This post is about solution of optional calculus questions of past papers. In this post questions are from different paper from May 2014 to Nov 2017. By this post students will come to know verity of questions asked in previous year papers. The questions type in this post is calculator based. IB
You are browsing archives for
Category: Optional Calculus
IBDP Math HL Paper 3 Calculus
This post is about questions of optional calculus from past papers. In this post questions are from different paper of May 2014 to Nov 2017. By this post students will come to know verity of questions asked in previous year papers. The questions type in this post is calculator based. IB
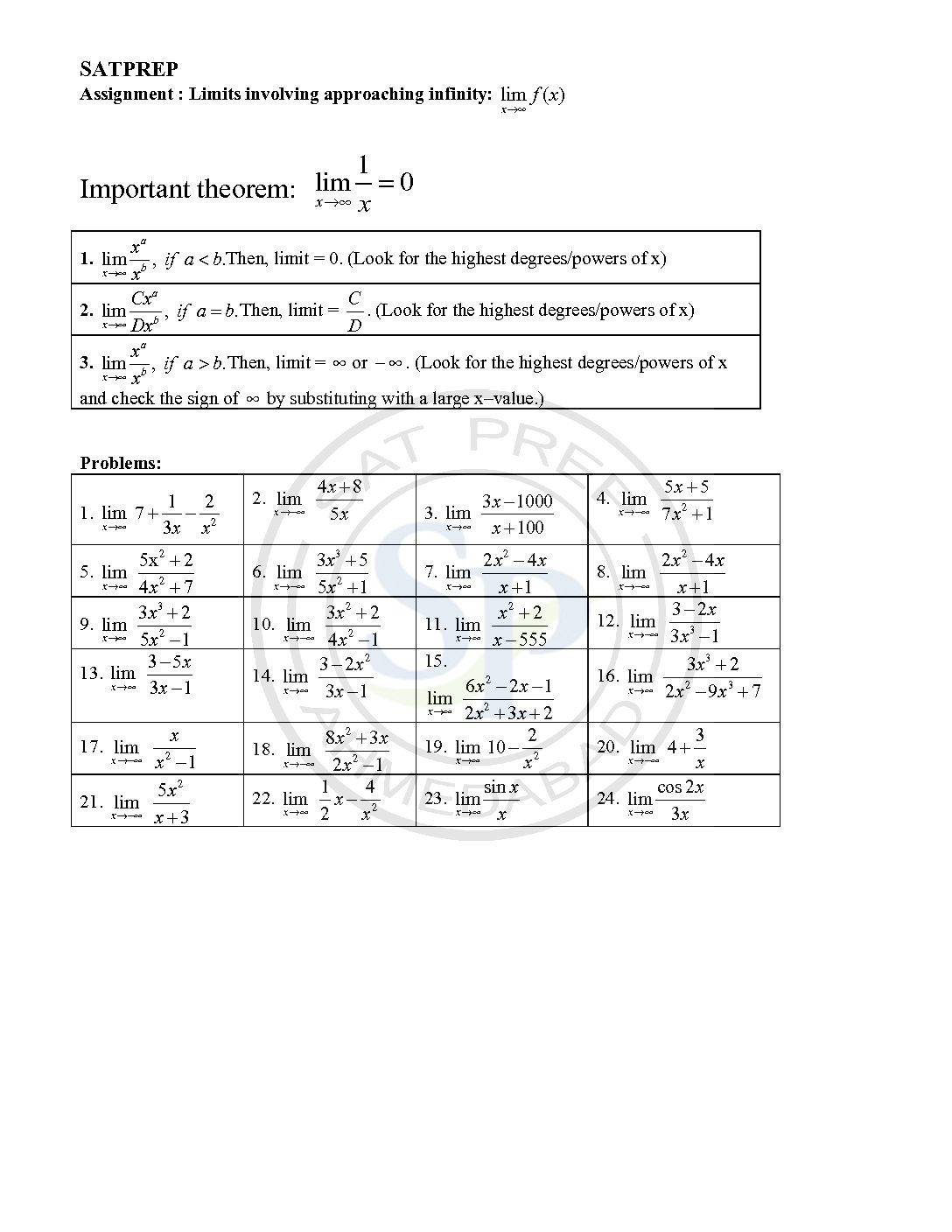
Limit
