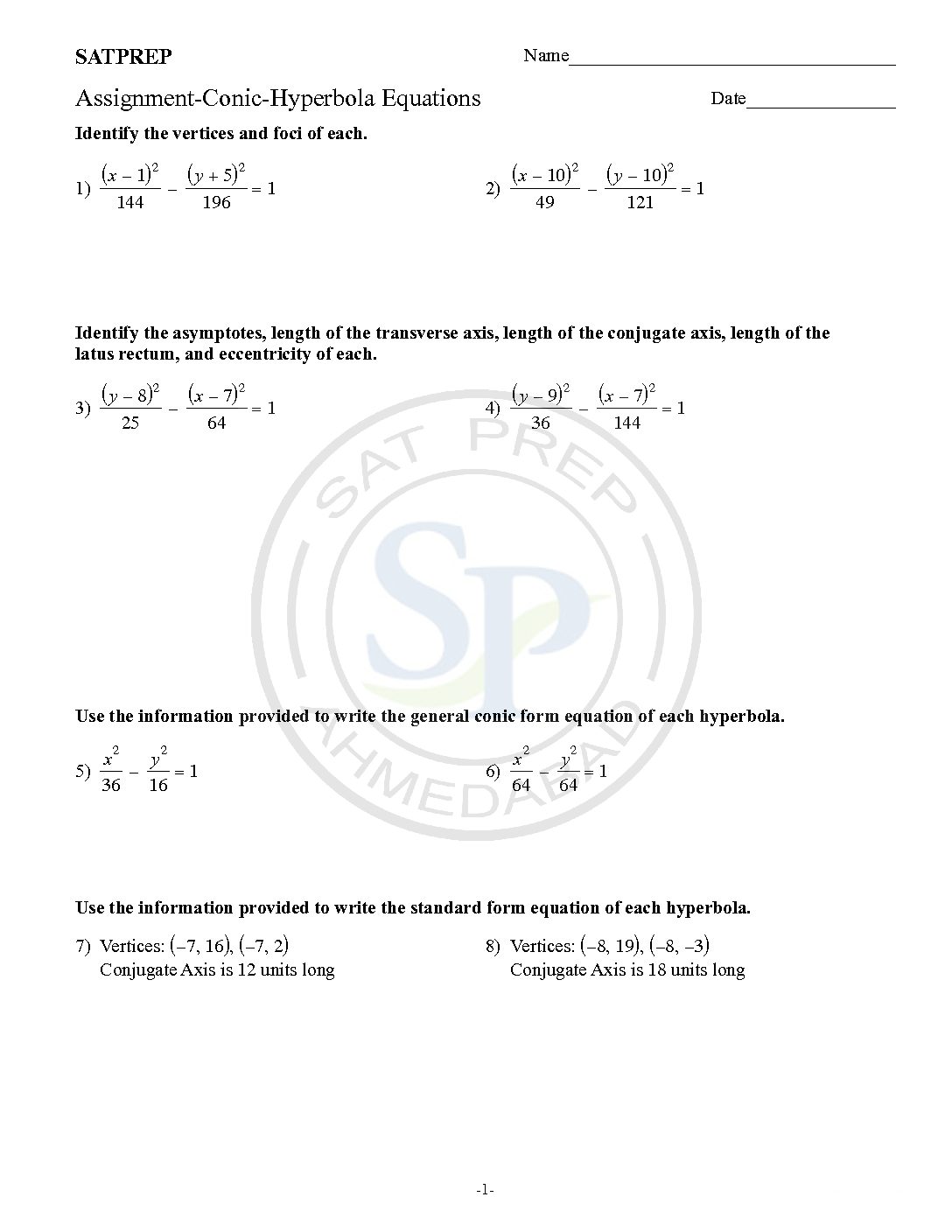
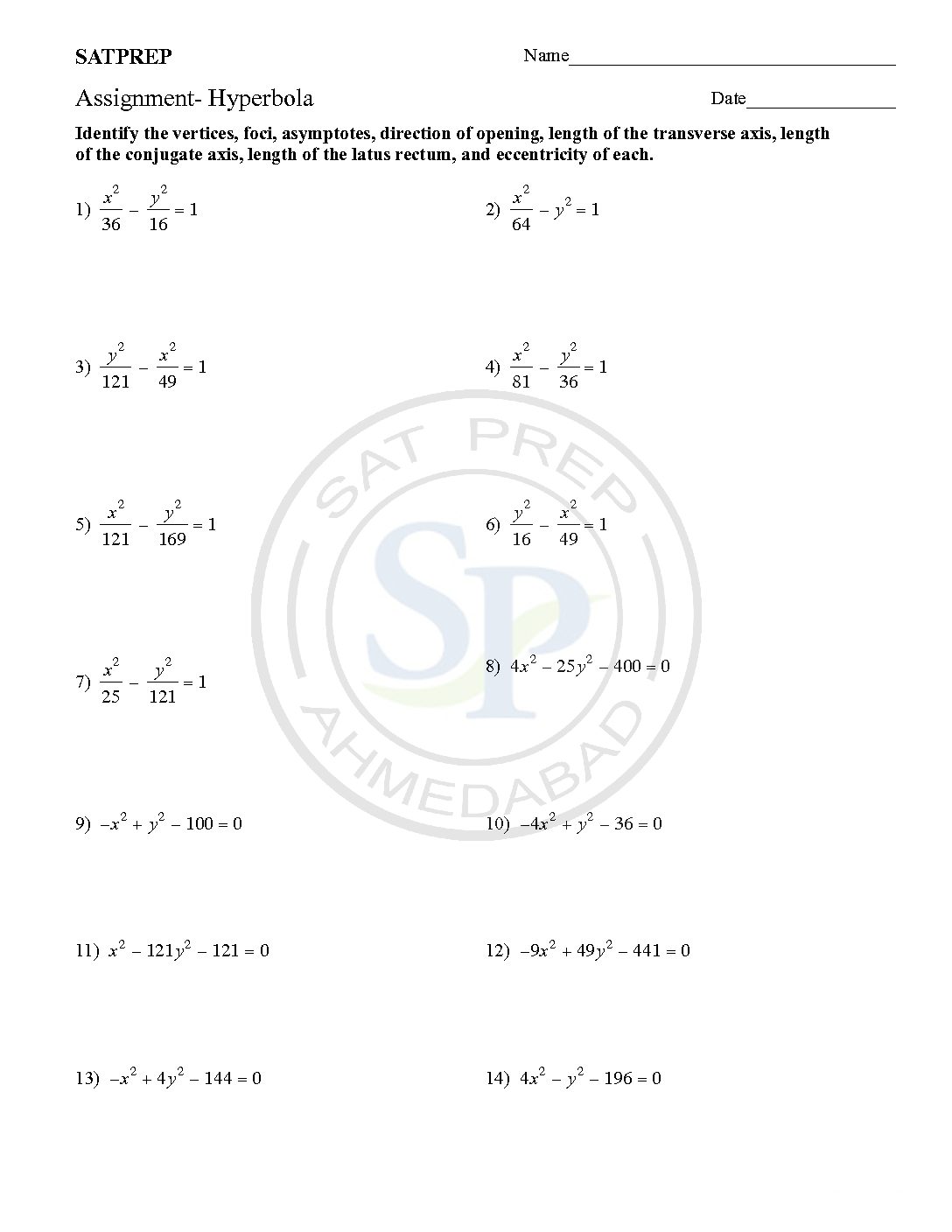
This post is about hyperbola section. Hyperbola basically, a graph of reciprocal function. It is part of conic section. Normally , it is the part of syllabus of SAT subject test. A hyperbola is an open curve with two branches, the intersection of a plane with both halves of a double cone. The plane does […]
You are browsing archives for
Category: Geometry
Ellipse
