Kinematic is the branch of classical mechanics. describes the motion of points, objects and systems of groups of objects, without reference to the causes of motion. The symbol a stands for the acceleration of the object. And the symbol v stands for the instantaneous velocity of the object. The derivative of displacement with time is velocity […]
You are browsing archives for
Category: IB Maths HL
Binomial Theorem
Binomial theorems is another ways of expansion of two terms. Another way it is generalised form of expansion. Due to expansion of two term it is binomial. “What are the binomial coefficients?” . It shows how to calculate the coefficients in the expansion of (a + b) n. The symbol for a binomial coefficient nCr. As well as pascal […]
Volume of revolution
To get a solid of revolution we start out with a function, y=f (x), on an interval [a,b]. We then rotate this curve about a given axis to get the surface of the solid of revolution Volume of Revolution
Binomial Distribution
The Binomial distributions Number of successes in a specified number of independent trials of an experiment . Symbol: B (n, p), where n is the number of trials and p the probability of success in each. As there are two parameter therefore it is Binomial distribution. Hence it used for discrete values. Binomial Theorem
Double angle trigonometric equation
Double angle equations are allowing the expression of trigonometric functions of angles equal to 2u in terms of u. The double angle formulas can simplify the functions and gives ease to perform more complex calculations. The double angle formulas are useful for finding the values of unknown trigonometric functions. Therefore in double angle equation we need to consider two rotation. […]
