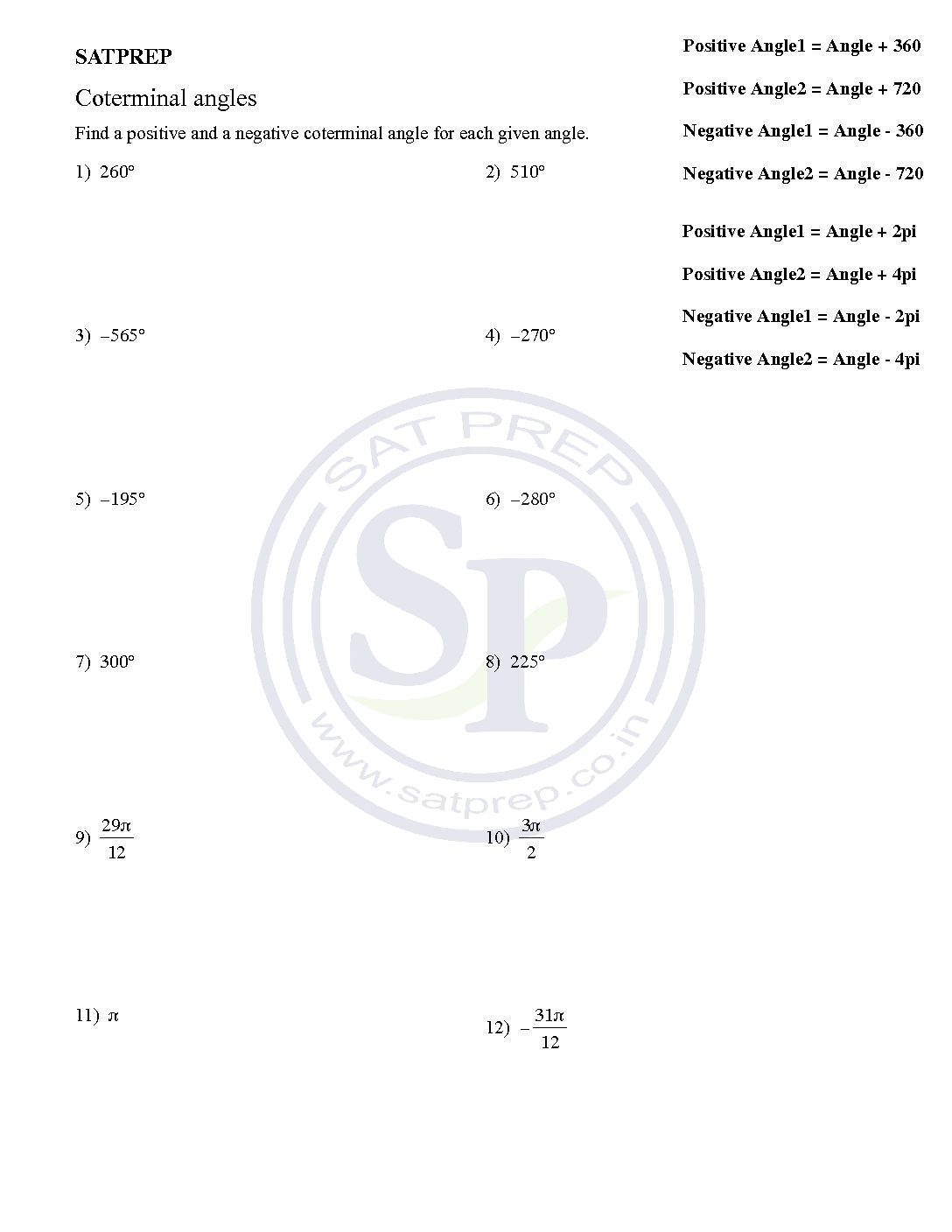
Coterminal angles are angles in standard position (angles with the initial side on the positive x -axis) that have a common terminal side. For example 30 ° , − 330 ° and 390 ° are all coterminal Coterminal angle
You are browsing archives for
Category: Trignometry
Procedure to prove identity and Solve tr...
