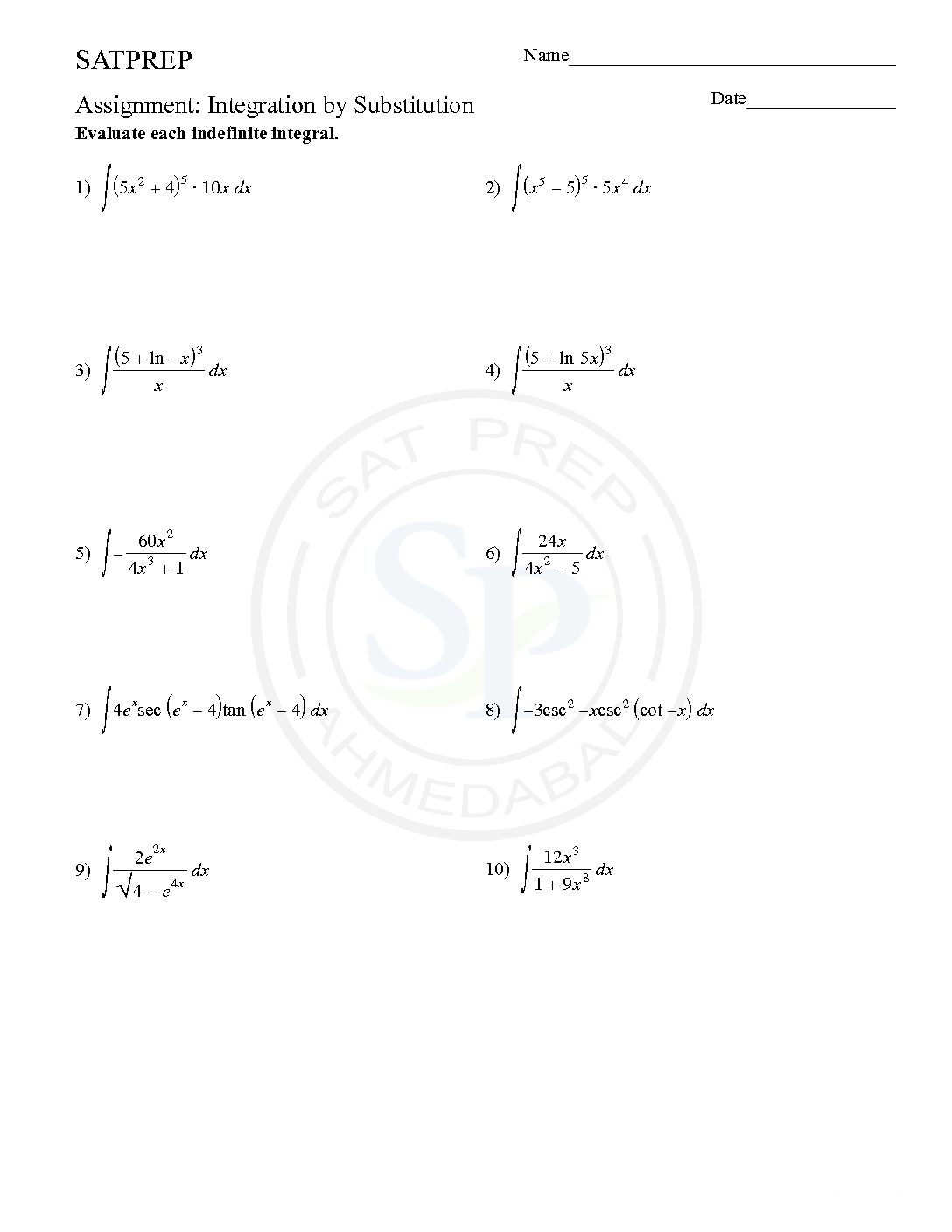
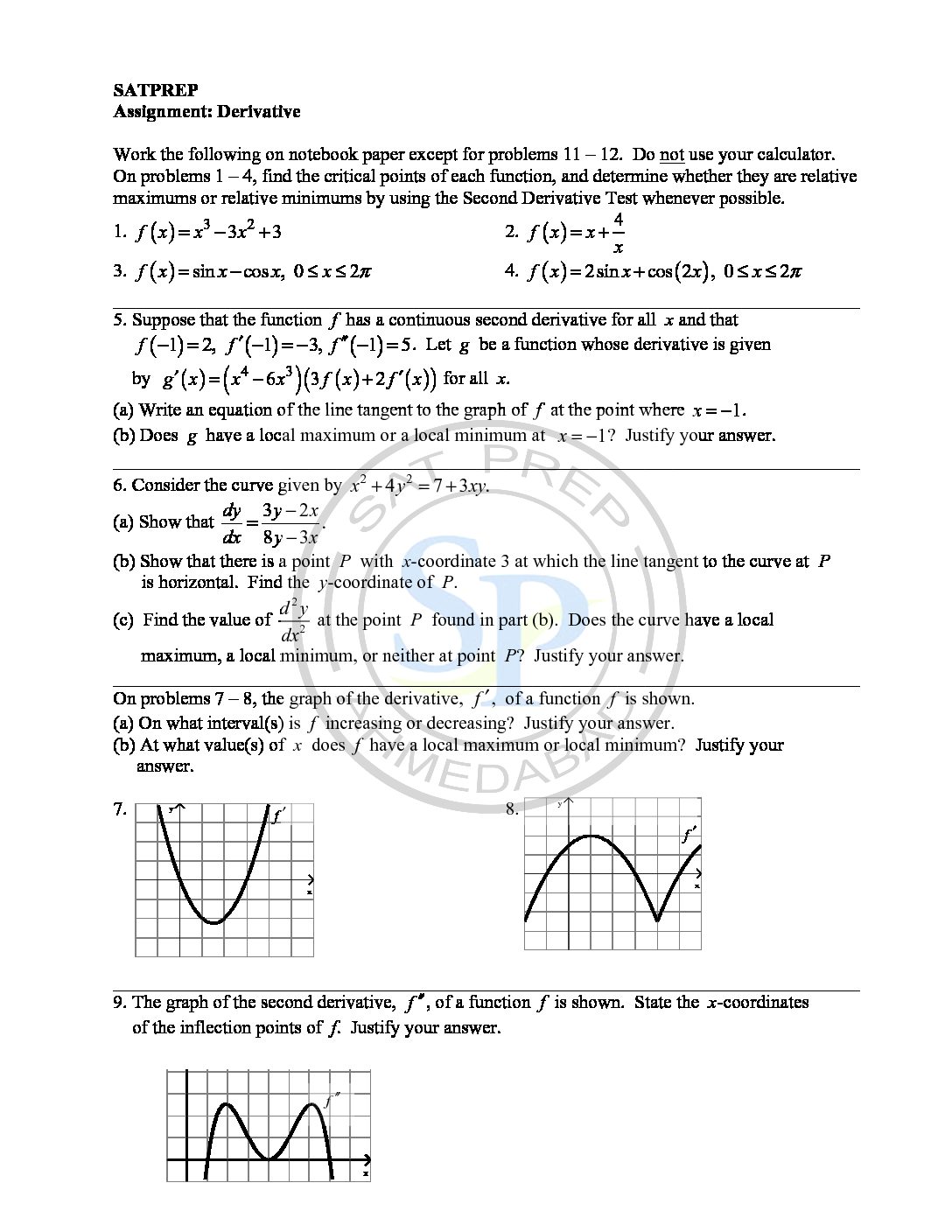
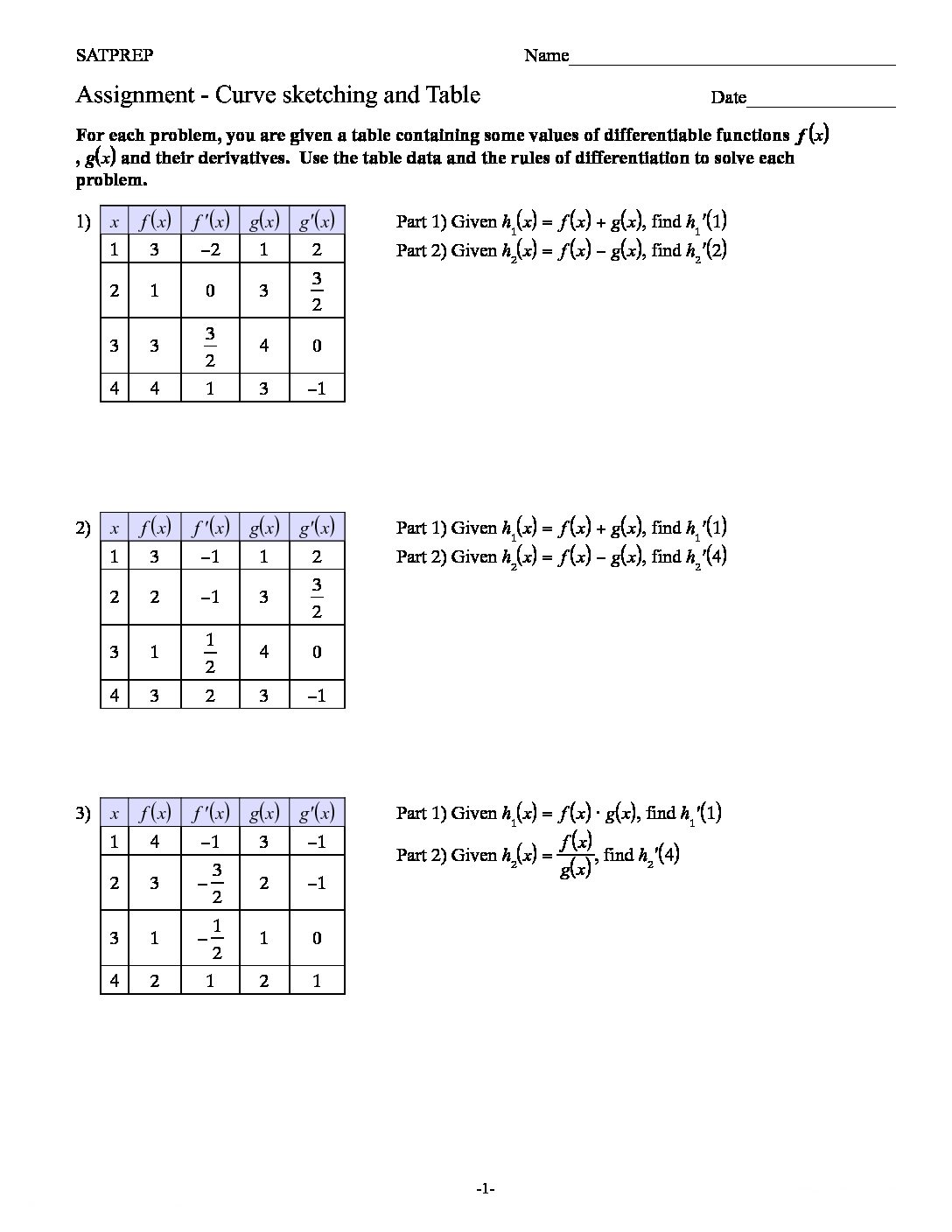
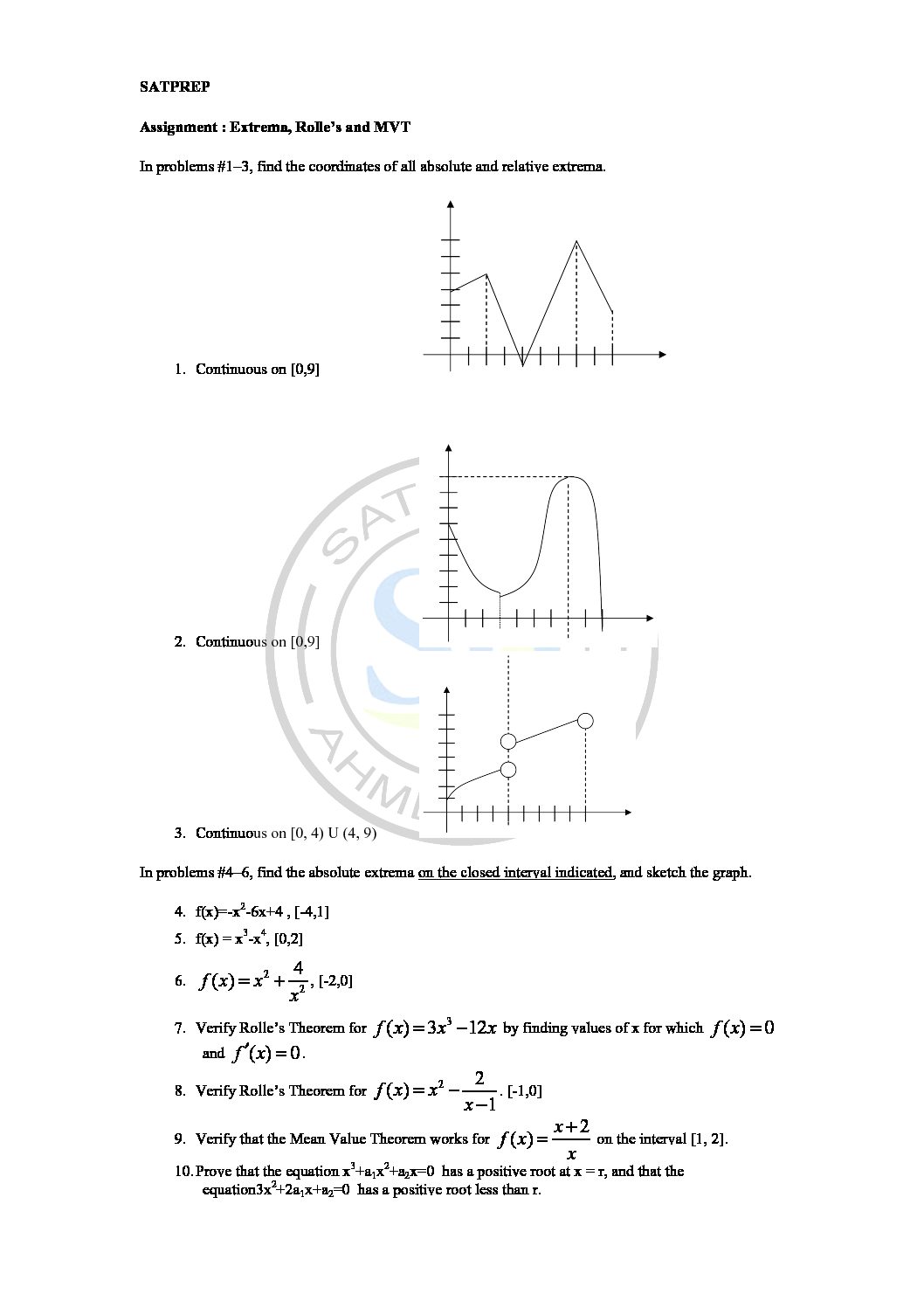
This post is about worksheet of integration by logarithmic substitution. It also one of most important concept of integral calculus . The function ƒ(φ(t))φ′(t) is also integrable on [a,b] Integration by logarithmic substitutions
You are browsing archives for
Category: AP
Integration by Parts
By parts apply for integration when different functions are in product form . As well as one derivative of another. By parts
Derivative
