Solving Log Equations There are two basic forms for solving logarithmic equations: Not every equation will start out in these forms, but you’ll be able to use the tricks from the last section to get them there. Hence log also solve by quadratics and linear. Log
You are browsing archives for
Category: mc
Binomial and Sequence
General term of sequence is calculate by pattern of sequence as common ratio or common difference. Hence we can identify sequence Arithmetic or geometric by common ratio or common difference. Series when terms are in addition. Therefore common ratio of series is less than 1 then geometric series is called convergent series . Binomial expansion […]
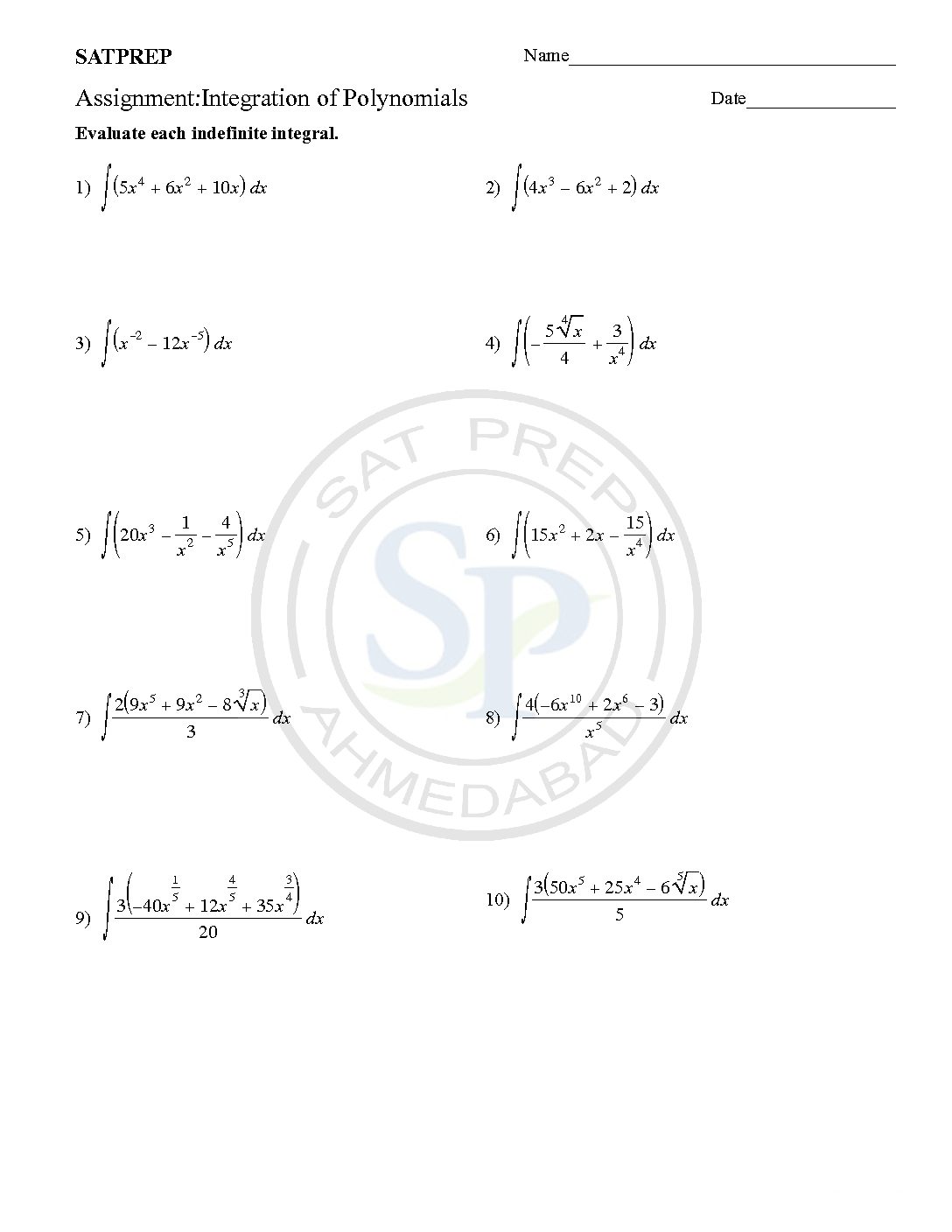
Integration of polynomial
Integration is way of adding functions to find the sum. Due to this concept can find areas and volumes. This also used to find equation of curve from derivative. Hence integration also called anti derivative. It is another method of Integration Numerical integration. It computing an integral with a numerical method. Integration