Limits are the concept of function. So, we have to solve function for given limits. Due to different type of limits , function cannot solve. limit
Second fundamental theorem of Calculus-2
Second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Then F ( x) is an antiderivative of f ( x )—that is, F ‘( x) = f ( x) for all x in I. That business about the interval I is to make sure we only get limits of integration that are are reasonable for your function. Some things […]
Differential Eq
Differential Equation is a function and one or more of its derivatives. Hence it solve by variable seperable and linear differential eq method. Also it solve by homogeneous. Differential Equation
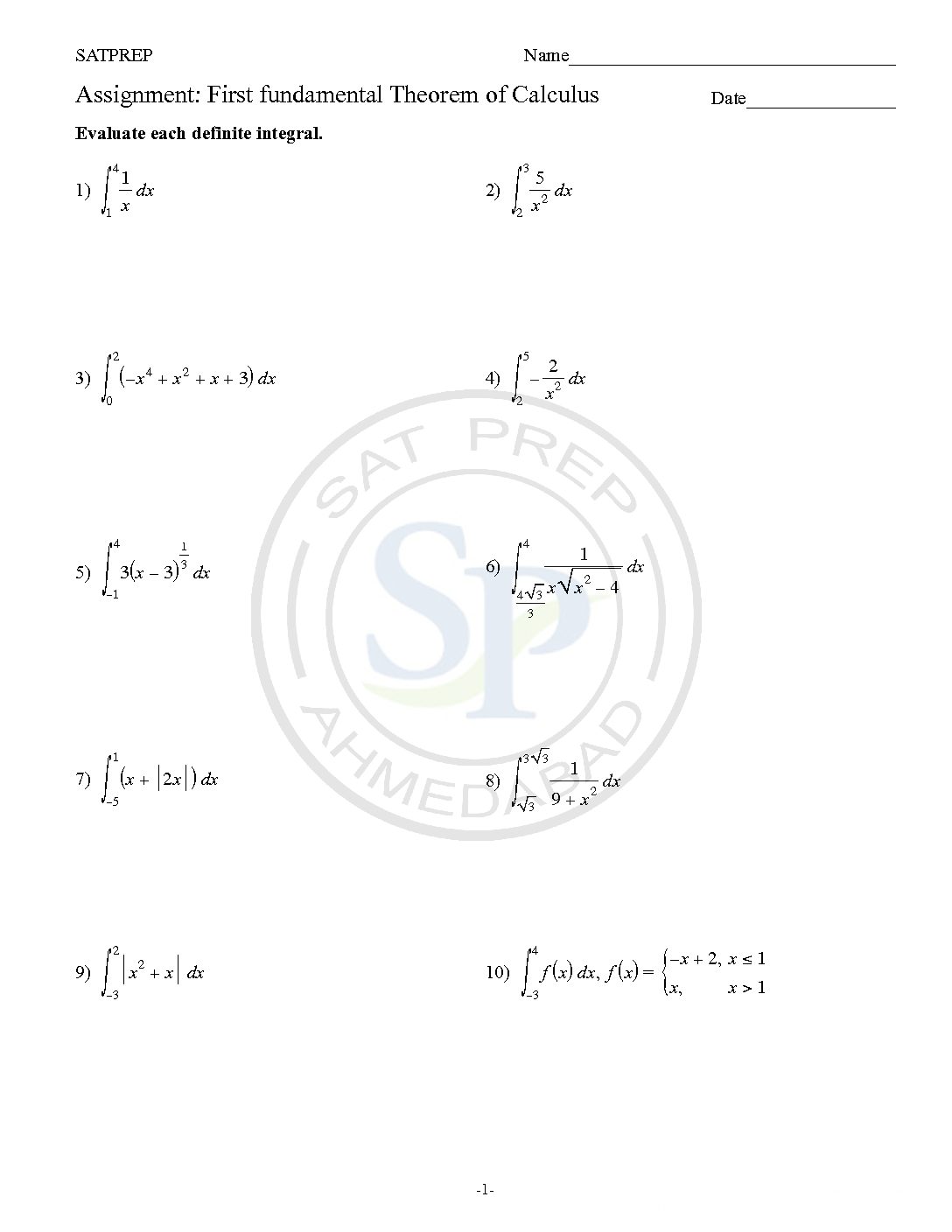
First fundamental Theorem of Calculus
