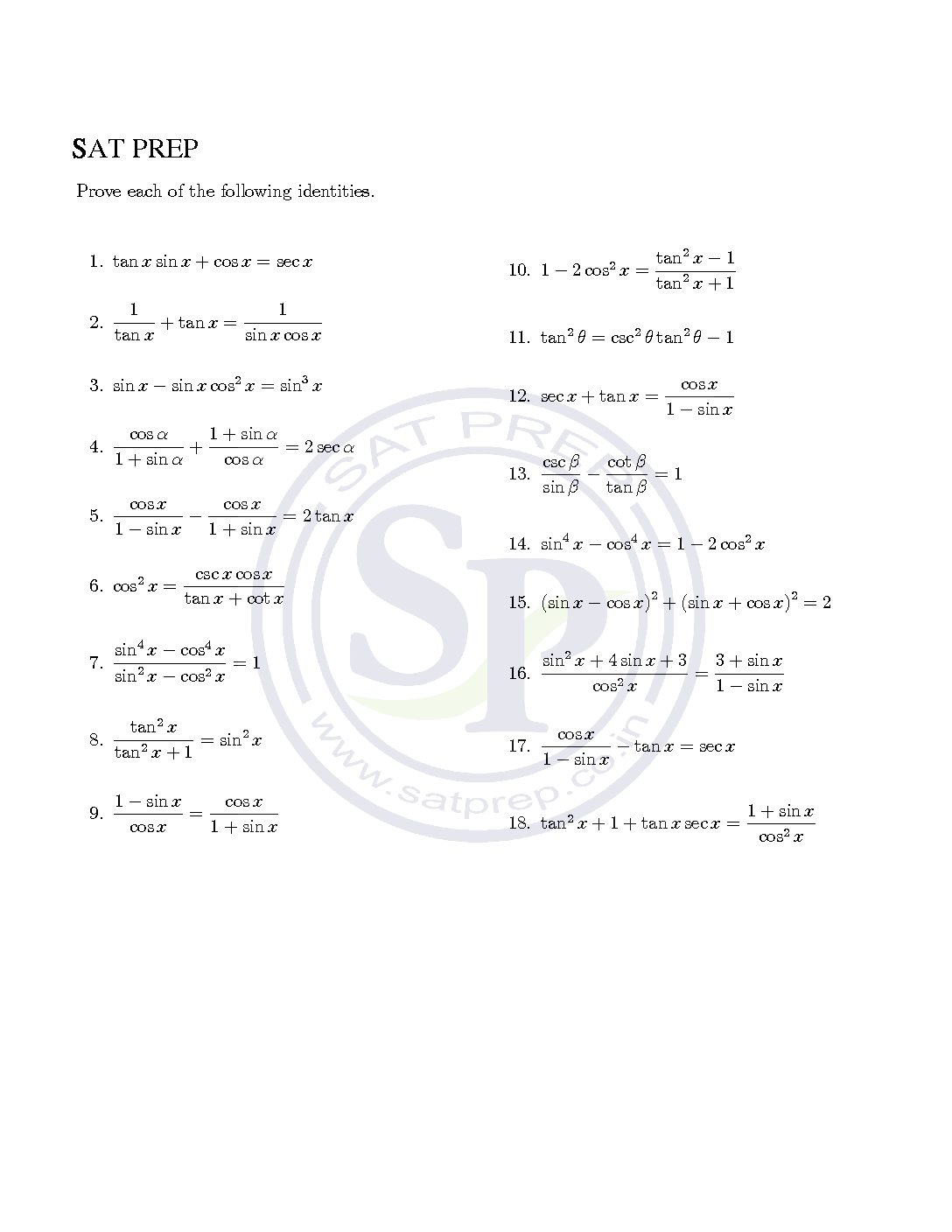
Worksheet of trigonometric identities . To prove that the left side is equal to the right side. Hence we have to use all six ratio their reciprocal. Also we have to use trigonometric relationship. As well as we use algebraic identity. Trigonometric identity