This post is about ellipse section. Ellipse basically, a function of circle with different size axes. It is part of conic section. Normally , it is the part of syllabus of SAT subject test. A ellipse section is a close curve along with major and minor axis, the ellipse will be symmetrical in any case. ellipse
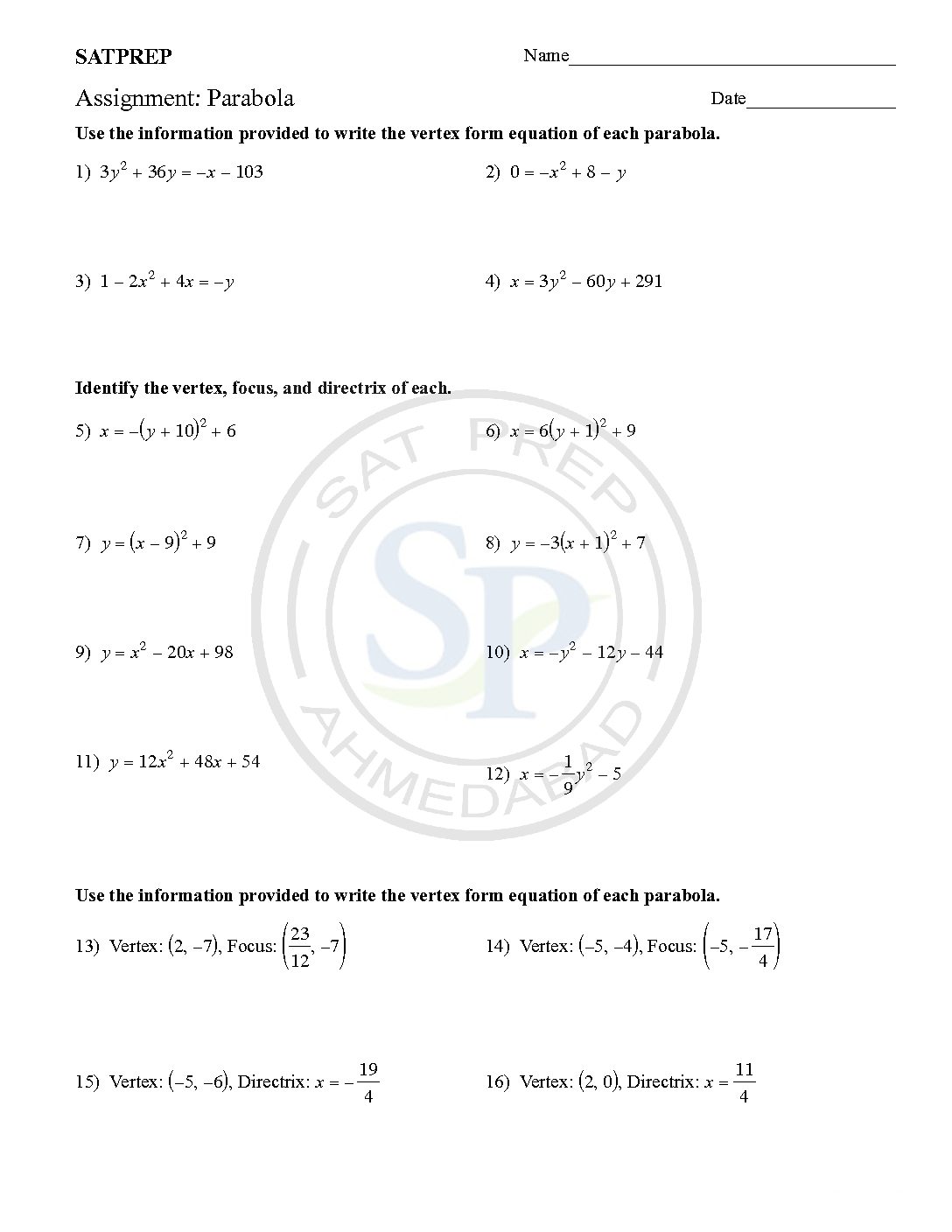
Parabola
This post is about parabola section. parabola basically, a graph of quadratic function. Also it is part of conic section. It is the part of syllabus of SAT subject test, SAT, Math of AS/A level