Volume of revolution. To get a solid of revolution we start out with a function, y=f (x), on an interval [a,b]. We then rotate this curve about a given axis to get the surface of the solid of revolution. For purposes of this discussion let’s rotate the curve about the x -axis, although it could be any vertical […]
You are browsing archives for
Category: Applications of Definite Integrals
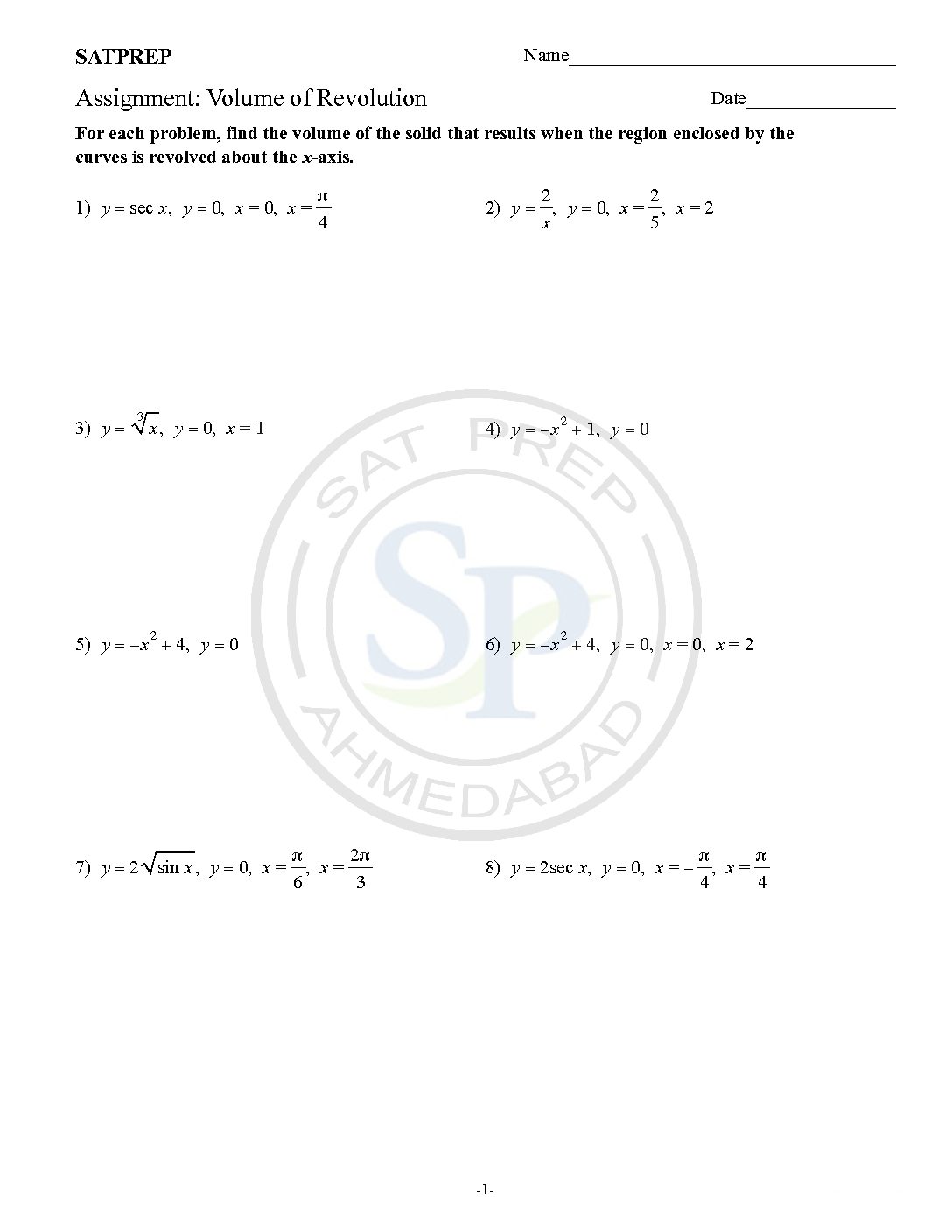
Volume of revolution of solid
Volume with Rings. To get a solid of revolution we start out with a function, y=f (x), on an interval [a,b]. We then rotate this curve about a given axis to get the surface of the solid of revolution. For purposes of this discussion let’s rotate the curve about the x -axis, although it could be any vertical or […]
Applications of Integration(Kinematics)
This post about Application of Integration into Kinematics. Solve for displacement given a velocity function in time. Solve for displacement and velocity given an acceleration function in time, & distinguish between displacement and total distance. kinematics
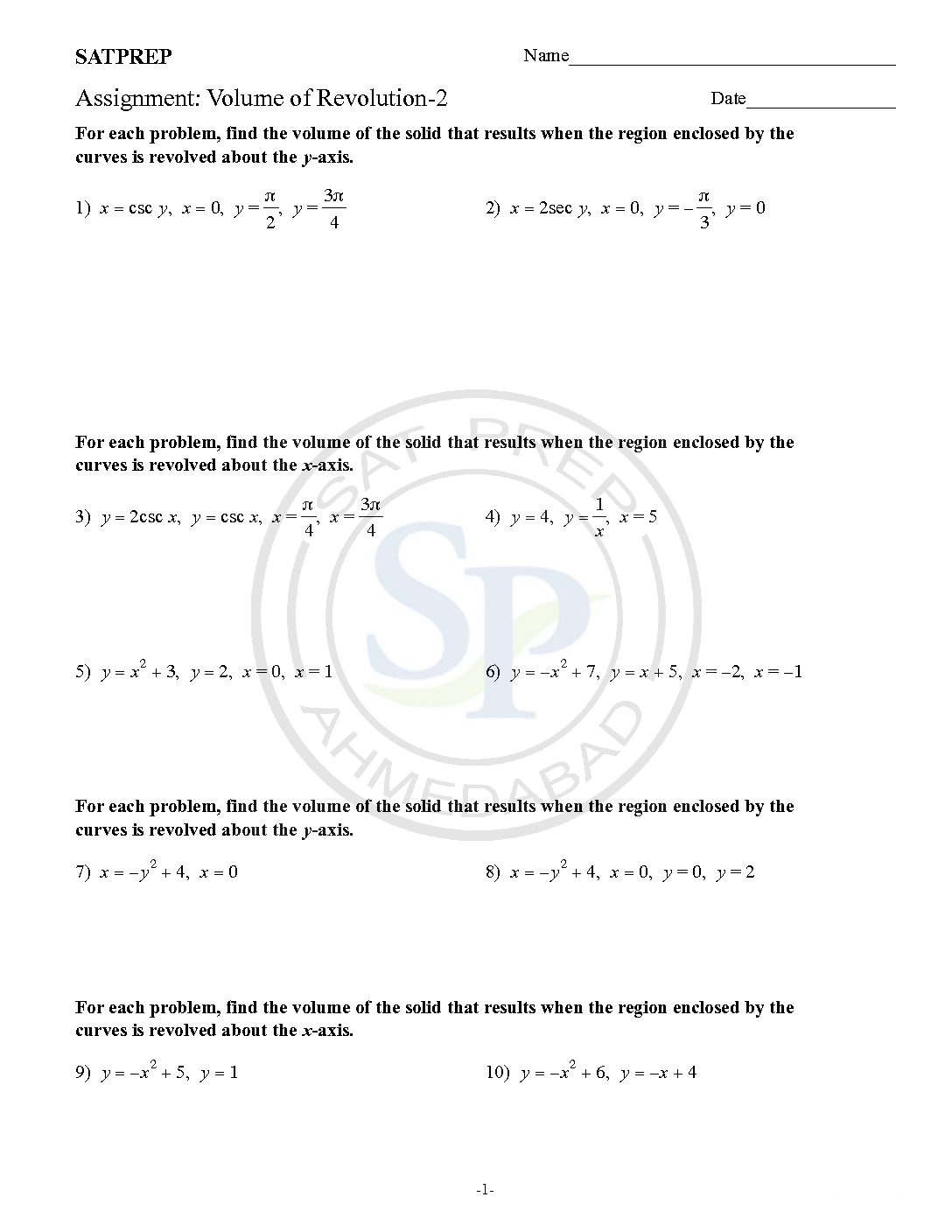
Volume -2