You are browsing archives for
Category: Graphs
Compound Angle Identity
Compound angle Identities. An Compound angles are angles which are the algebraic sum of two (or more) angles. also identity form by compound angle . Compound angle identity
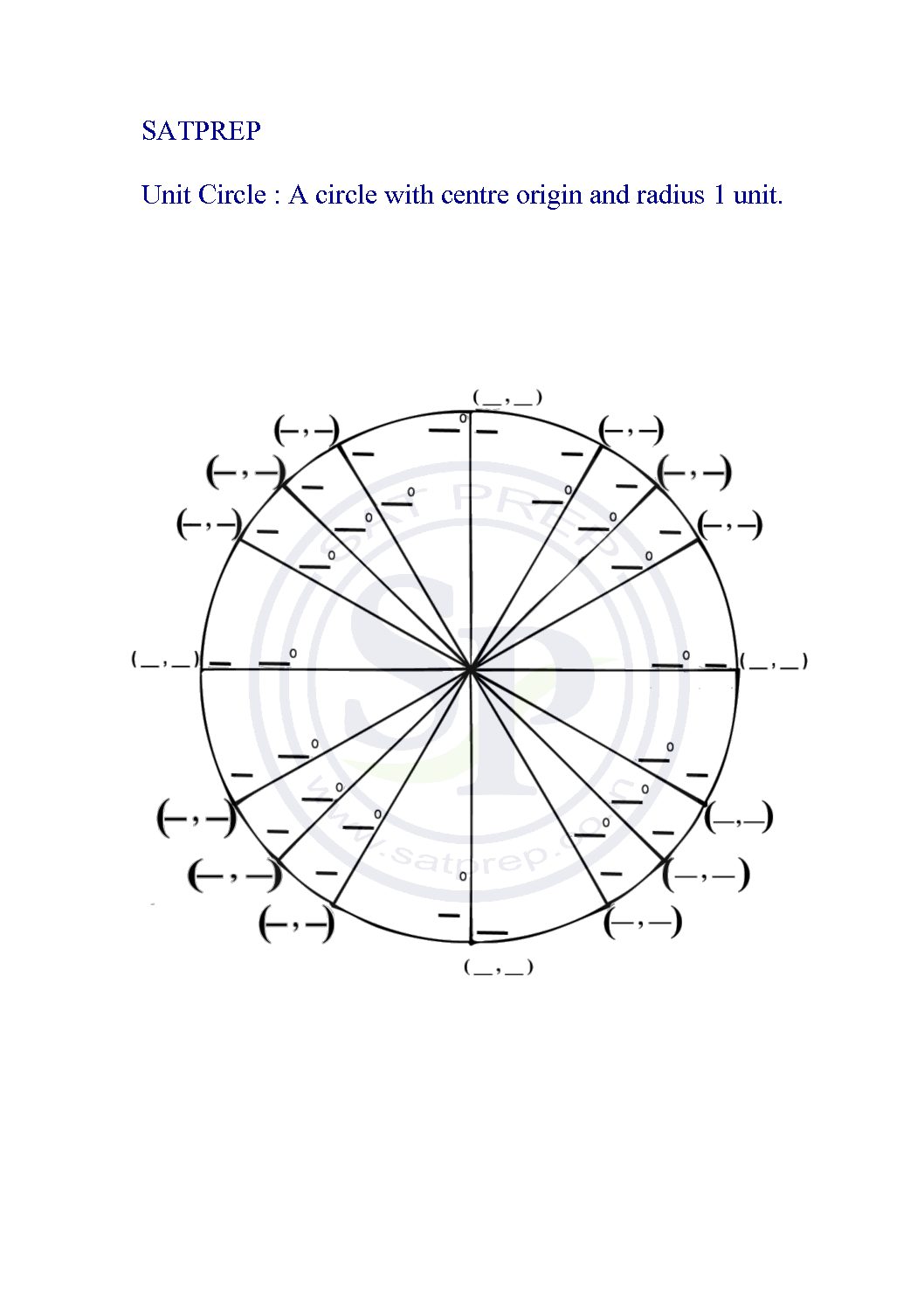
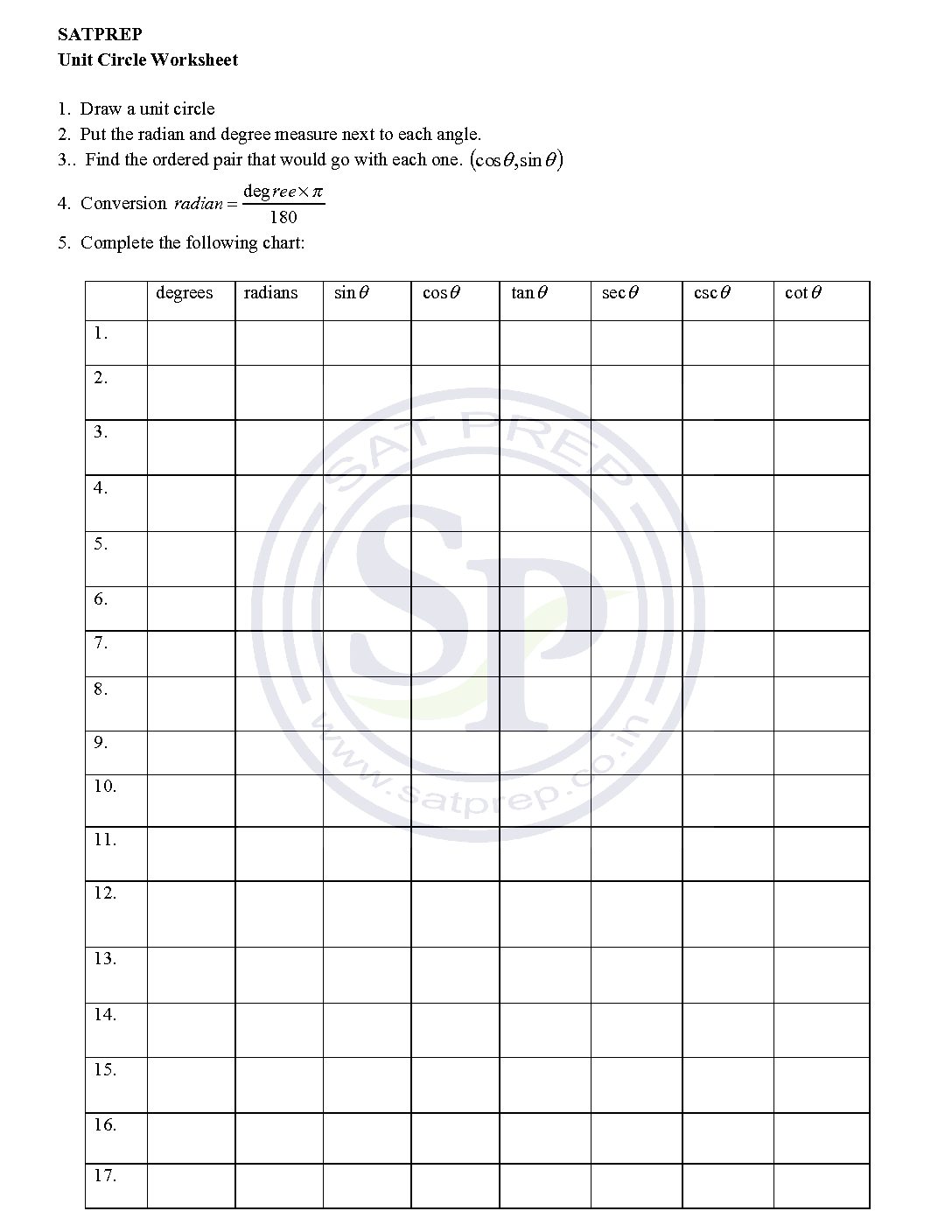