and IBDP HL/SL. A parabola is an open curve on axes in both direction. The parabola will be symmetrical about […]
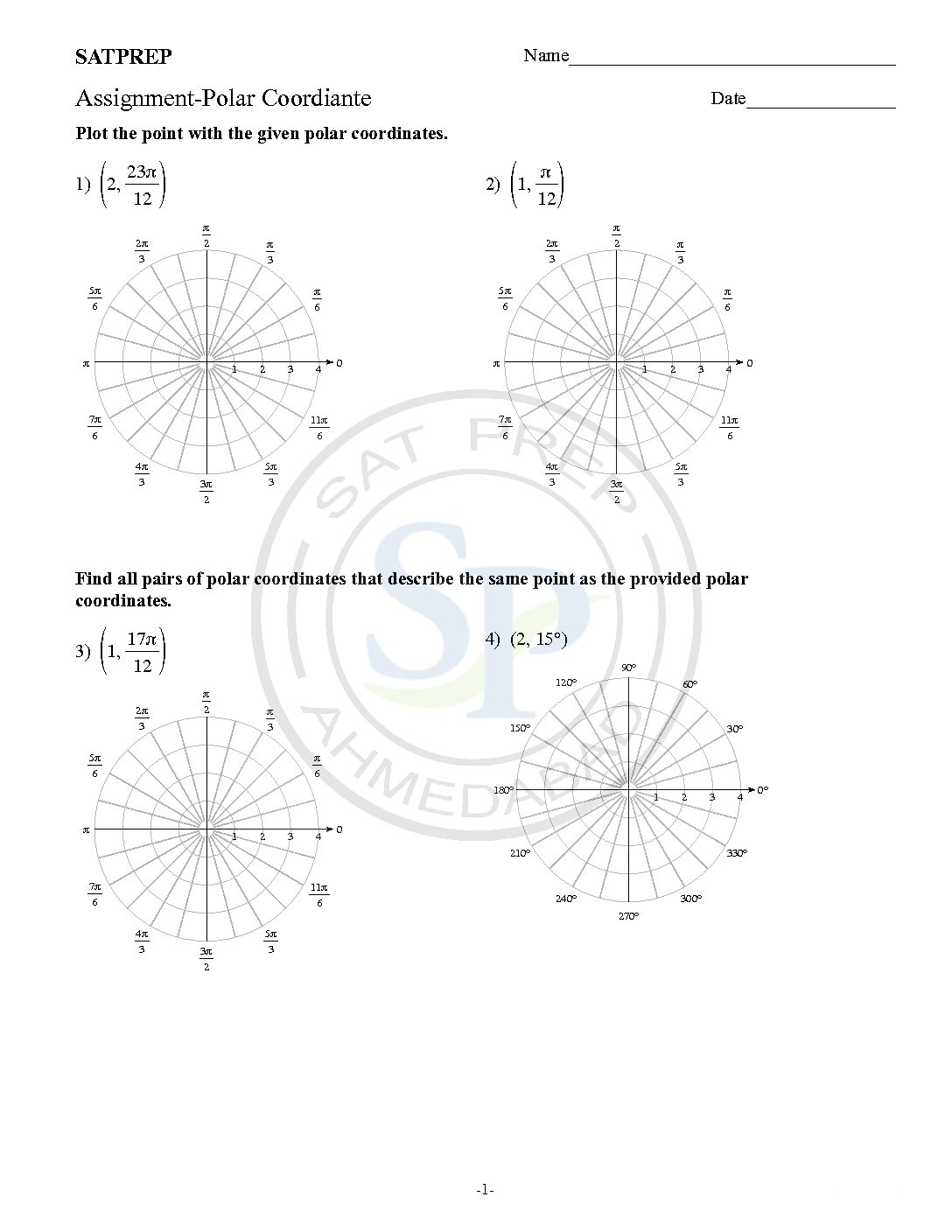
Polar Co-ordinate
This post is about conversion of polar coordinate to cartesian and also vice versa coordinate system. Furthermore polar coordinate represent in r and theta form. Polar coordinate
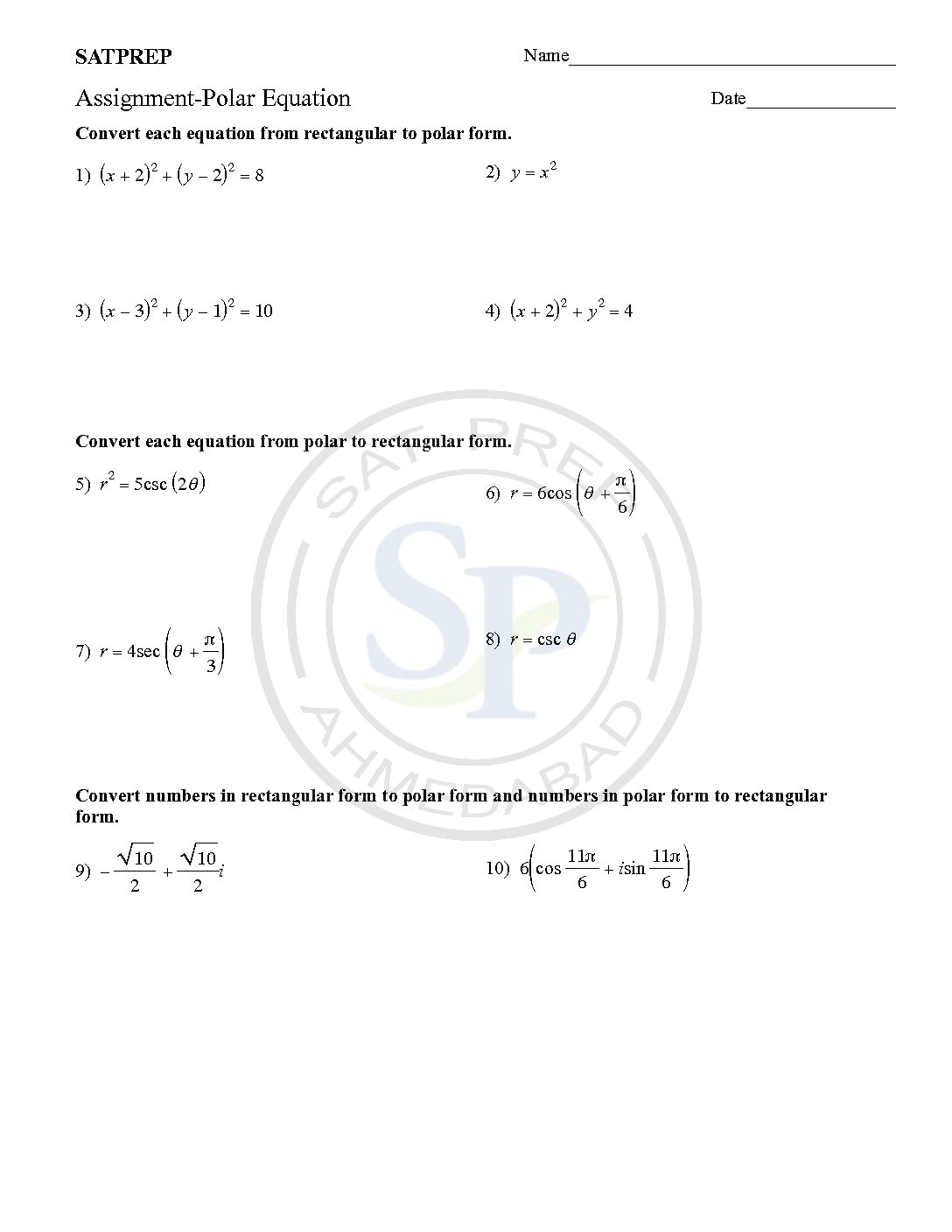
Polar Equation
Polar System
Polar systems is system which defined in term of magnitude and angle , coordinates