To get a solids of revolution we start out with a function, y=f (x), on an interval [a,b]. We then rotate this curve about a given axis to get the surface of the solid of revolution. Volume
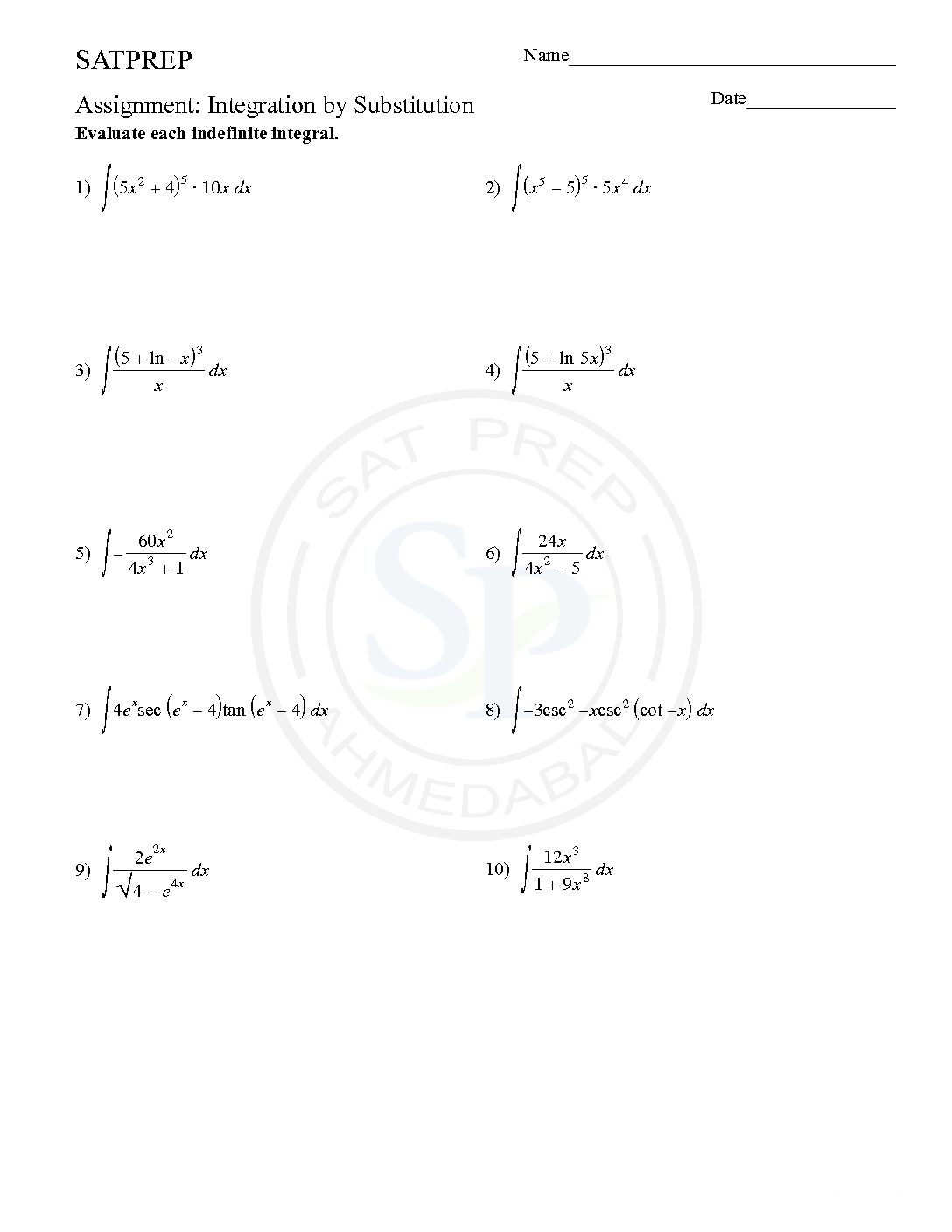
Integration by substitution -1
This post is about worksheet of Integration by exponential substitutions. It also one of most important concept of integral calculus . The function ƒ(φ(t))φ′(t) is also integrable on [a,b] Integration by exponential substitution
Integration by substitution -2