Unit Circle Worksheet
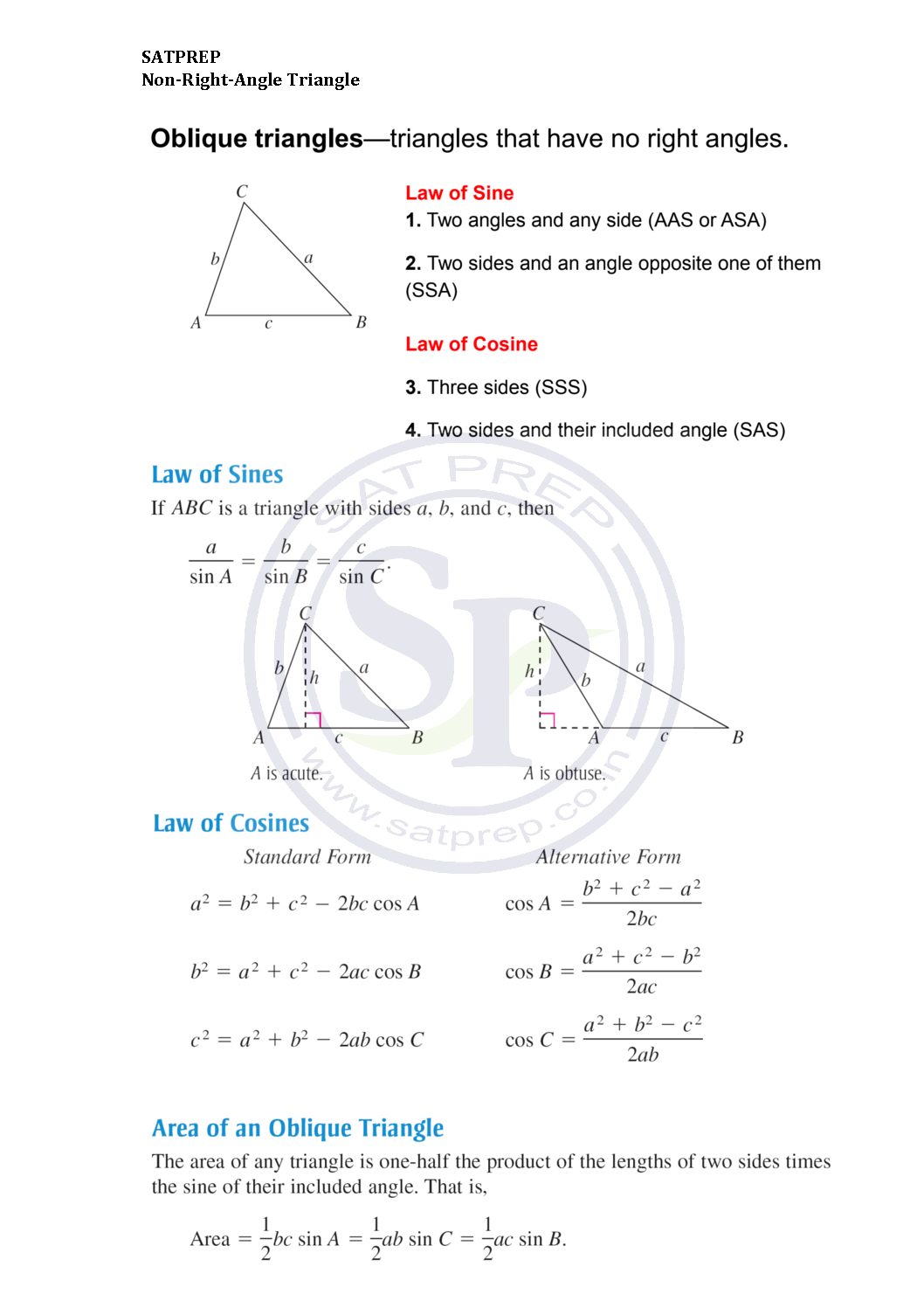
Formulae for Non-Right angle Triangle
Non-right angle triangle . triangle that is not a right triangle is an oblique triangle. Solving an oblique triangle means finding the measurements of all three angles and all three sides. Non right angle triangle
