Process of integration when two different functions are in product form. By part method one function get differentiate while other integrate as per formula. Integration by parts
You are browsing archives for
Category: Integration
Integration By Parts
Method of integration when two different functions are in product form. By part method one function get differentiate while other integrate as per formula. Integration by Parts
Equation of curve
Equations of curve evaluate by doing integration of derivative curve. The gradient and a point the curve passes through are given as.. Gradient: dy/dx = 6sqrt(x) Point the curve passes through: (4,1) I need to find the equation of the curve. Therefore integration is process of finding equation of the curve. Equation of curve
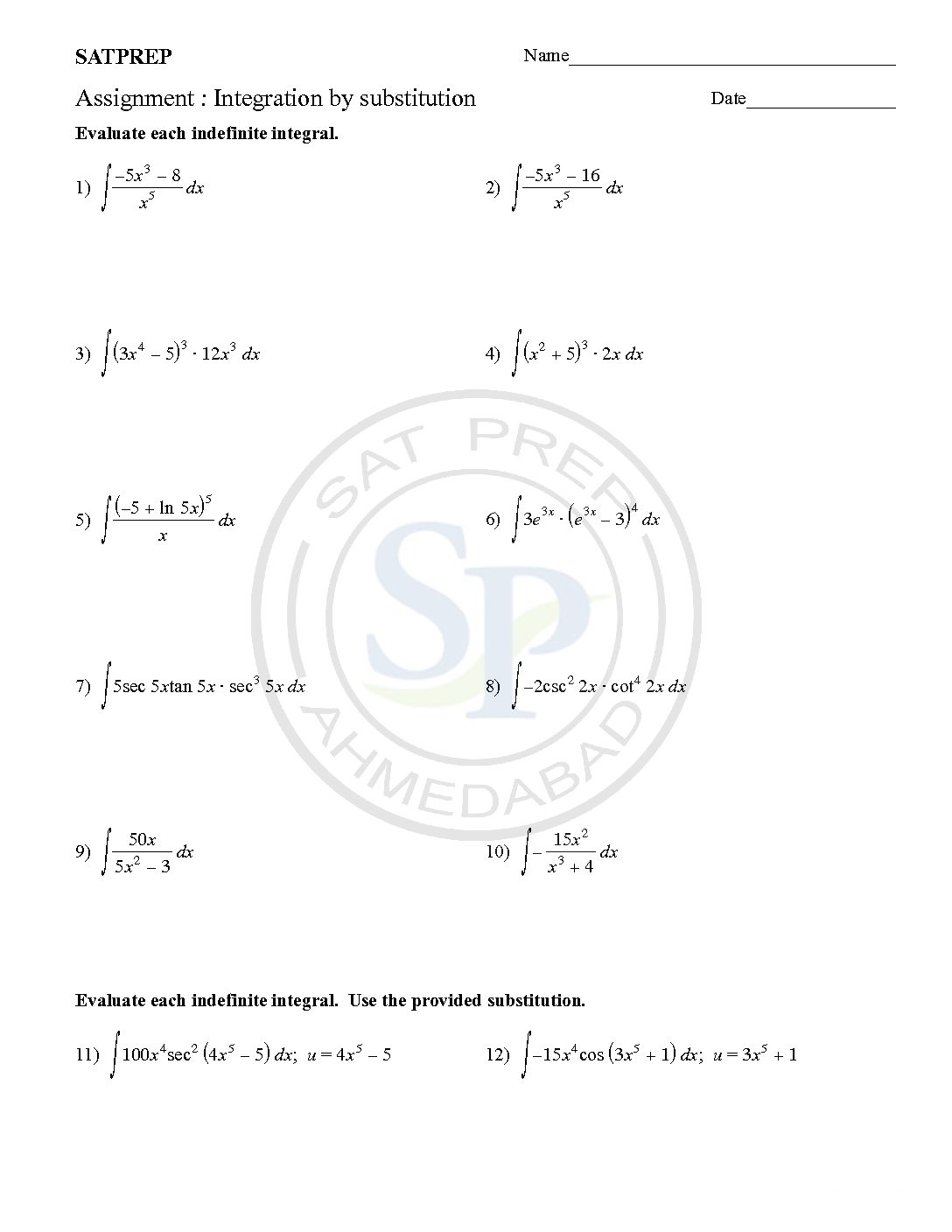
Integration by substitution
This post is about worksheet of Integration by substitutions. It also one of most important concept of integral calculus . The function ƒ(φ(t))φ′(t) is also integrable on [a,b] Integration by substitution
Product to Sum
Product‐Sum and Sum‐Product Identities. The process of converting products into sums can make a difference . Integrate \( \int \! \sin 3x \cos 4x \, \mathrm{d}x.\) This problem may seem tough at first, but after using the product-to-sum trigonometric formula, this integral very quickly changes into a standard form . Converting a sum of trig functions into a product. Write as and then […]
Integration by trigonometric substitutio...