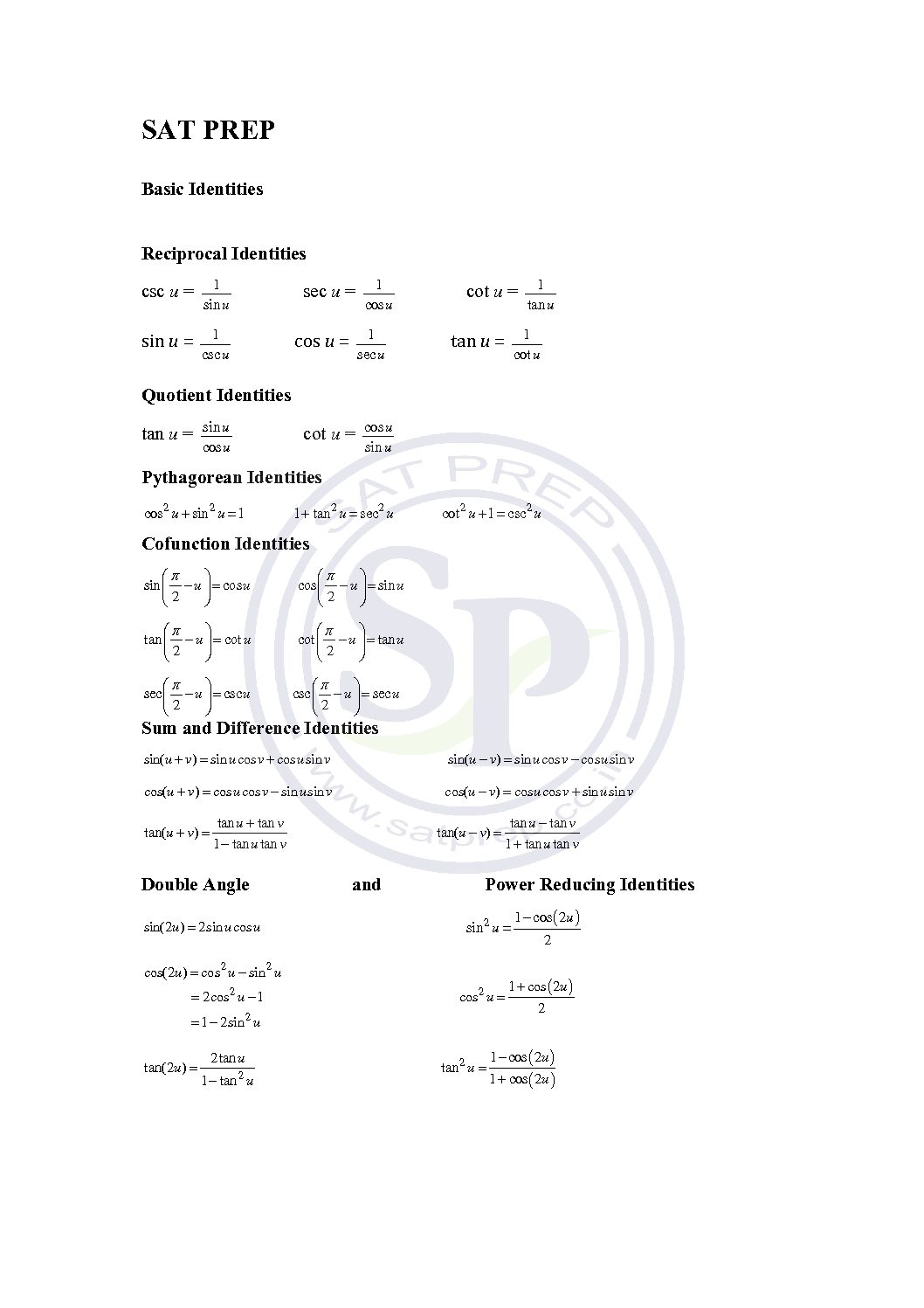
Solving trigo equations proceeds by studying arc x on the trig circle and by using trig conversion table (or calculator). Hence use of calculator and table is must. Also we need know trigonometric plan. Further sign convention in