are also defined in terms of magnitude and angle. Polar equation define in terms of magnitude and angle. Hence, graph of equation in polar system sketch by using magnitude and angle Polar system P P p
Conics
Conics section is a curve section of cone. Conic section is obtained as the intersection of the surface of a cone with a plane. Because of this is called cone. Conic graphs can be “slanty”, Therefore conics equation is seems like circle. Because a conics generated by the intersection of a plane and a circular cone […]
The Hyperbola
a graph of reciprocal function is Hyperbola. It is part of conic section. Normally , it is the part of syllabus of SAT subject test. A hyperbola is an open curve with two branches, the intersection of a plane with both halves of a double cone. The plane does not have to be parallel to […]
Ellipses
An Ellipses are a curve that is the locus of all points in the plane. The sum of whose distances and from two fixed points and (the foci) separated by a distance In mathematics, an ellipse is a curve in a plane surrounding two focal points such that the sum of the distances to the two focal points […]
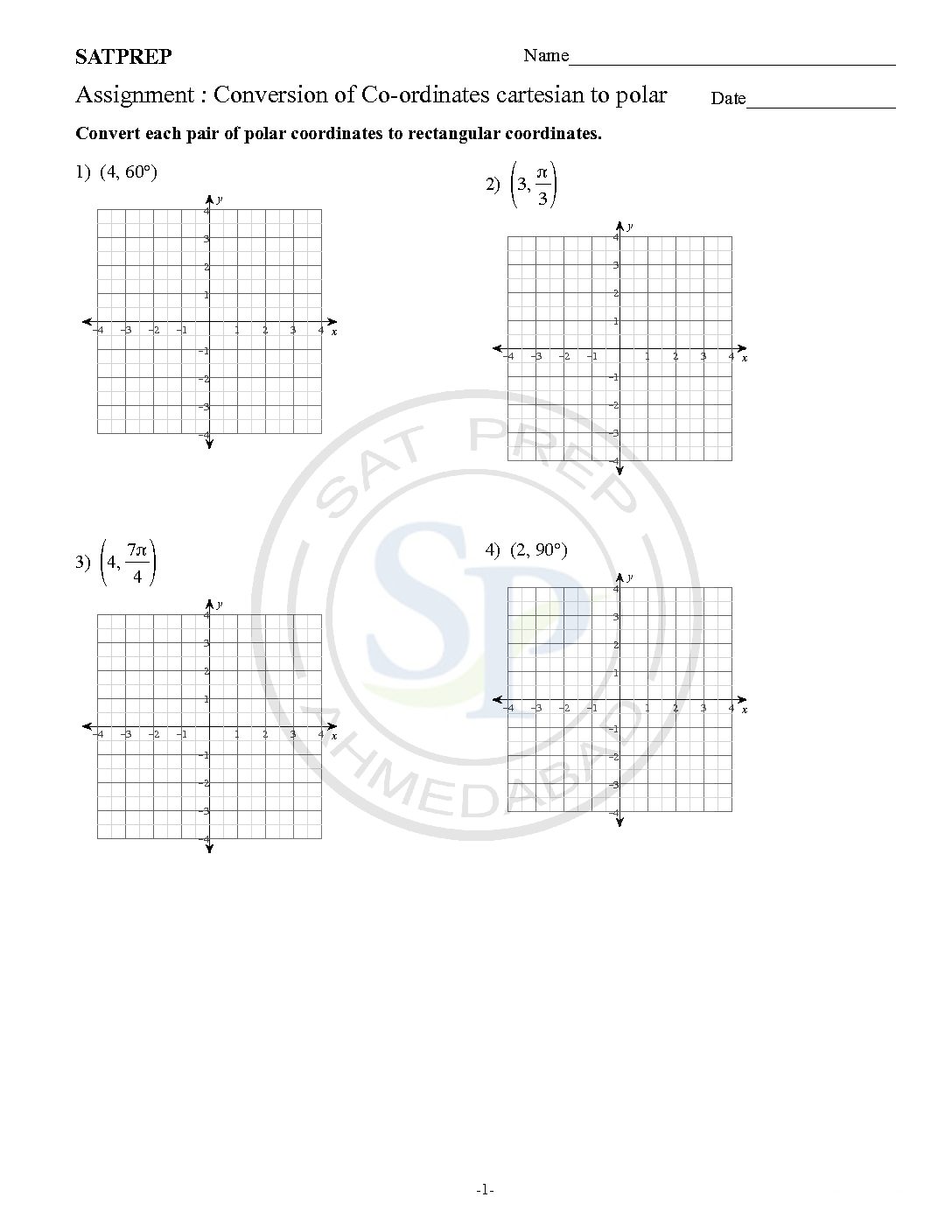
Conversion of Co-ordinates
Convert from Polar to Cartesian. When we know a point in Polar Coordinates (r, θ), and we want it in Cartesian Coordinates (x,y) . we solve a right triangle with a known long side and angle: Answer: the point (13, 22.6°) is almost exactly (12, 5) in Cartesian Coordinates. Polar to cartesian