Integration by Partial Fraction
Integration by Partial Fractions. Integration by Partial Fractions. We know that a rational function is a ratio of two polynomials P(x)/Q(x), where Q(x) ≠ 0. Now, if the degree of P(x) is lesser than the degree of Q(x), then it is a proper fraction, else it is an improper fraction. Because the partial fractions are each simpler. This can help solve the more complicated […]
Integration (Basic)
Integration is summation of function. Integration is a way of adding functions to find the sum of functions, also we find equation of curve. As well as Applications are area under the curve and volume. It can be used to find areas, volumes, central points and many useful things. it help you practice by showing you […]
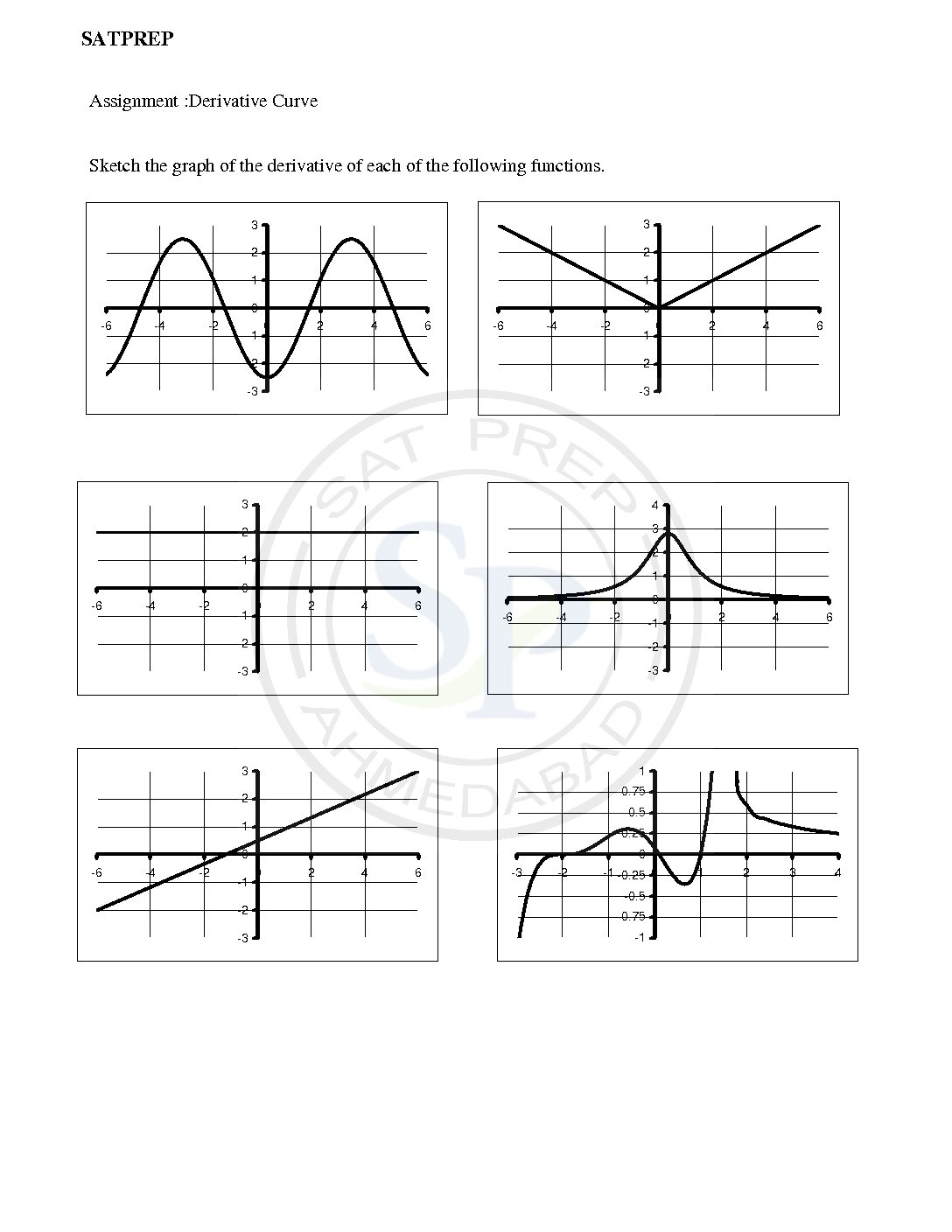
Derivative curve
This post about sketching of derivative curve from function curve. Given the graph of a function y = f(x) a standard approach is to identity intervals over which the graph is increasing, another intervals over which it is decreasing, and points at which the tangent line is horizontal. Derivative curve
