Rolle’s Theorem. Then there is a number c such that a<c<b and f′(c)=0. Or, in other words f(x) has a critical point in (a,b). To see the proof of Rolle’s Theorem see the Proofs From Derivative Applications . Roll’s theorem
You are browsing archives for
Category: IB Maths HL
Derivative of polynomials
Derivative is product of differentiation. Differentiation has applications to nearly all quantitative disciplines. For example, in physics, the derivative of the displacement of a moving body with respect to time is the velocity of the body, and the derivative of velocity with respect to time is acceleration. Therefore differentiation is process Derivative
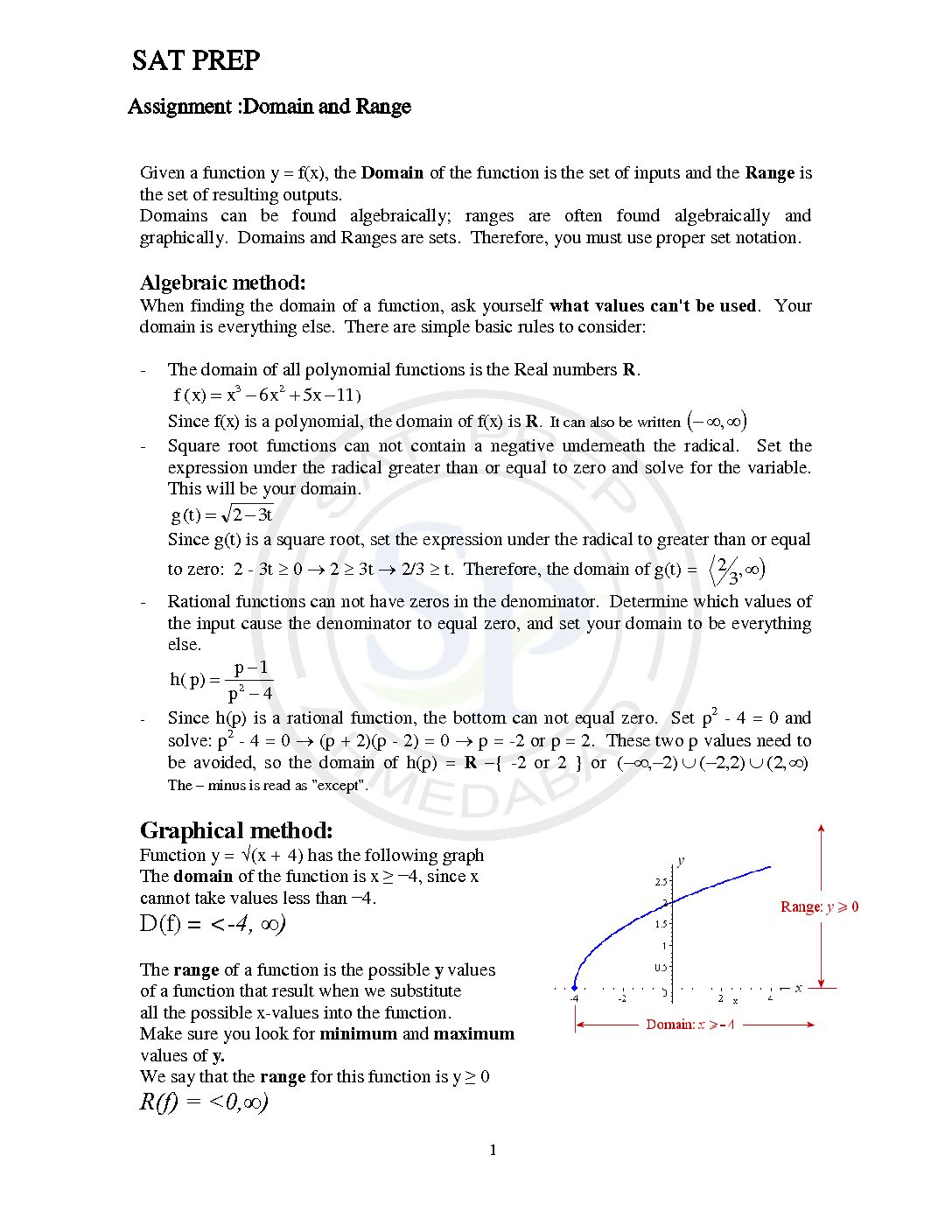
Domain and range
Domain represent values of x , while range represented by F(x) or y function. Mostly , functions are portrayed as a set of x/y coordinates. Therefore y-axis serving as a function of x. When we use function F(x) notation then one is independent variable and another dependent variable. Due to this on Y-axis F(x) represent. Domain and range
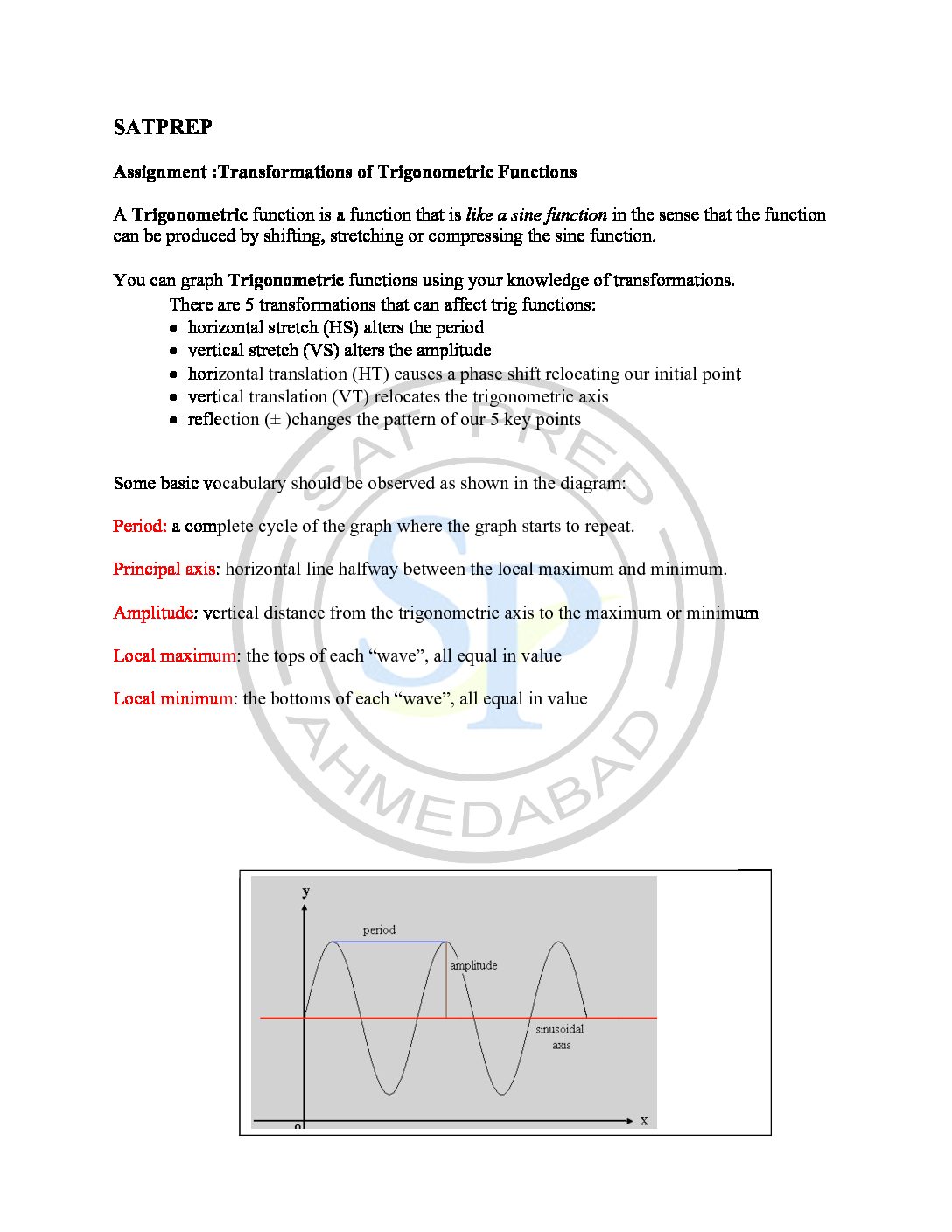