Binomial Distribution
The Binomial distributions Number of successes in a specified number of independent trials of an experiment . Symbol: B (n, p), where n is the number of trials and p the probability of success in each. As there are two parameter therefore it is Binomial distribution. Hence it used for discrete values. binomial distribution
Normal Distribution
A standard Normal Distribution graph is “Bell Curve”.The standard normal distribution has two parameters: mean and standard deviation. Hence it use for continuous random variable as well as it use for continuous values. Due to continuous values we use area under the curve for calculating probability. Normal
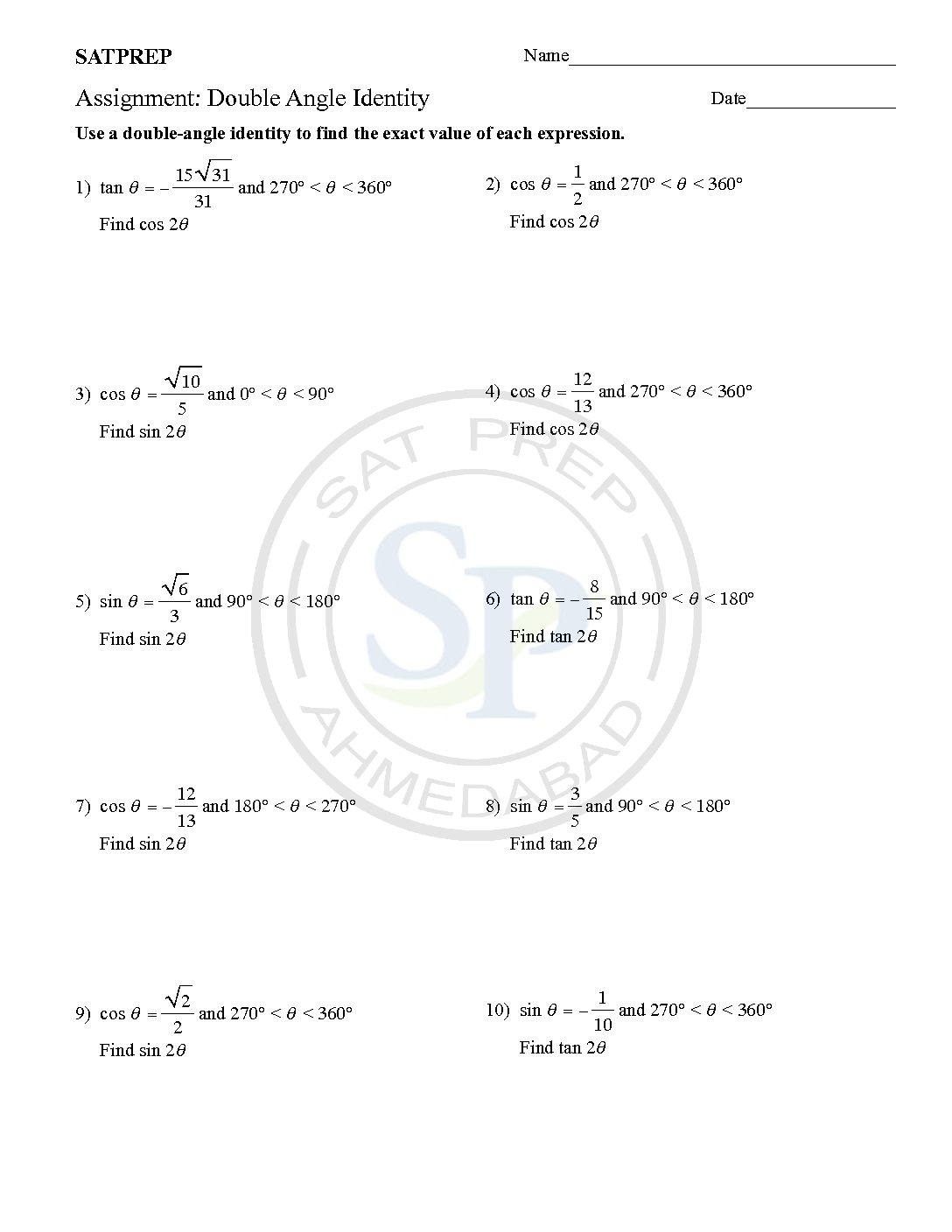
A Double angles identity
A Double angles identity is written2θ, for example, as sin 2θ, cos 2α, or tan 2x, where 2θ, 2α, and 2x. The angle measures and the assumption is that you mean sin(2θ), cos(2α), or tan(2x). Because tangent is equal to the ratio of sine and cosine . Therefor its identity comes from their double-angle identities. double angle identity
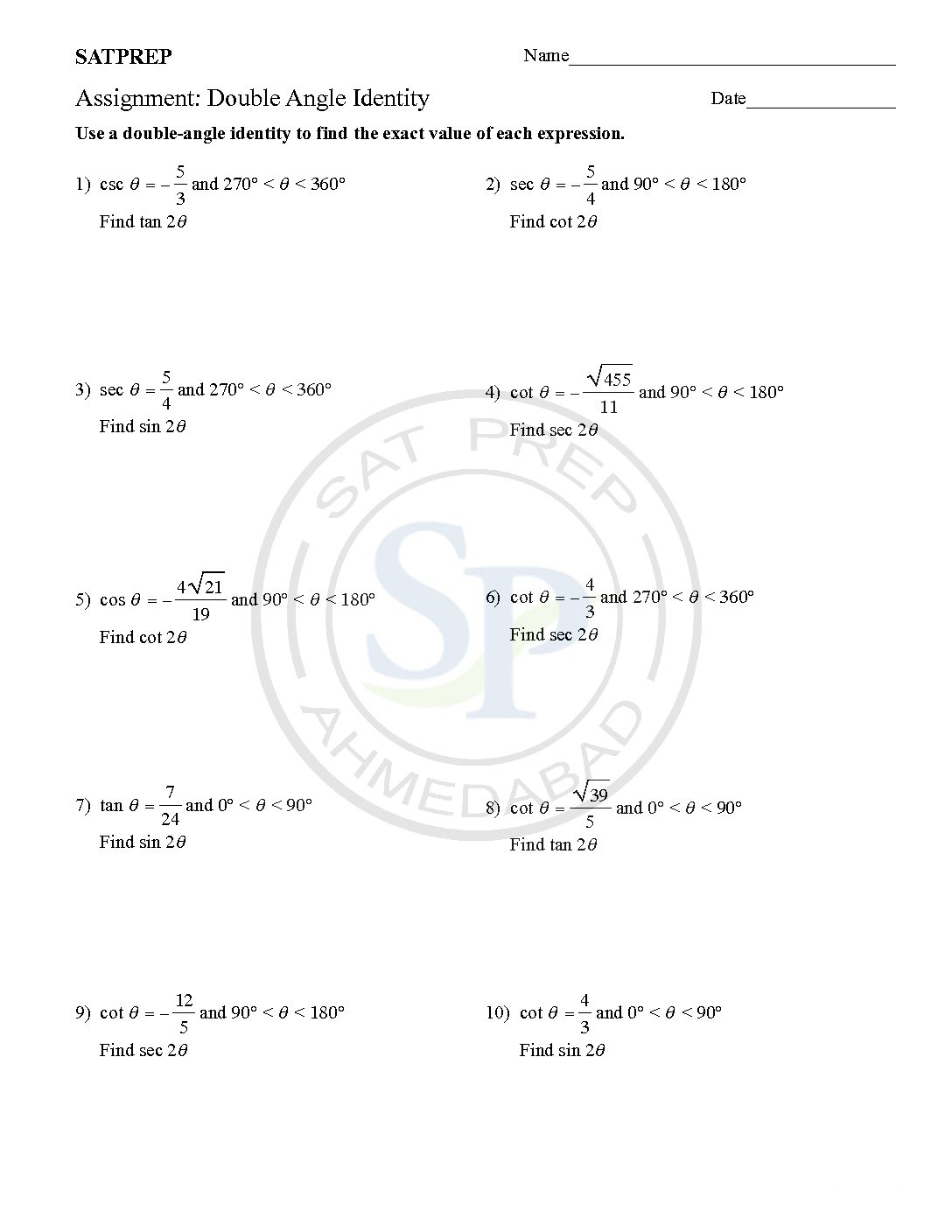
Double Angle trigonometric Identity
A Double angles identity is written2θ, for example, as sin 2θ, cos 2α, or tan 2x, where 2θ, 2α, and 2x. The angle measures and the assumption is that you mean sin(2θ), cos(2α), or tan(2x). Because tangent is equal to the ratio of sine and cosine . Therefor its identity comes from their double-angle identities. Double angle
Equation of Tangent and Normal
Tangents to a curve are a line that touches the curve at one point and has the same slope as the curve at that point. A normal to a curve is a line perpendicular to a tangent to the curve. Tangent and Normal