This post is about worksheet of Integration by trigonometric substitution. It also one of most important concept of integral calculus . The function ƒ(φ(t))φ′(t) is also integrable on [a,b] Integration by substitution
Second fundamental theorem of Calculus-2
Second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Then F ( x) is an antiderivative of f ( x )—that is, F ‘( x) = f ( x) for all x in I. That business about the interval I is to make sure we only get limits of integration that are are reasonable for your function. Some things […]
Integration by substitution
This post is about worksheet of integration by trigonometric substitution. It also one of most important concept of integral calculus . The function ƒ(φ(t))φ′(t) is also integrable on [a,b] Integration by trigonometric substitutions
Second fundamental Theorem of Calculus
Then F ( x) is an antiderivative of f ( x )—that is, F ‘( x) = f ( x) for all x in I. That business about the interval I is to make sure we only get limits of integration that are are reasonable for your function. Some things that wouldn’t be reasonable: Choosing […]
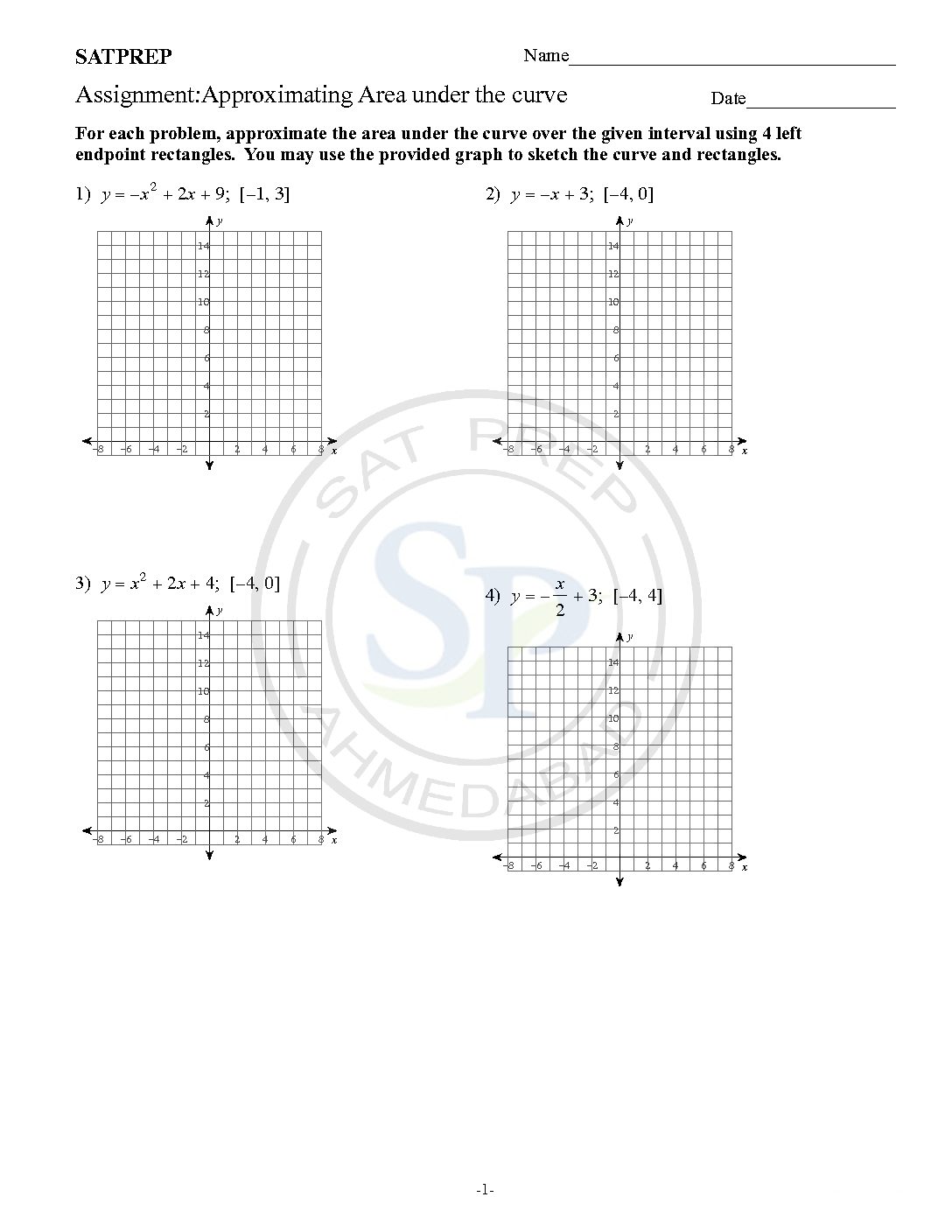
Approximating area under the curve
Approximate area of under a curve. Compute left, right, and midpoint Hence Riemann sums use with n rectangles are computed. Due to the this it approximate area. Approximate area under