Tangent and Normal Lines for implicit curves are a line that touches the implicit curve at one point and has the same slope as the curve at that point. A normal to a curve is a line perpendicular to a tangent to the curve. tangent and normal
You are browsing archives for
Category: IB Maths HL
Trigonometric Graph
Graphs of Trigonometric Functions. Below are the graphs of the six trigonometric functions: sine, cosine, tangent, cosecant, secant, and cotangent. Explore the amplitude, period, and phase shift by examining the graphs of various trigonometric functions. Graph of y = sin x. Graph of y = sin ax. Graph of y = cos x. Graph of y […]
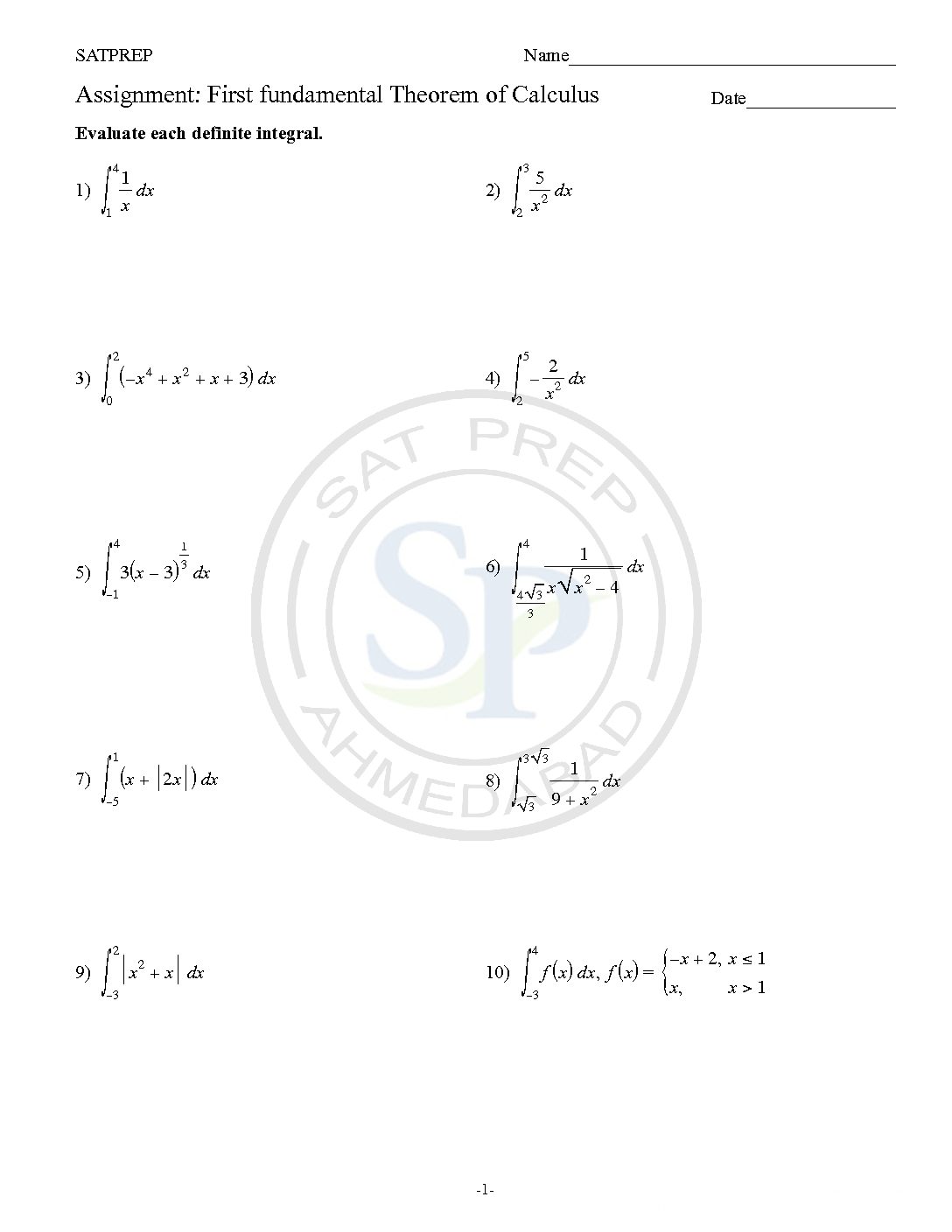
First fundamental Theorem of Calculus
