to be equivalent to the exponential equation x = ay. y = logax only under the following conditions: x = ay, a > 0, and a≠1. It is called the logarithmic function with base […]
Combinations And Permutations
Combinations is a very important topic of mathematics as well as the quantitative aptitude section. In permutation we arrange object while in combination we select items. Combination and permutation
Binomial theorem
The expansion of two terms is know as Binomial theorems . Another way it is generalised form of expansion. Due to expansion of two term it is binomial. “What are the binomial coefficients?” . It shows how to calculate the coefficients in the expansion of (a + b) n. The symbol for a binomial coefficient nCr. As well as […]
Imaginary No
A number is an imaginary number when it multiplied by square root of negative no. An imaginary number is the square root of a negative number and does not have a tangible value.”Complex” numbers have two parts, a “real” part (being any “real” number that you’re used to dealing with) and an “imaginary” part (being any number with an […]
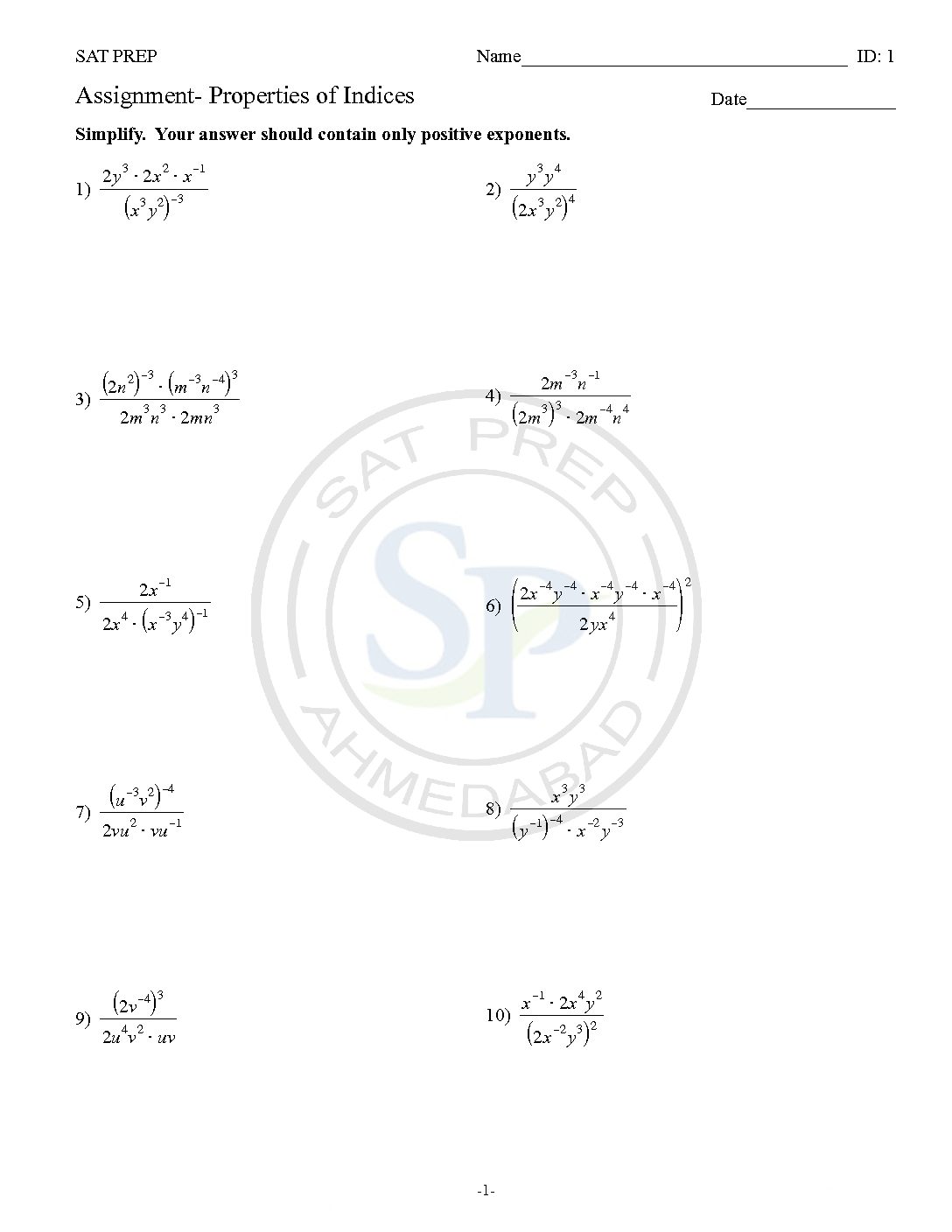
Properties of indices
Laws of Exponents. Exponents are also called Powers or Indices. The exponent of a number says how many times to use the number in a multiplication. Law of Indices. To manipulate expressions, we can consider using the Law of Indices. These laws only apply to expressions with the same base, for example, 3 4 and 3 2 can be manipulated […]
Basics of Permutation and Combination
Combinations and permutation and is a very important topic of mathematics as well as the quantitative aptitude section. In permutation we arrange object while in combination we select items. Permutation and combination
Fundamentals of Counting Principal , Per...
The Fundamental Counting Principle and Permutations is a way to figure out the total number of ways different events can occur. In combinatorics, the rule of product or multiplication principle is a basic counting it is the idea . Hence this principle also used in permutation and combination. Counting Principles