quadrants also need to know. Trigonometric identities are true for all replacement values for the variables. Procedure
Double angle identity
Use the double‐angle identity to find the exact value for cos 2 x given that sin x = . Because sin x is positive, angle x must be in the first or second quadrant. The sign of cos 2 x will depend on the size of angle x. Double angle Identity
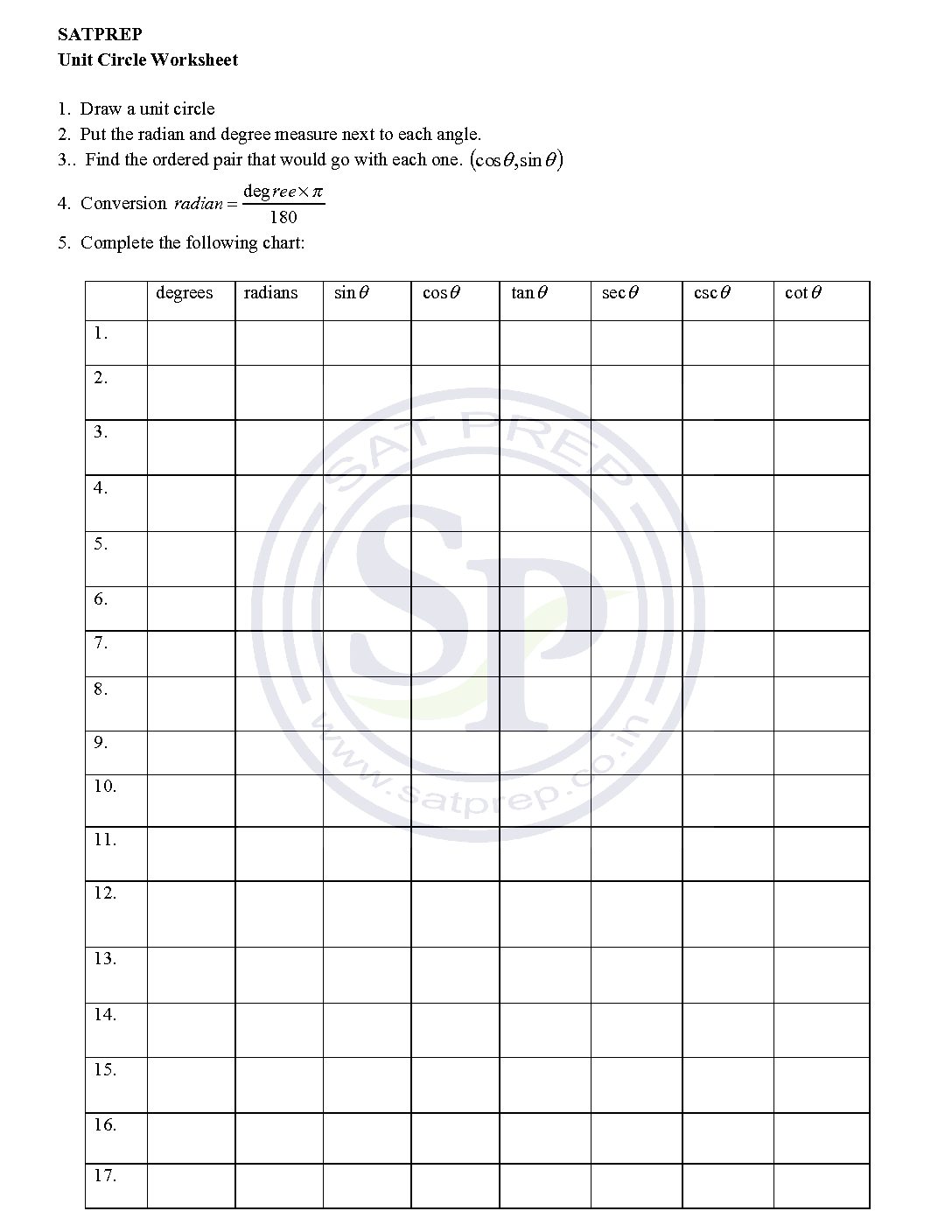
Unit Circle Worksheet
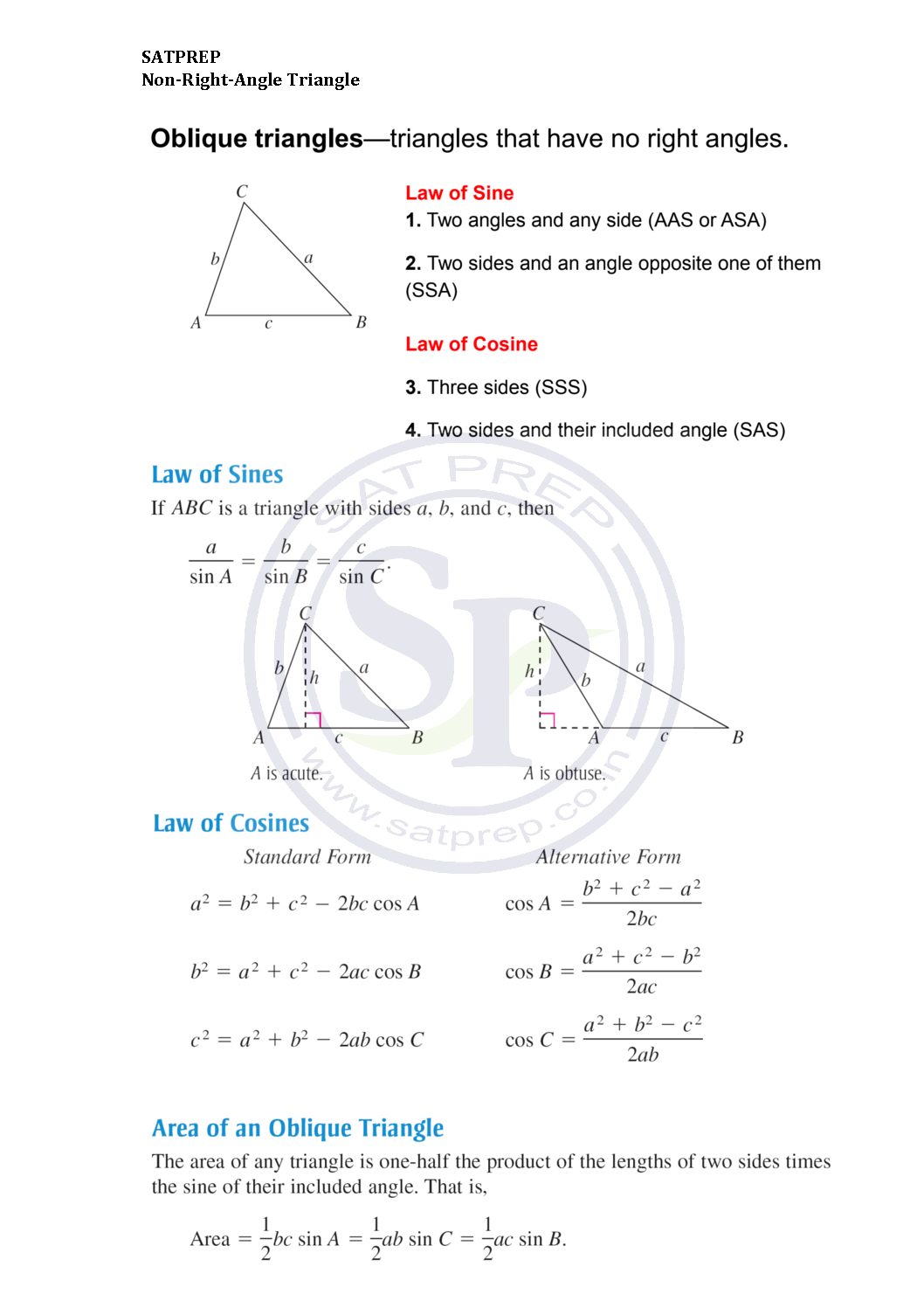
Formulae for Non-Right angle Triangle