Unit circle Worksheet
Unit circle plays an vital role in trigonometry. The unit circle provide values of T -ratios for given angles. Unit circle worksheet
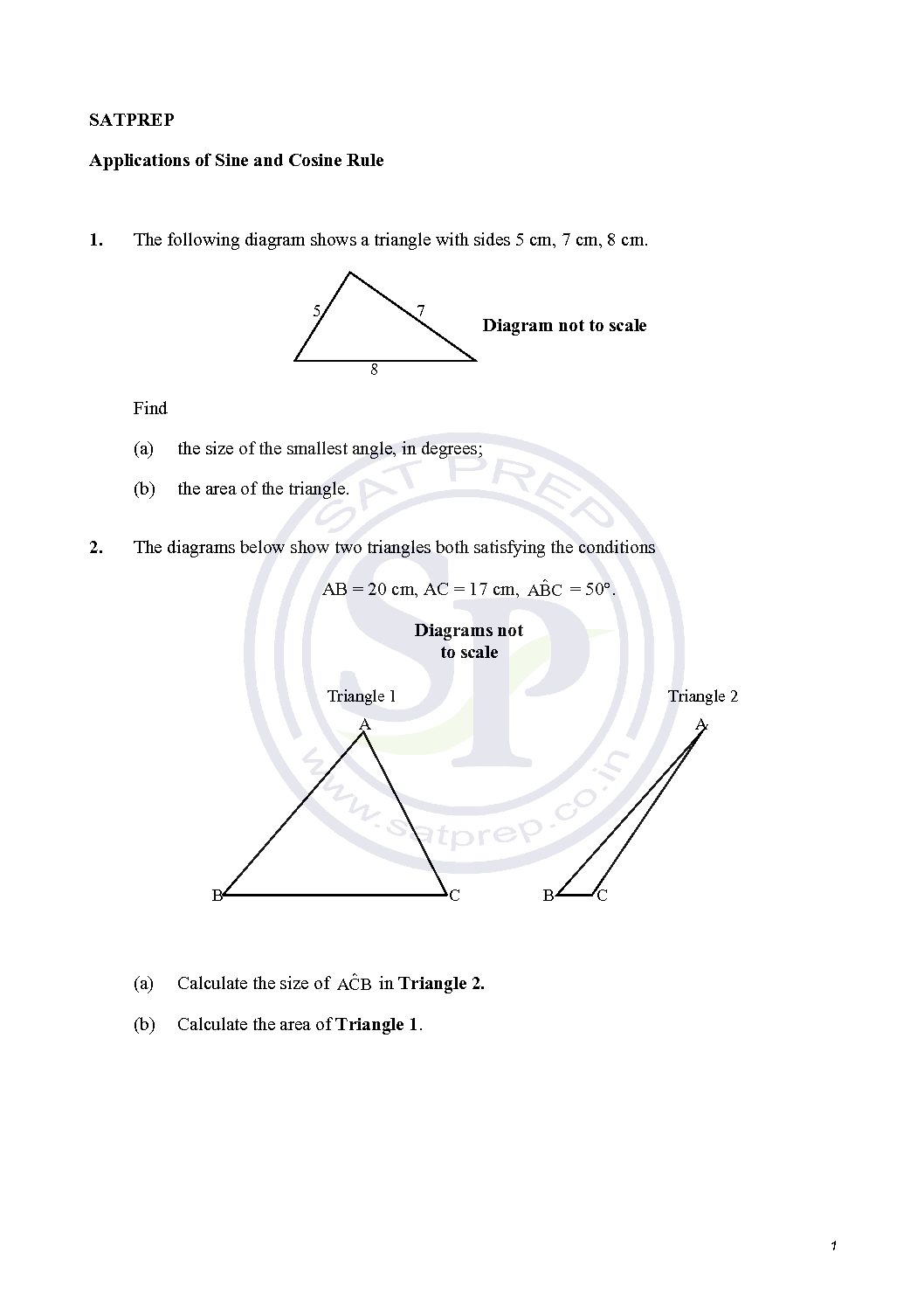
Applications of Sine and Cosine Rules
Sine and Cosine Rule. Non right angle triangle can be