Optimisation – 3
Process of finding optimal value of function at maximum or minimum value of the curve. It also give greatest or least point. Optimisation
Optmization-3
Process of optimisation means optimal value of function at turning point (maximum or minimum ) value of the curve. Therefore second derivative use to find greatest or least value . Also it show greatest value. Optimization
Derivative
First derivative for stationary point of the curve. If the derivative changes from positive (increasing function) to negative (decreasing function), the function has a local (relative) maximum at the critical point. Second Derivative 1. If , then has a local minimum at . 2. If , then has a local maximum at . The extremum test gives slightly more […]
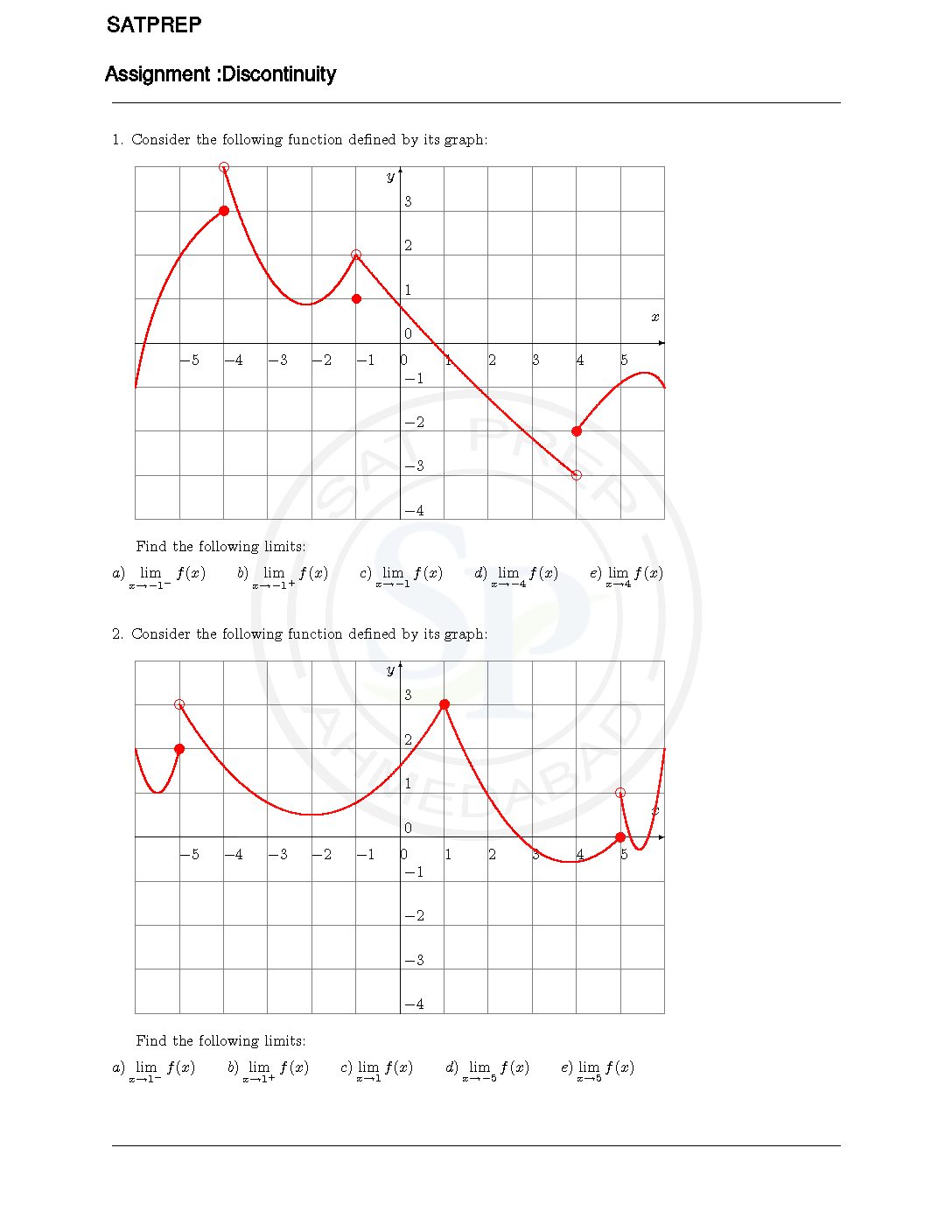
Discontinuity and Limit
An infinite discontinuity exists when one of the one-sided limits of the function is infinite. If the two one-sided limits have the same value, then the two-sided limit will also exist. Discontinunity and limit