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus. If we define an area function, F (x), as the area under the curve y=f (t) from t=0 to t=x, then the area function in this case is F (x)=c∗x. We would like to be able to evaluate more integrals with a process like this, The fundamental theorem of calculus tells us that if f […]
Second fundamental Theorem of Calculus
Then F ( x) is an antiderivative of f ( x )—that is, F ‘( x) = f ( x) for all x in I. That business about the interval I is to make sure we only get limits of integration that are are reasonable for your function. Some things that wouldn’t be reasonable: Choosing […]
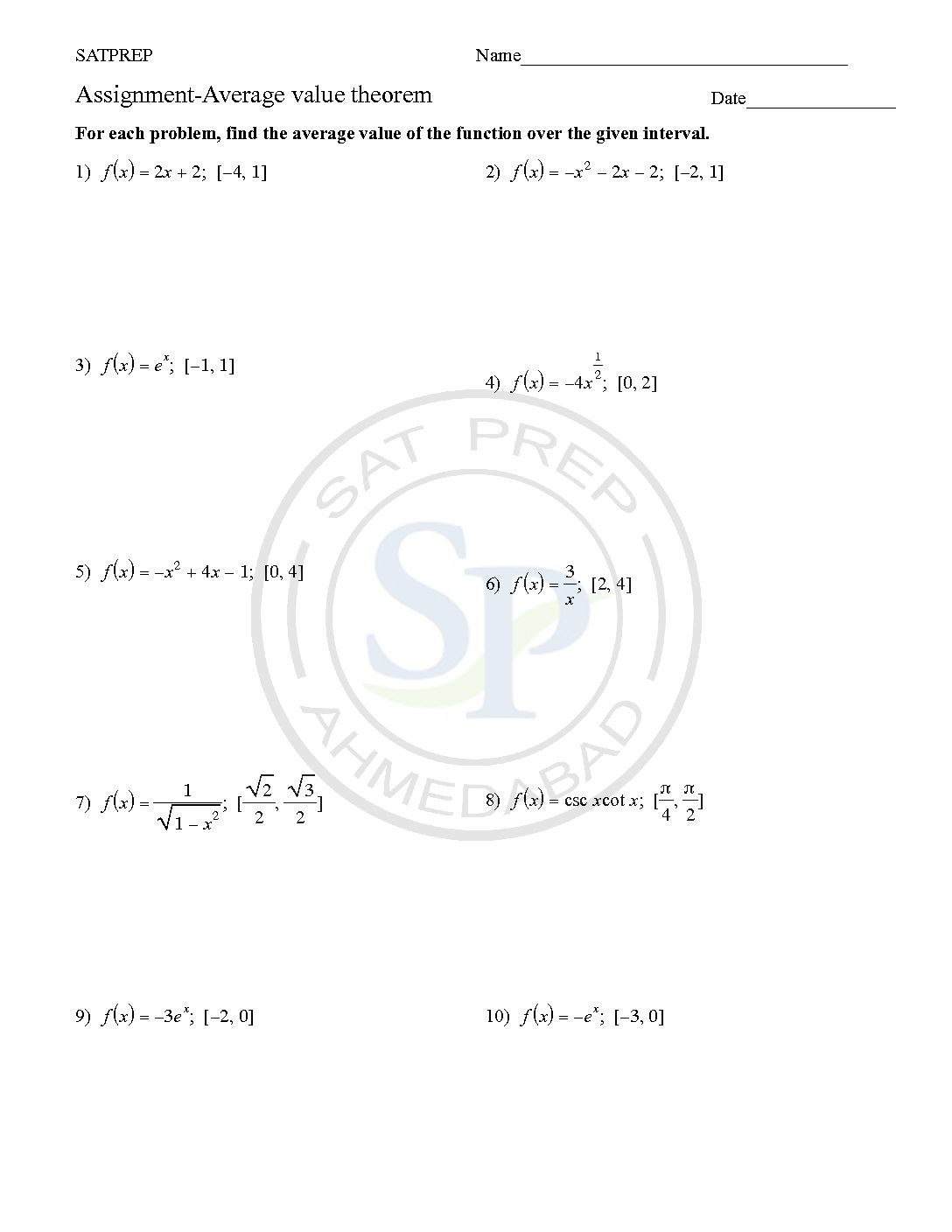
Average value theorem
Average values theorem of the function f(x) on the interval [a,b] is the integral of the function. Hence it give exact of a function on an interval. Also in decimal within interval. Average value