Non-right angle triangle . triangle that is not a right triangle is an oblique triangle. Solving an oblique triangle means finding the measurements of all three angles and all three sides. Non right angle triangle
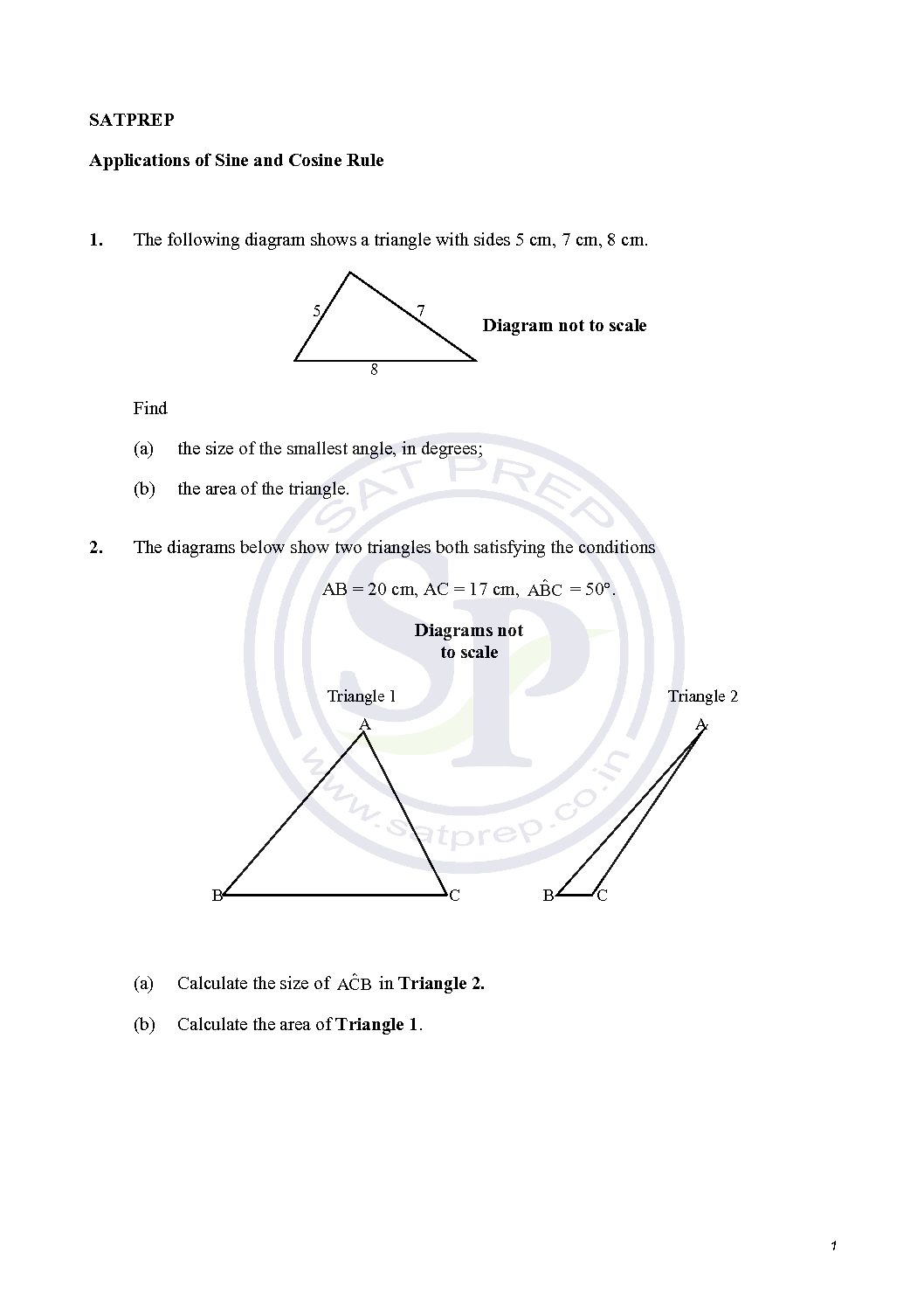
Applications of sine/ cosine rules.