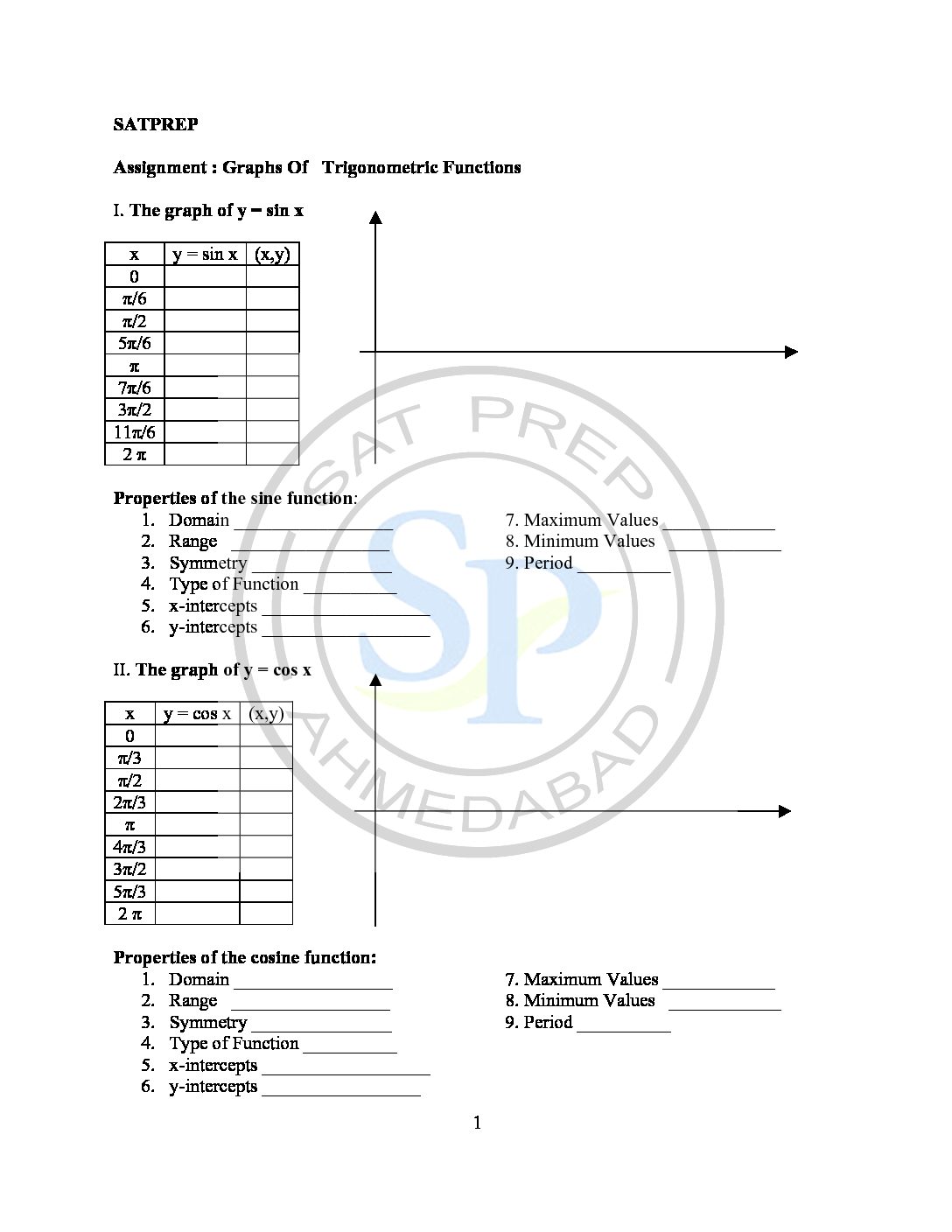
Graph of Trigo function
Trigo functions definition is – a function of an arc or angle most simply expressed in terms of the ratios of pairs of sides of a right-angled triangle —called also circular function. standard unit circle (a circle with radius 1 unit), starting at the origin and making some angle with the x -axis, the sine of the angle gives the […]
Graph of Trig Function
Graph of trigonometric functions definition is – a function of an arc or angle most simply expressed in terms of the ratios of pairs of sides of a right-angled triangle —called also circular function. standard unit circle (a circle with radius 1 unit), starting at the origin and making some angle with the x -axis, the sine of the […]
Trigonometric function
Graph of trigonometric functions definition is – a function of an arc or angle most simply expressed in terms of the ratios of pairs of sides of a right-angled triangle —called also circular function. standard unit circle (a circle with radius 1 unit), starting at the origin and making some angle with the x -axis, the sine of the […]
Optimization-2
Process of optimisation means optimal value of function at turning point (maximum or minimum ) value of the curve. Therefore second derivative use to find greatest or least value . Also it show greatest value. Optimization
Related Rates -2
First of all related rate problems are applications of derivative . One of the hardest calculus problems that students have trouble . Because each application question has a different approach in solving the problem. Hence called rate of change. Related rates
Kinematics
Describes the motion of points, objects and systems of groups of objects, without reference to the causes of motion. The symbol a stands for the acceleration of the object. And the symbol v stands for the instantaneous velocity of the object. The derivative of displacement with time is velocity ( v = ds/dt ). The […]
Optimisation
Process of calculating optimal value of function at turning point (maximum or minimum )value of the curve. Hence we use second derivative. It also give greatest or least value of curve. Optimisation