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus. If we define an area function, F (x), as the area under the curve y=f (t) from t=0 to t=x, then the area function in this case is F (x)=c∗x. We would like to be able to evaluate more integrals with a process like this, The fundamental theorem of calculus tells us that if f […]
Second fundamental Theorem of Calculus
Then F ( x) is an antiderivative of f ( x )—that is, F ‘( x) = f ( x) for all x in I. That business about the interval I is to make sure we only get limits of integration that are are reasonable for your function. Some things that wouldn’t be reasonable: Choosing […]
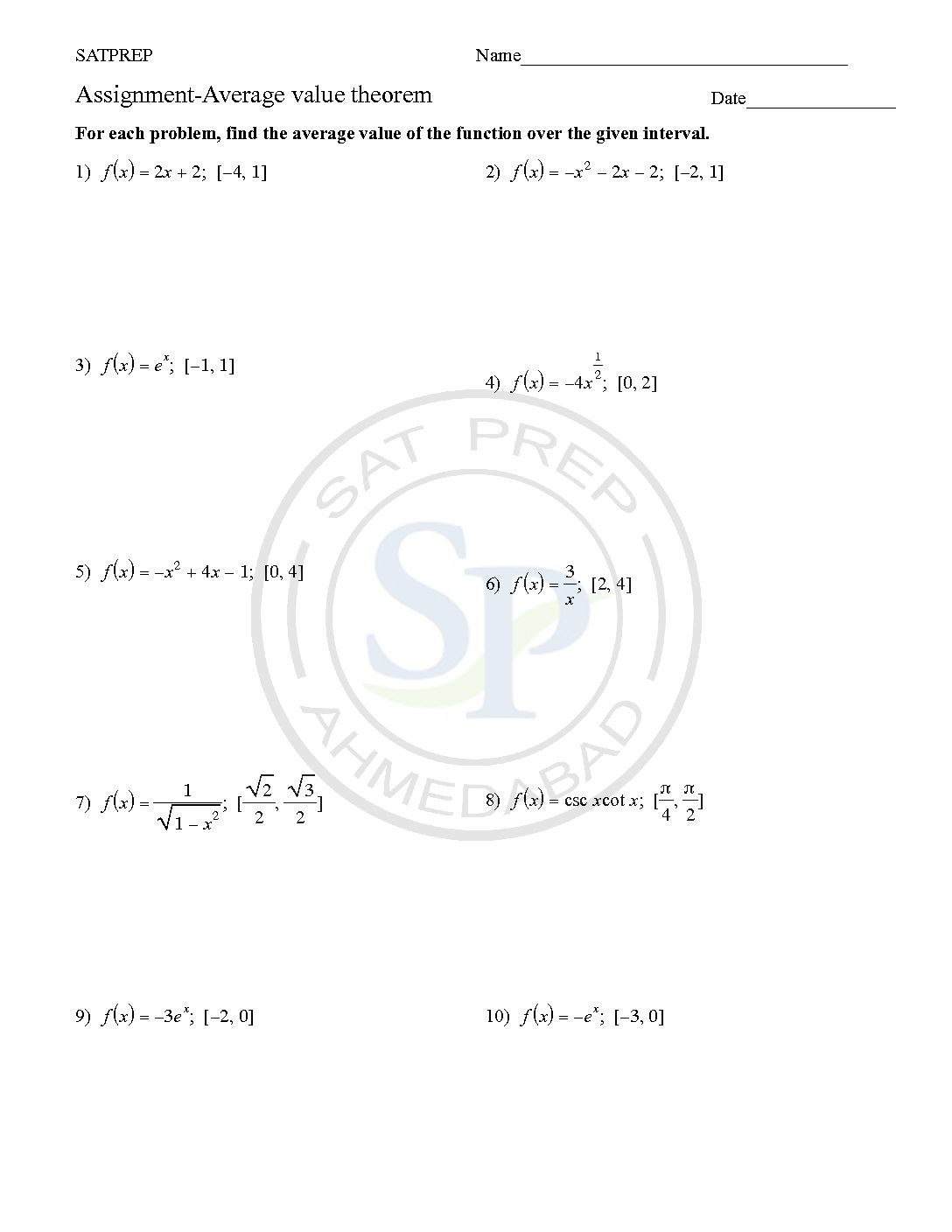
Average value theorem