This post is about worksheet of integration by logarithmic substitution. It also one of most important concept of integral calculus . The function ƒ(φ(t))φ′(t) is also integrable on [a,b] Integration by logarithmic substitutions
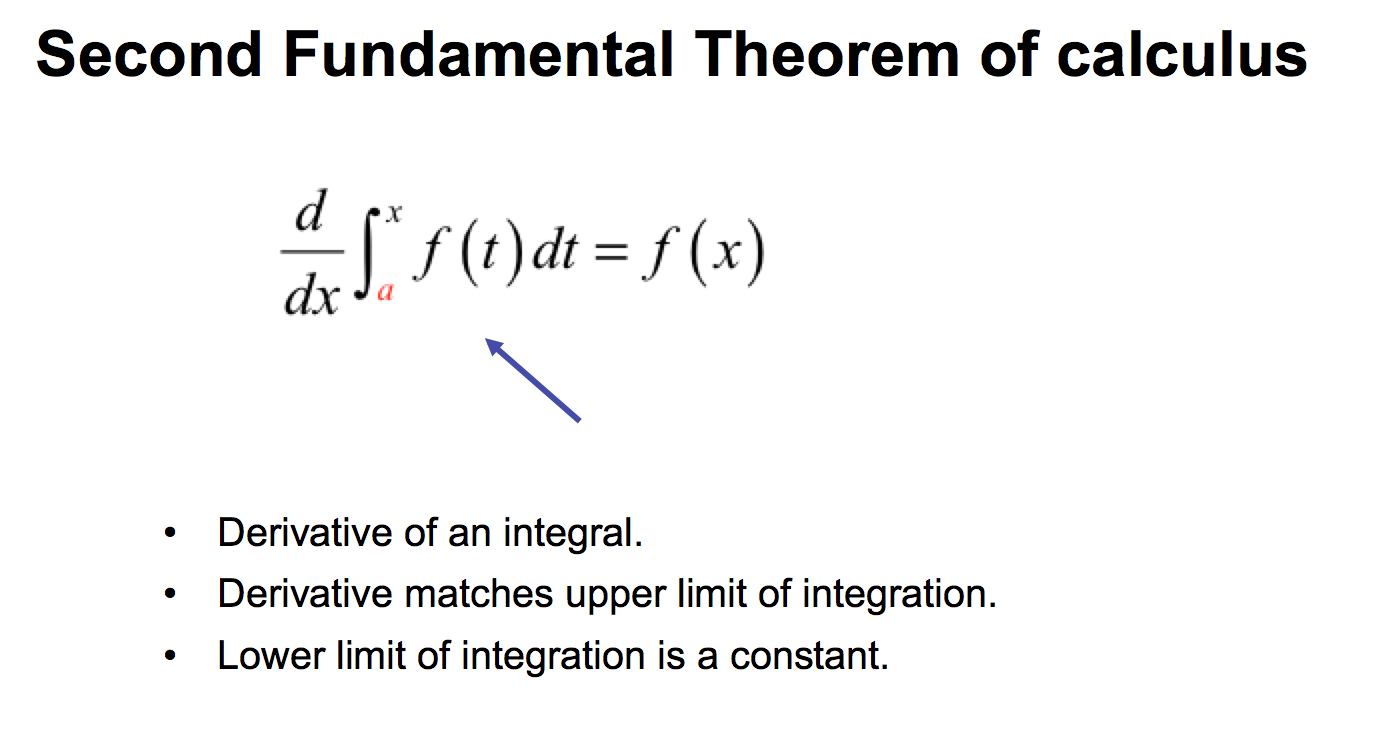
Kinematics
Describes the motion of points, objects and systems of groups of objects, without reference to the causes of motion. The symbol a stands for the acceleration of the object. And the symbol v stands for the instantaneous velocity of the object. The derivative of displacement with time is velocity ( v = ds/dt ). The […]