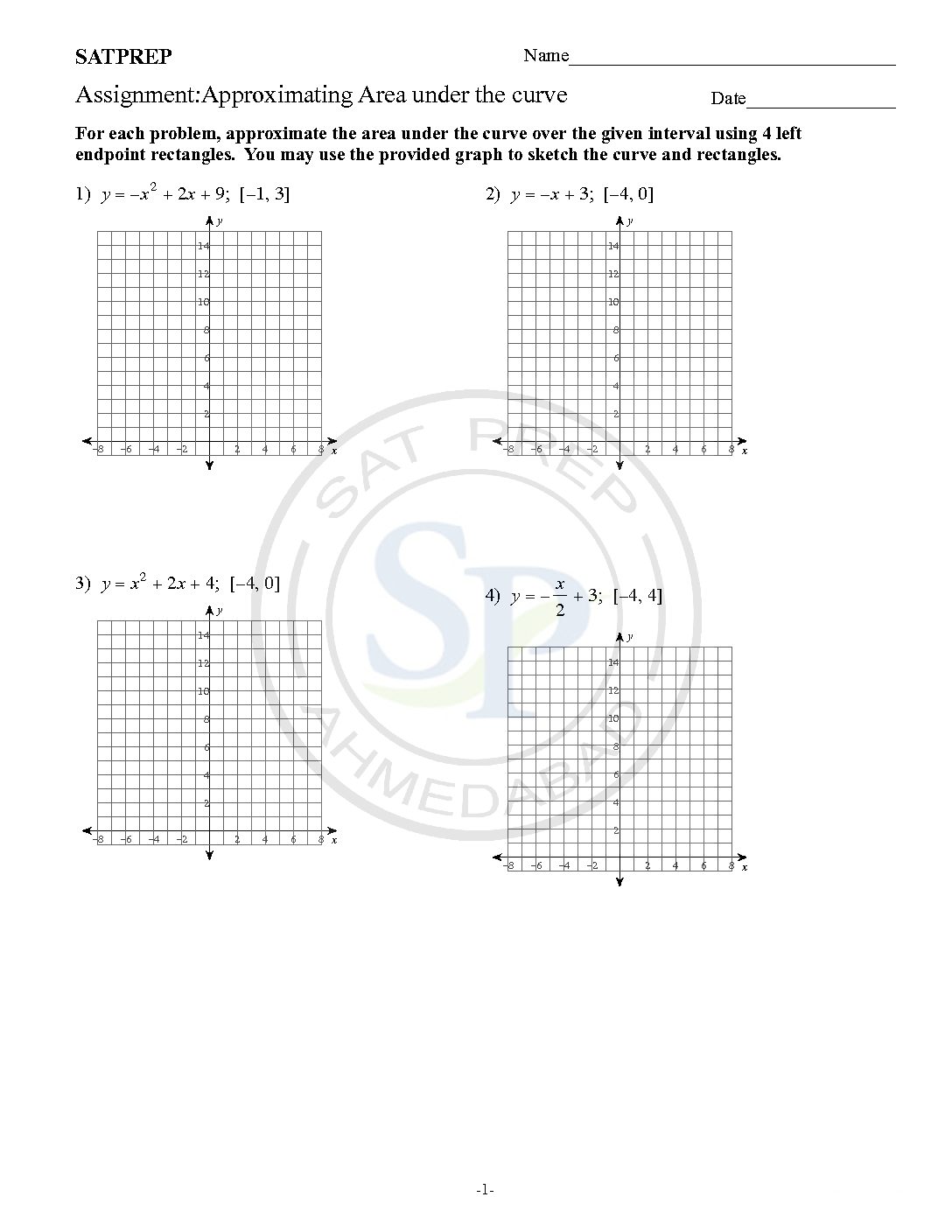
Approximating area under the curve
Approximate area of under a curve. Compute left, right, and midpoint Hence Riemann sums use with n rectangles are computed. Due to the this it approximate area. Approximate area under
Riemann sum( table)
A Riemann sums is an approximation of a region’s area. It obtained by adding up the areas of multiple simplified slices of the region. It is applied in calculus to determine the area of a region. Hence it give approximate area of region. It is also give right and left sum. Riemann sum
Probability