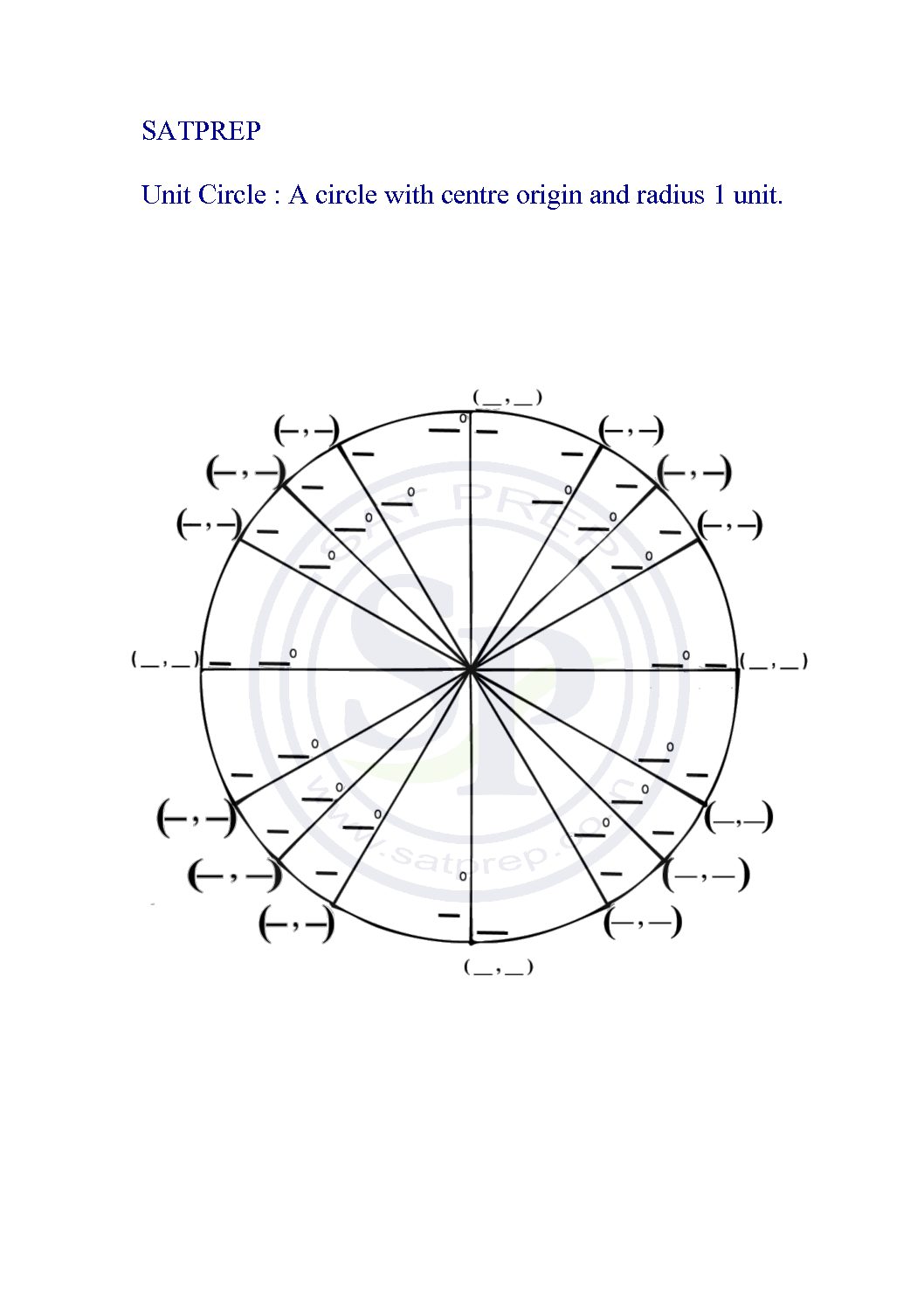
Unit circle Worksheet
Unit circle plays an vital role in trigonometry. The unit circle provide values of T -ratios for given angles. Unit circle worksheet
Applications of Sine and Cosine Rules
Sine and Cosine Rule. Non right angle triangle can be done with the Law of Sine and Law of Cosine. Hence we apply this concept for non right-angle triangle. Also we apply for angle when three sides given. Sine and Cosine Rules.
