Product‐Sum and Sum‐Product Identities. The process of converting products into sums can make a difference . Integrate \( \int \! \sin 3x \cos 4x \, \mathrm{d}x.\) This problem may seem tough at first, but after using the product-to-sum trigonometric formula, this integral very quickly changes into a standard form . Converting a sum of trig functions into a product. Write as and then […]
You are browsing archives for
Category: Integration
Integration by trigonometric substitutio...
This post is about worksheet of Integration by trigonometric substitution. It also one of most important concept of integral calculus . The function ƒ(φ(t))φ′(t) is also integrable on [a,b] Integration by substitution
Improper integral
an improper definite integral, or an improper integral. And we would denote it as 1 is our lower boundary, but we’re just going to keep on going forever as our upper boundary. So our upper boundary is infinity. And we’re taking the integral of 1 over x squared dx. An improper integral is a type of definite integral in which the integrand is undefined at […]
Applications of Integration(Kinematics)
This post about Application of Integration into Kinematics. Solve for displacement given a velocity function in time. Solve for displacement and velocity given an acceleration function in time, & distinguish between displacement and total distance. kinematics
Volume -2
To get a solids of revolution we start out with a function, y=f (x), on an interval [a,b]. We then rotate this curve about a given axis to get the surface of the solid of revolution. Volume
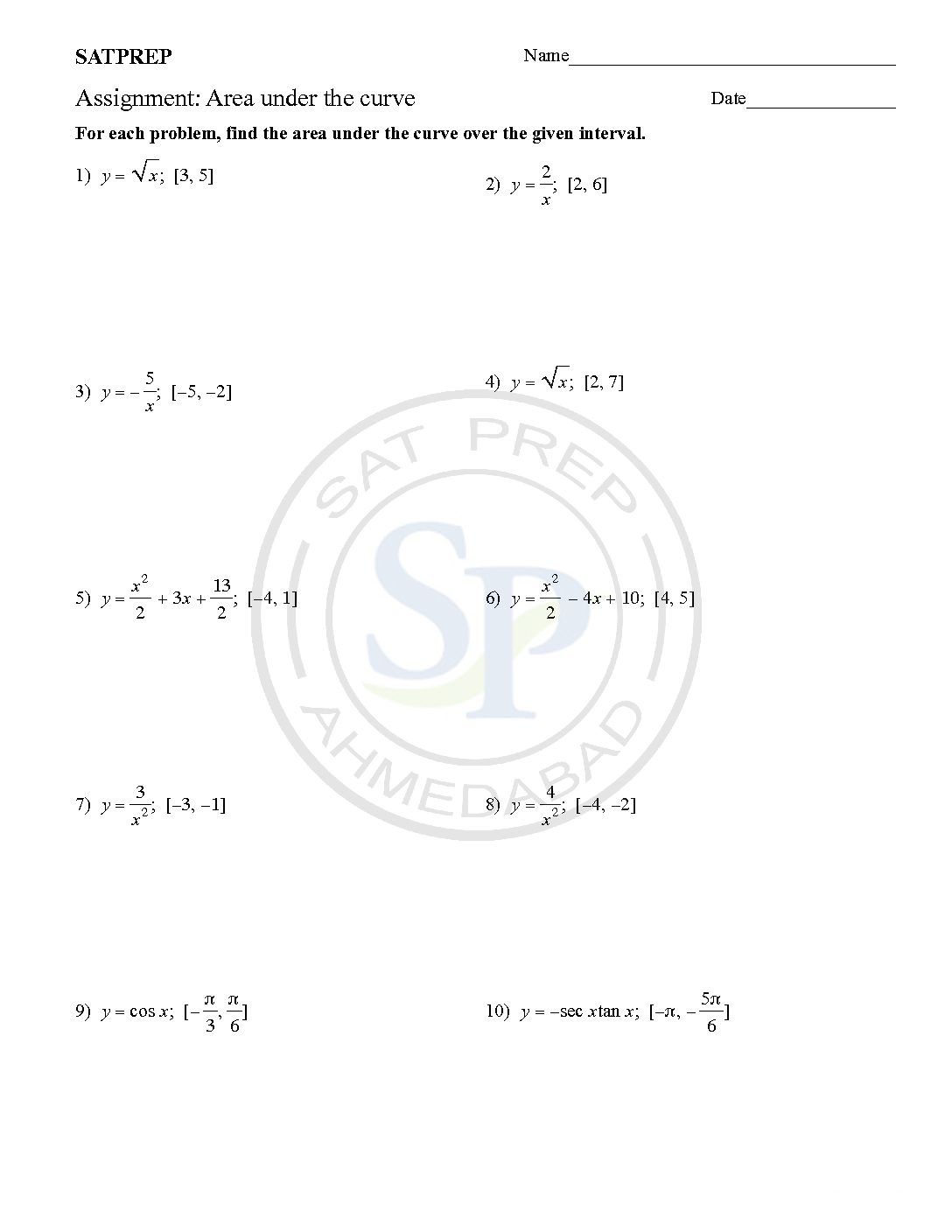
Area under the curve
To find the area under the curve y = f (x) between x = a and x = b, integrate y = f (x) between the limits of a and b. Areas under the x-axis will come out negative and areas above the x-axis will be positive. Area under the curve
Second fundamental theorem of Calculus-2
Second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Then F ( x) is an antiderivative of f ( x )—that is, F ‘( x) = f ( x) for all x in I. That business about the interval I is to make sure we only get limits of integration that are are reasonable for your function. Some things […]
Integration by substitution
This post is about worksheet of integration by trigonometric substitution. It also one of most important concept of integral calculus . The function ƒ(φ(t))φ′(t) is also integrable on [a,b] Integration by trigonometric substitutions
Differential Eq
Differential Equation is a function and one or more of its derivatives. Hence it solve by variable seperable and linear differential eq method. Also it solve by homogeneous. Differential Equation
Trigonometric ratio-2
The ratios of the sides of a right triangle are called trigonometric ratios. Sine, Cosine and Tangent are main ratio while rest three reciprocal. Hence Sine and Cosine are the trigonometric ratios, whose values are less that 1 for an acute angle. Because they are periodic. www.kutasoftware.com