done with the Law of Sine and Law of Cosine. Hence we apply this concept for non right-angle triangle. Also we apply for angle when three sides given. Sine and Cosine Rules.
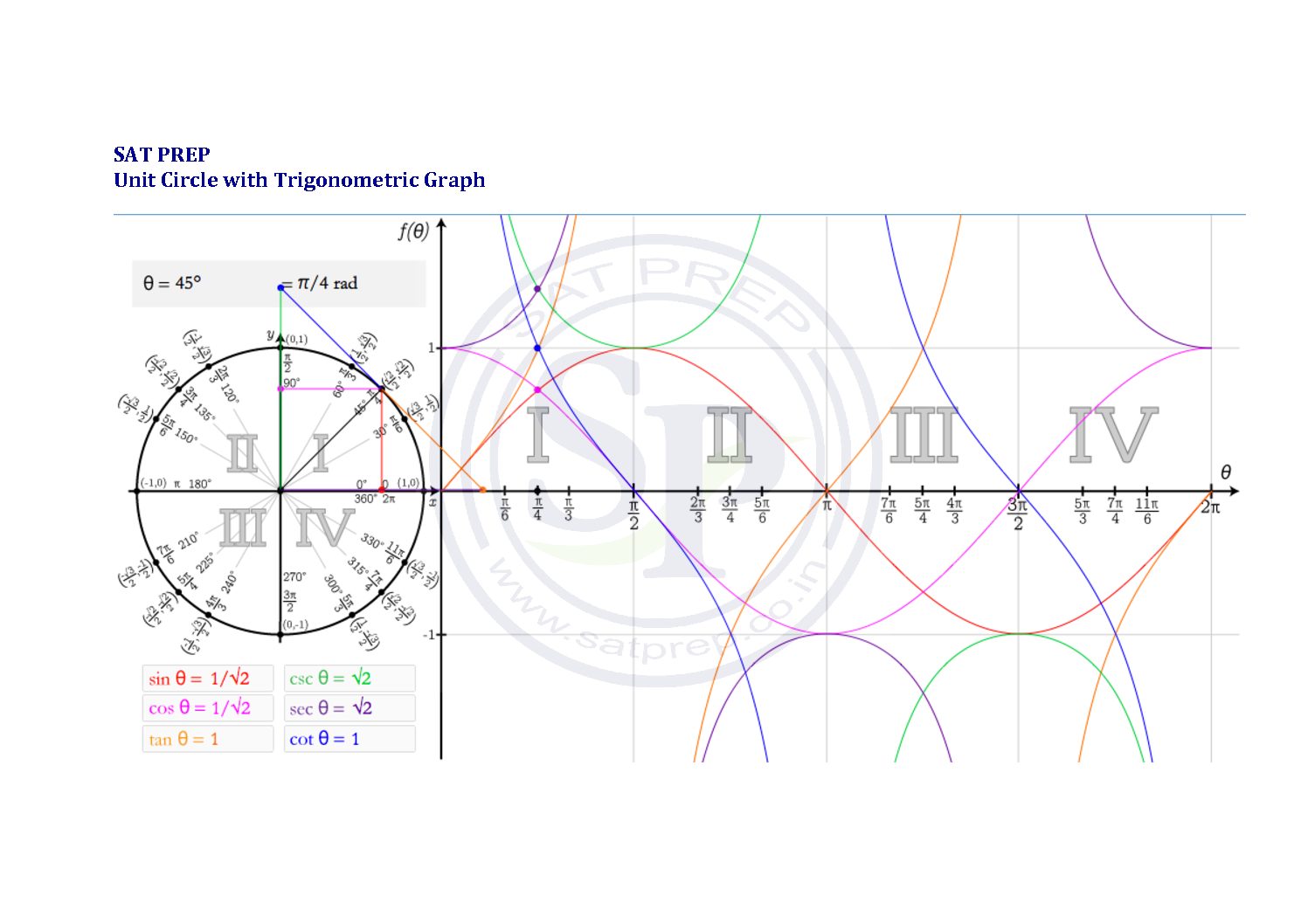
Unit circle and trigonometric graph
Unit circle is the source for the generation of the