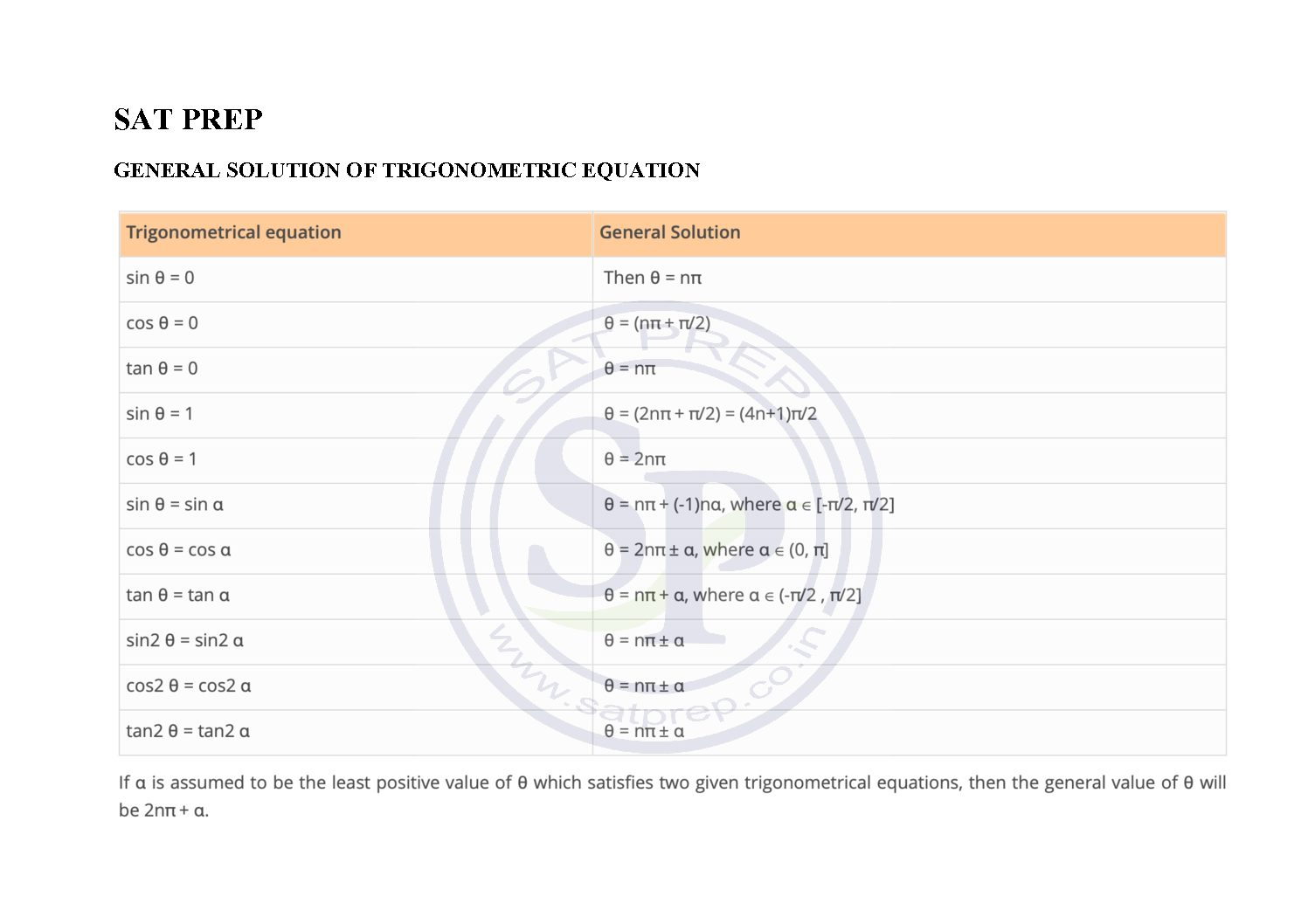
General solution of trigonometric Equati...