Average values theorem of the function f(x) on the interval [a,b] is the integral of the function. Hence it give exact of a function on an interval. Also in decimal within interval. Average value
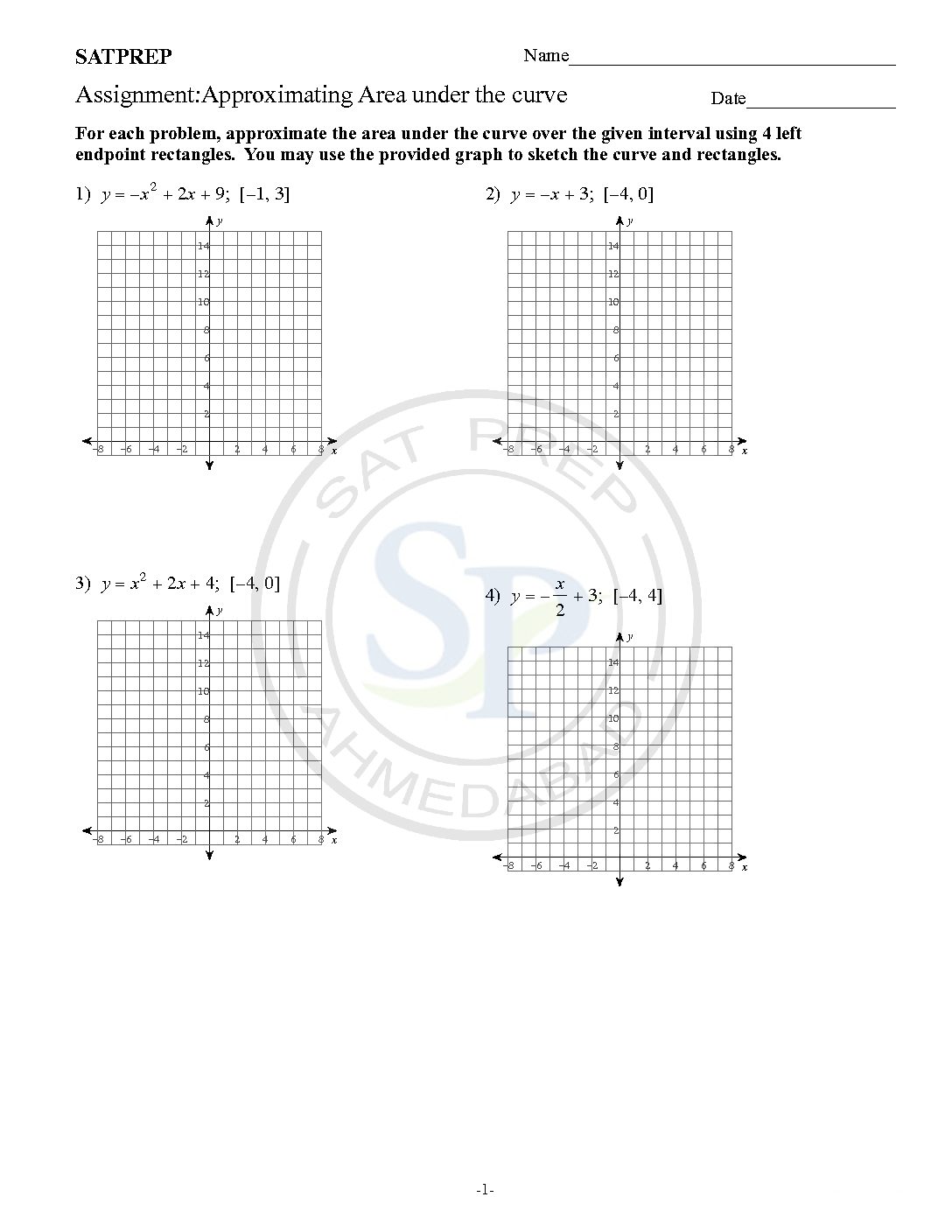
Approximating area under the curve
Approximate area of under a curve. Compute left, right, and midpoint Hence Riemann sums use with n rectangles are computed. Due to the this it approximate area. Approximate area under
Riemann sum( table)
A Riemann sums is an approximation of a region’s area. It obtained by adding up the areas of multiple simplified slices of the region. It is applied in calculus to determine the area of a region. Hence it give approximate area of region. It is also give right and left sum. Riemann sum