trigonometric function graphs. The quadrants from the unit circle, when placed horizontally in numerical order, create the basis for the trigonometric graphs. Hence This process of creating graphs from the unit circle is often called “unwrapping” the unit circle. Unit circle with Trigo Graph
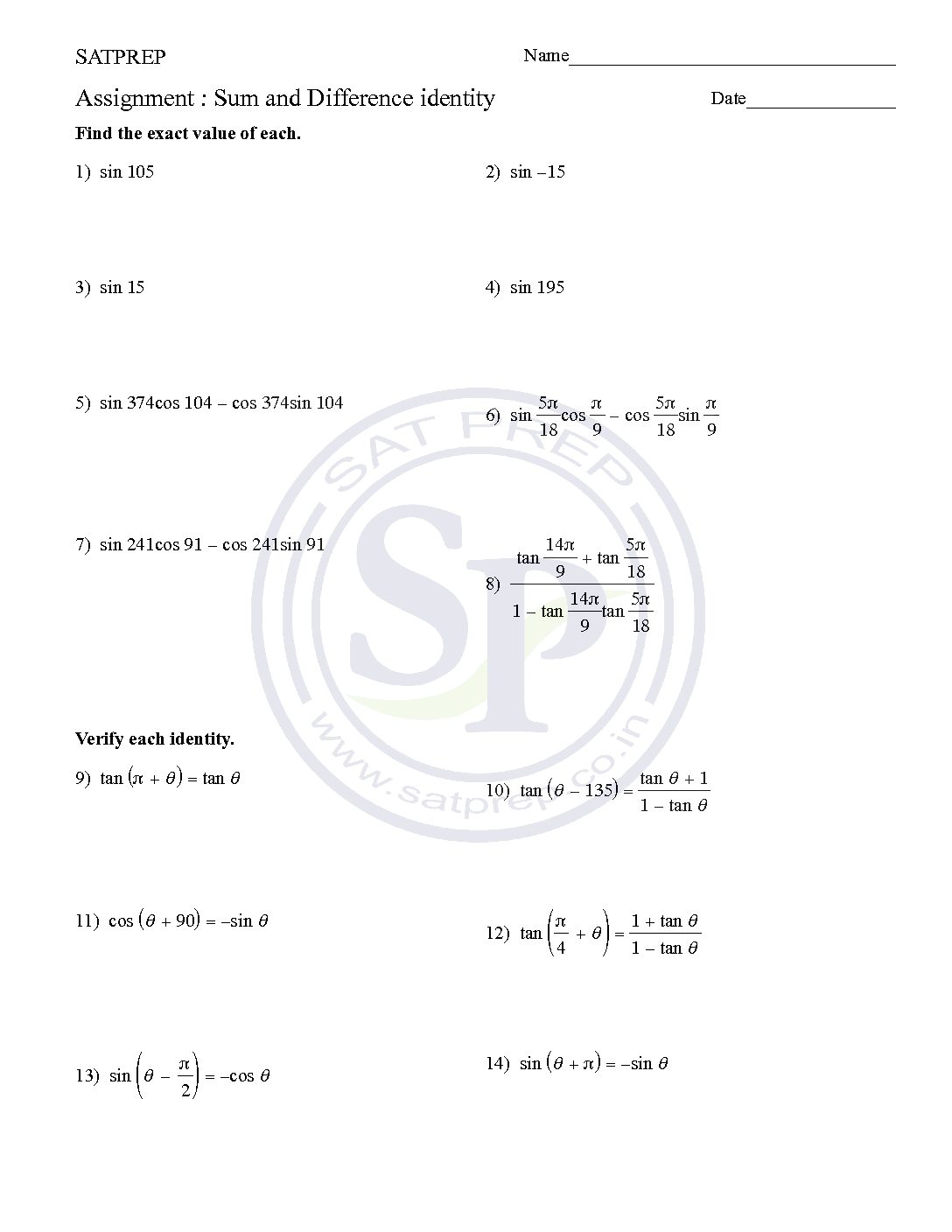
Sum and Difference identity
Sum or difference of angle is called compound angle. Similarly algebraic sum of two or more angles also called compound angle . Hence it solve . Sum and Difference identity
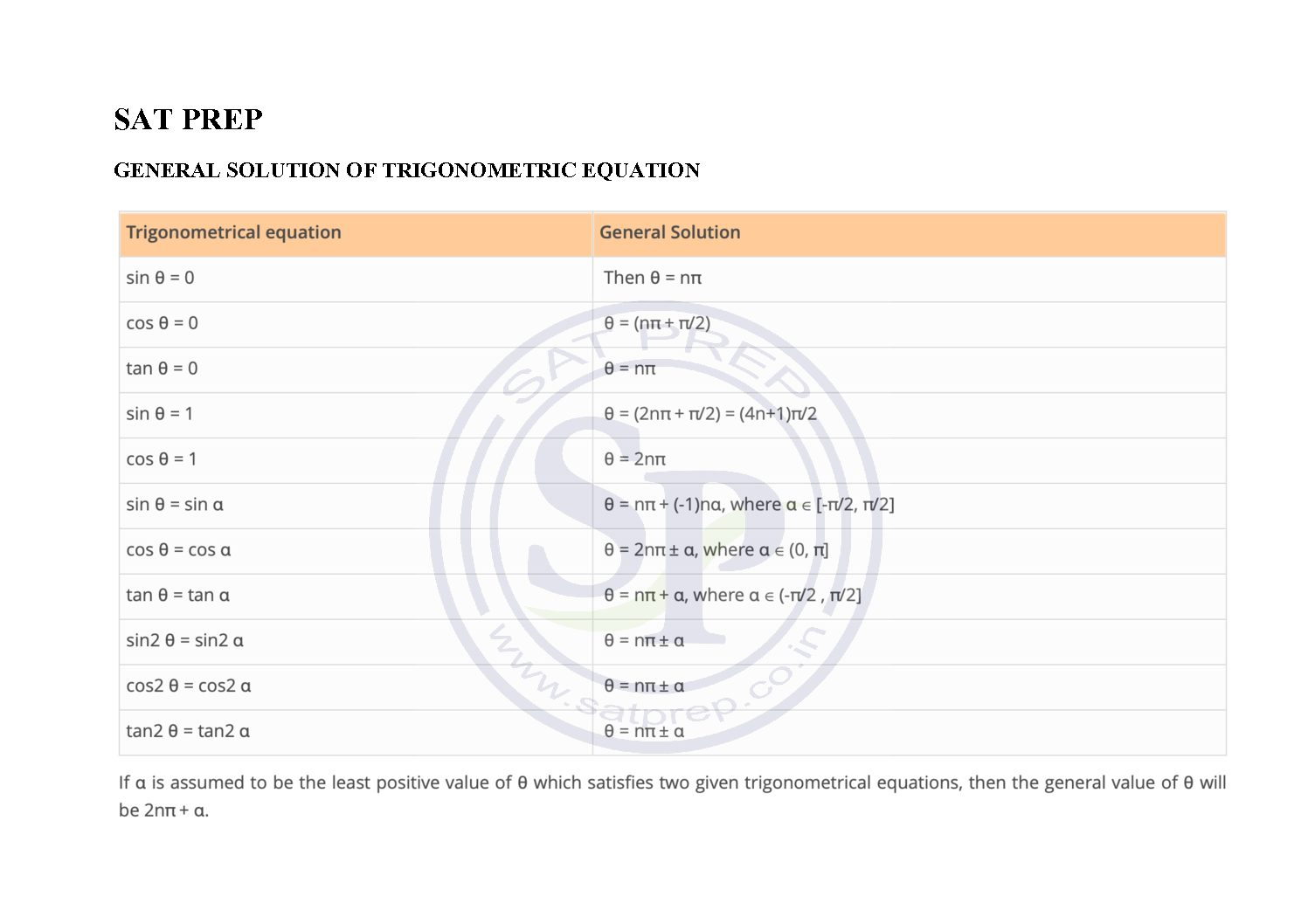
General solution of trigonometric Equati...