General Solutions of a Trig Equation. From the following diagram we see that sin( π -θ) = sin θ and cos ( -θ) = cos θ. General Solution of trigonometric eq
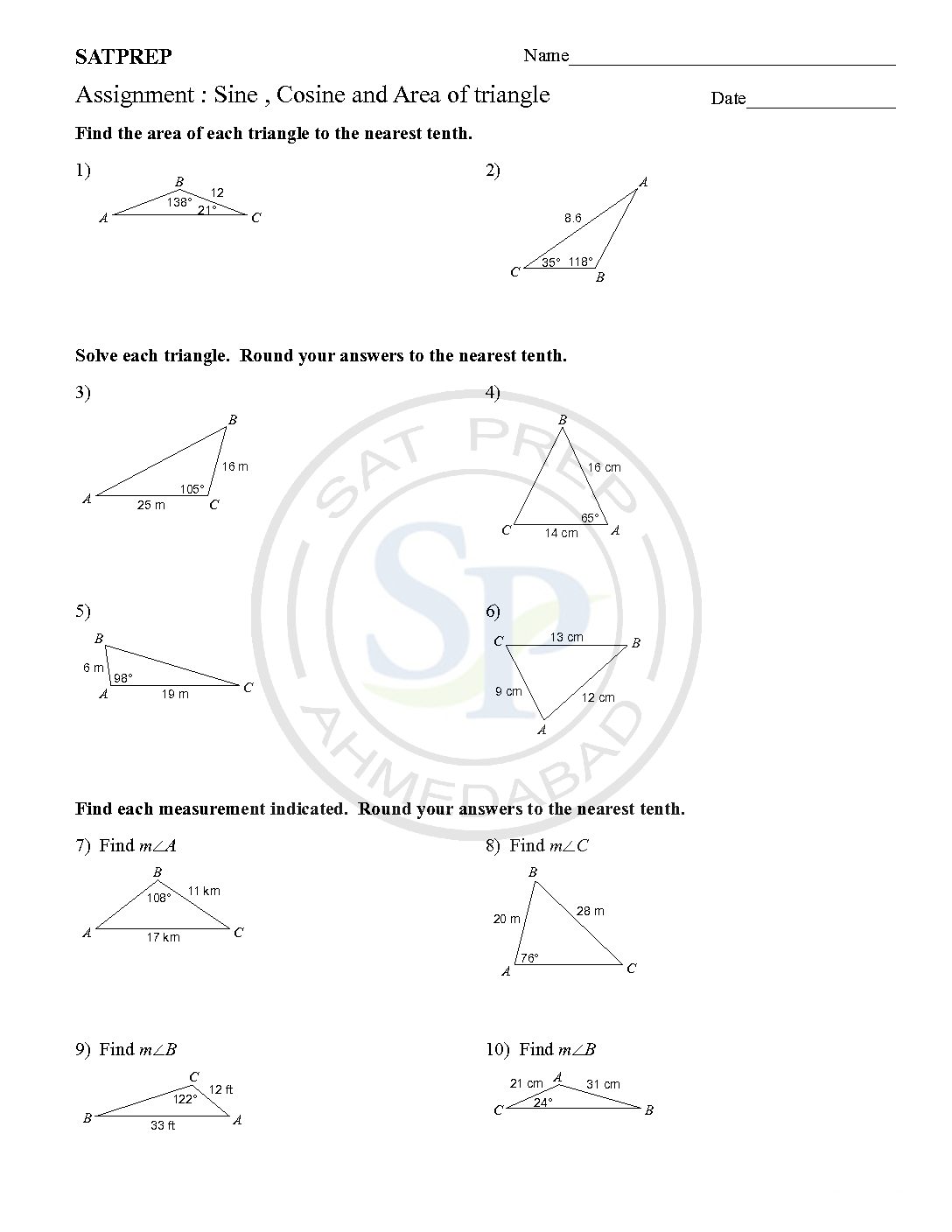
Sine Cosine and Area of triangle
Law of Cosines (also called the Cosine Rule) says: c2 = a2 + b2 − 2ab cos(C ). Law of Sines (or Sine Rule) is very useful for solving triangles: a sin A = b sin B = c … sine of angle B, and also equal to side c divided by the sine of […]