Rules for derivatives. Rules for derivatives. Sum rule: The derivative of the sum or difference of two functions is the sum or difference of their derivatives. (u + v)’ = u’ + v’ Constant multiple: The derivative of a constant times a function is the constant times the derivative of the function. (ku)’ = ku’ Rules for derivative
You are browsing archives for
Tag: AS-Level
Rules of derivative
Rule for derivatives. Rules for derivatives. Sum rule: The derivative of the sum or difference of two functions is the sum or difference of their derivatives. (u + v)’ = u’ + v’ Constant multiple: The derivative of a constant times a function is the constant times the derivative of the function. (ku)’ = ku’ Rules of derivative
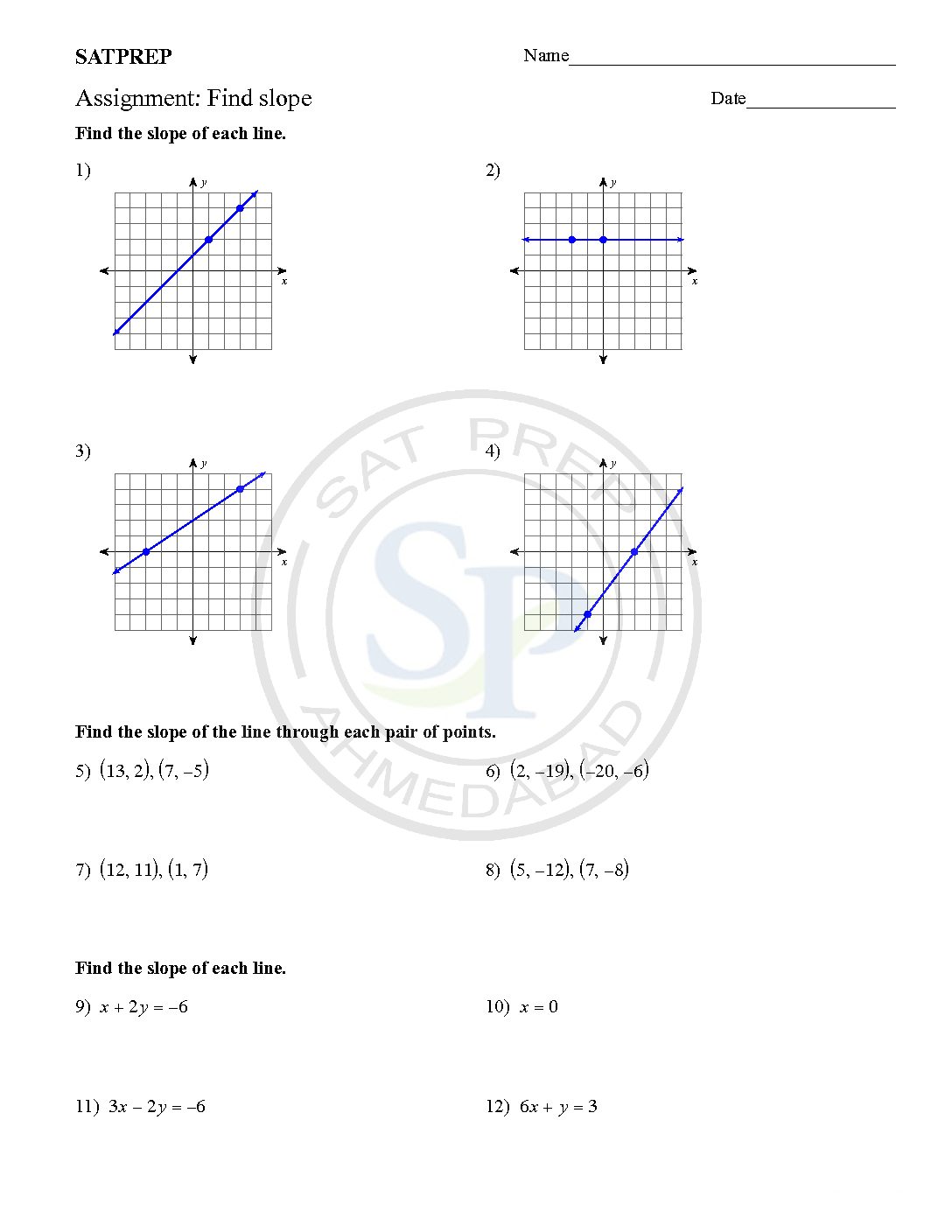
Find slope
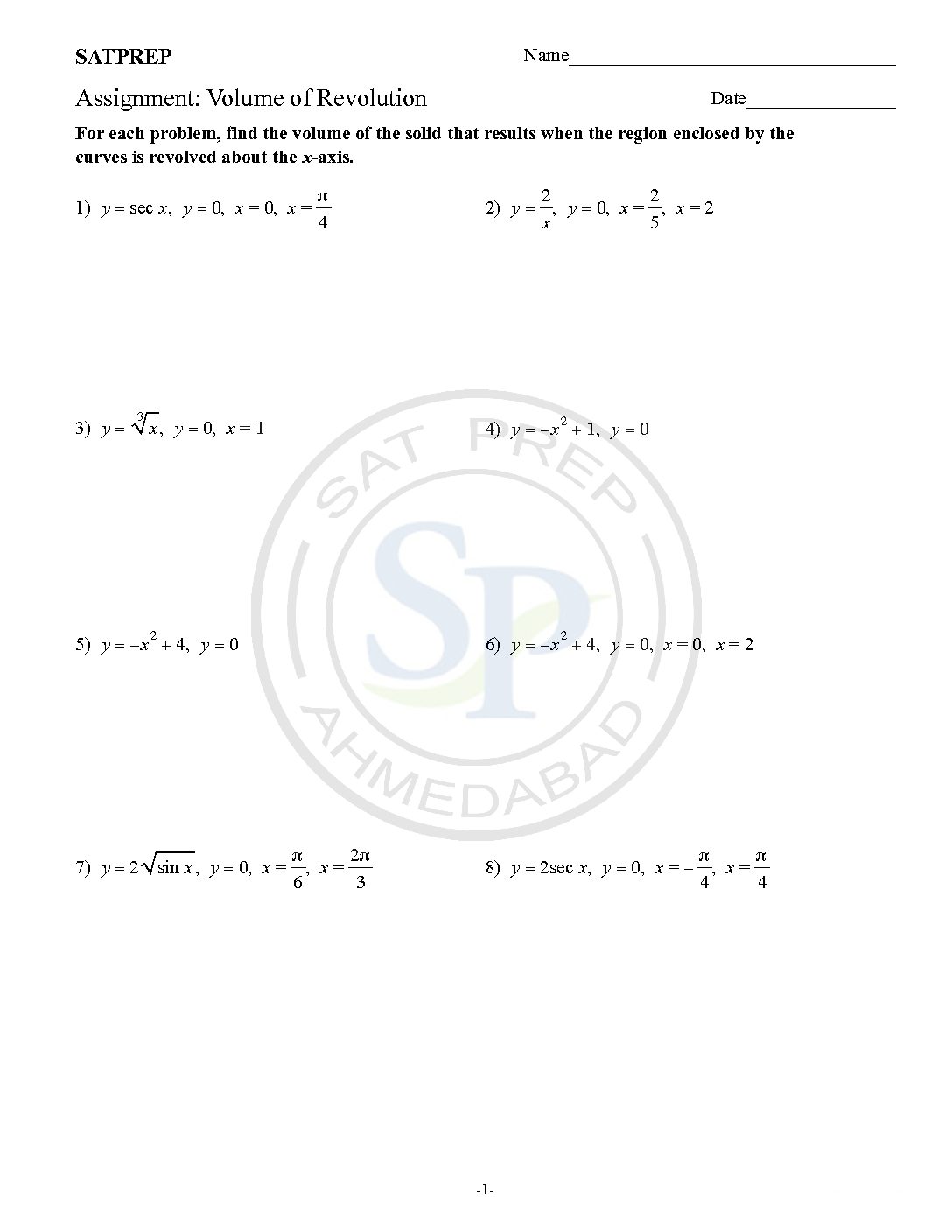
Volume of revolution of solid
Volume with Rings. To get a solid of revolution we start out with a function, y=f (x), on an interval [a,b]. We then rotate this curve about a given axis to get the surface of the solid of revolution. For purposes of this discussion let’s rotate the curve about the x -axis, although it could be any vertical or […]
Area Under the Curve
This post about Area under a Curve. The area between the graph of y = f ( x ) and the x -axis is given by the definite integral. This formula gives a positive result for a graph above the x -axis, and a negative result for a graph below the x -axis. Because of enclosed region by limit. Hence , we use definite integration. Similarly for volume […]
Binomial Distribution
The Binomial distributions Number of successes in a specified number of independent trials of an experiment . Symbol: B (n, p), where n is the number of trials and p the probability of success in each. As there are two parameter therefore it is Binomial distribution. Hence it used for discrete values. Binomial Theorem
Binomial Distribution
The Binomial distributions Number of successes in a specified number of independent trials of an experiment . Symbol: B (n, p), where n is the number of trials and p the probability of success in each. As there are two parameter therefore it is Binomial distribution. Hence it used for discrete values. binomial distribution
Normal Distribution
A standard Normal Distribution graph is “Bell Curve”.The standard normal distribution has two parameters: mean and standard deviation. Hence it use for continuous random variable as well as it use for continuous values. Due to continuous values we use area under the curve for calculating probability. Normal
Trigonometric equations
Trigonometric equations use both the reference angles and trigonometric identities The general method of solving an equation is to convert it into the form of one ratio only. Hence, we can obtain solutions. Trigonometric Equation
Trigonometric Equation
Solving trigonometric equations use both the reference angles and trigonometric identities The general method of solving an equation is to convert it into the form of one ratio only. Then, using these results, hence, we can obtain solutions. Trigonometric Equation