General Solutions of a Trig Equation. From the following diagram we see that sin( π -θ) = sin θ and cos ( -θ) = cos θ. General Solution of trigonometric eq
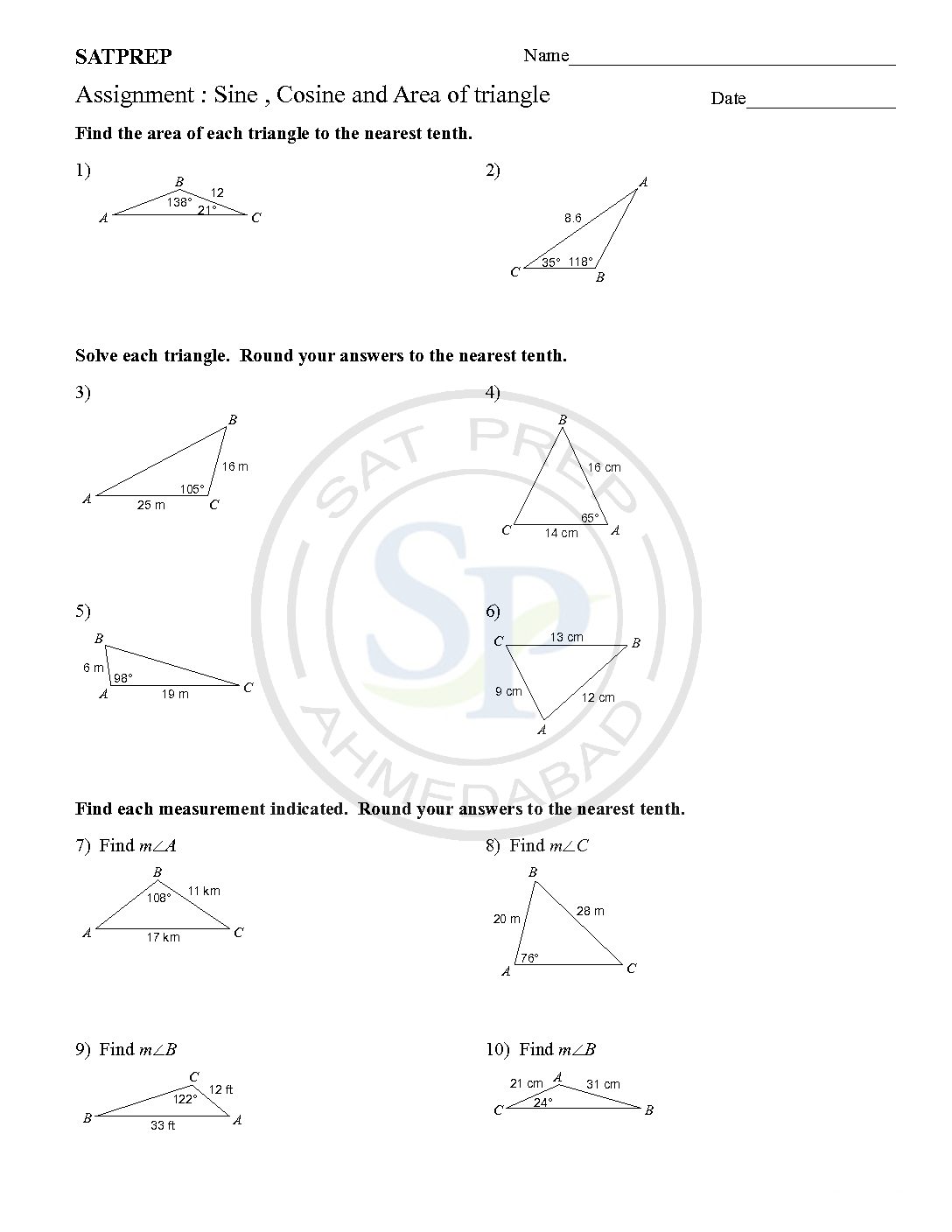
Sine Cosine and Area of triangle
Law of Cosines (also called the Cosine Rule) says: c2 = a2 + b2 − 2ab cos(C ). Law of Sines (or Sine Rule) is very useful for solving triangles: a sin A = b sin B = c … sine of angle B, and also equal to side c divided by the sine of […]