Probabilities is the measure of the likelihood that an event will occur. A number between zero and one that shows how likely a certain event. Another probability of event A is the number of ways event A can occur divided by the total number of possible outcomes. Also expressed by the ratio of the number of actual occurrences […]
Mathematical Induction (Divisibility)
Mathematical induction is a special way of proving things. It has only 2 steps: Step 1. Show it is true for the first one Step 2. Show that if any one is true then the next one is true. Mathematical induction
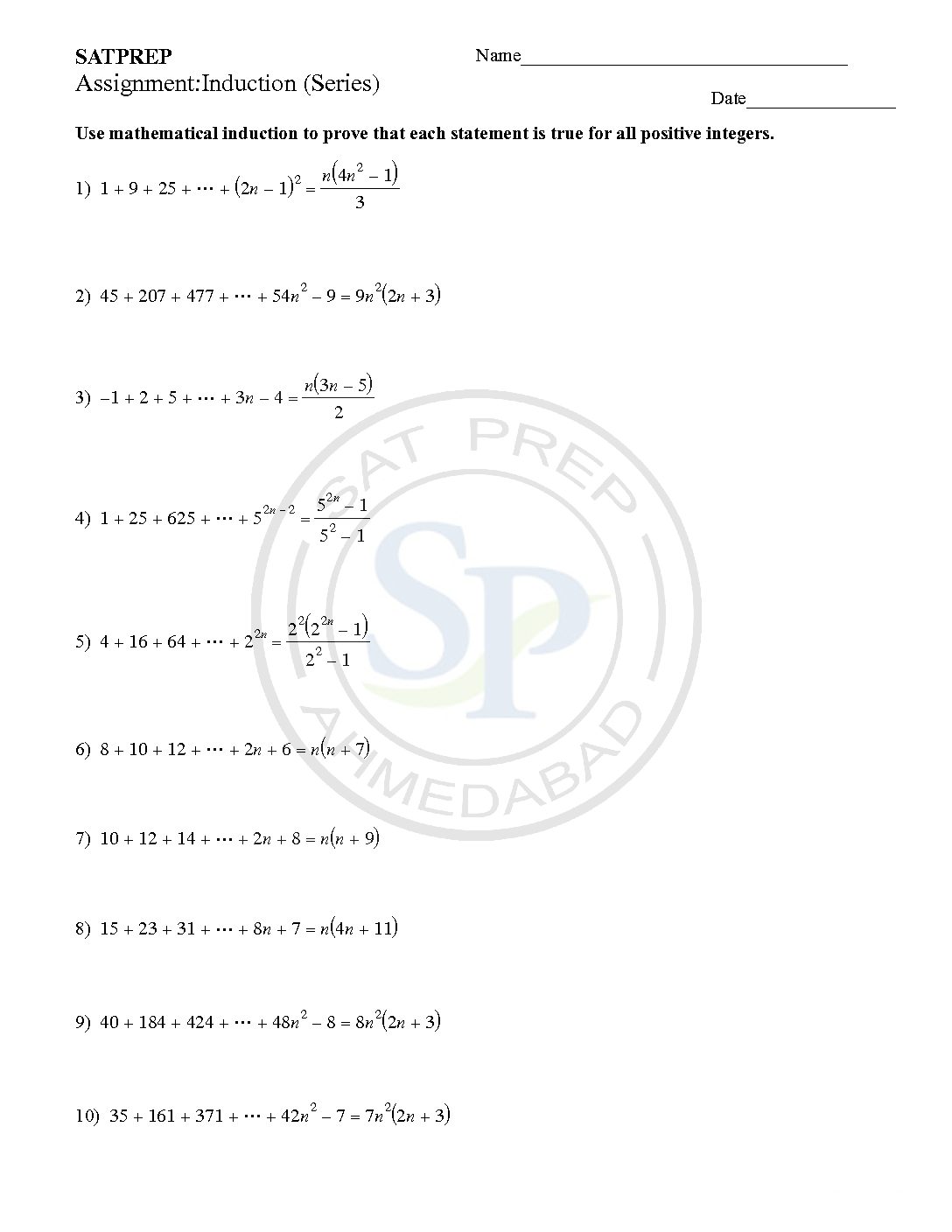
Mathematical Induction (Series)
Mathematical Inductions are a special way of proving things. It has only 2 steps: Step 1. Show it is true for the first one Step 2. Show that if any one is true then the next one is true. Mathematical Induction