The derivative of a function of a single variable at a chosen input value. Derivative is the slope of the tangent line to the graph of the function at that point. Hence derivative of a function y = f(x) of a variable x is a measure of the rate at which the value y of the function changes with respect to the change […]
Curve sketching
Curve Sketching. If f (-x) = -f (x) for all x in the domain, then f is odd and symmetric about the origin. d) Asymptotes: Find the asymptotes of the function using the methods described above. First attempt to find the vertical and horizontal asymptotes of the function. Curve sketching
Curve Sketching -2
the sketching of curve though coordinate of turning and axes intercepts . So equation of the curve is given. Curve sketching
Curve sketching
Coordinate of turning point and axes intercepts for the sketching of curves though . So equation of the curve is given. Curve sketching
Extrema, Rolle’s and MVT
MVT. Theorem states that if a function f is continuous on the closed interval [a,b] and differentiable on the open interval (a,b), then there exists a point c in the interval (a,b) such that f'(c) is equal to the function’s average rate of change over [a,b]. Mean value theorem
Rolle’s and MVT
Rolle’s Theorem. Then there is a number c such that a<c<b and f′(c)=0. Or, in other words f(x) has a critical point in (a,b). To see the proof of Rolle’s Theorem see the Proofs From Derivative Applications . Roll’s theorem
Derivative of polynomials
Derivative is product of differentiation. Differentiation has applications to nearly all quantitative disciplines. For example, in physics, the derivative of the displacement of a moving body with respect to time is the velocity of the body, and the derivative of velocity with respect to time is acceleration. Therefore differentiation is process Derivative
Parametric Equation
An equation with third parametric are called Parametric equations . In this type of equation two variable defines in terms of third variable to form two equation. Third common variable is know as parameter. Due to parameter these equation call parametric equation. Likewise x = f(t) and y = g(t), where t is parameter. Also […]