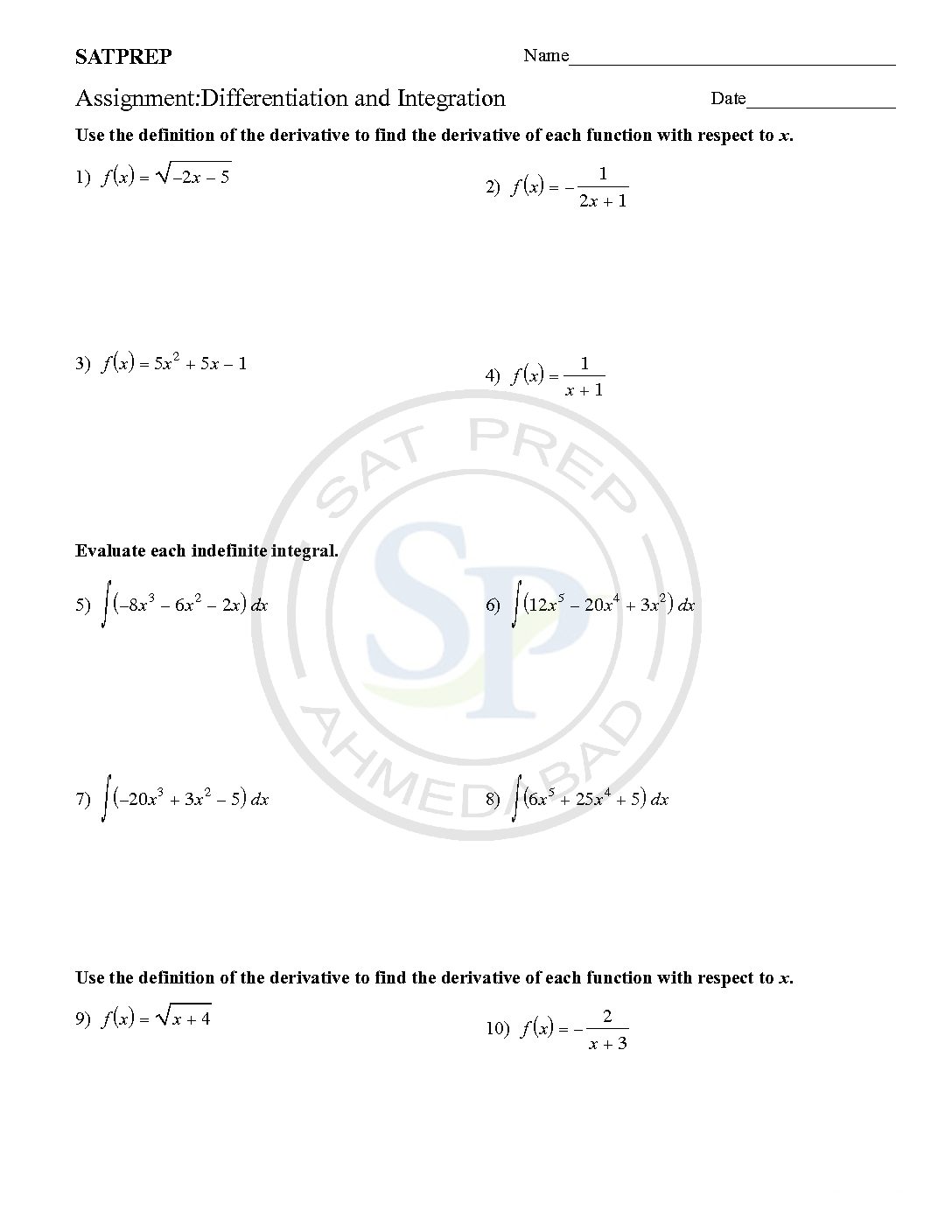
First of all differentiation and Integration are process of calculus. Due to differentiation we get derivative, while integration of derivative we get function back. Integration also called derivative. Differentiation and Integration
You are browsing archives for
Category: Pure Maths
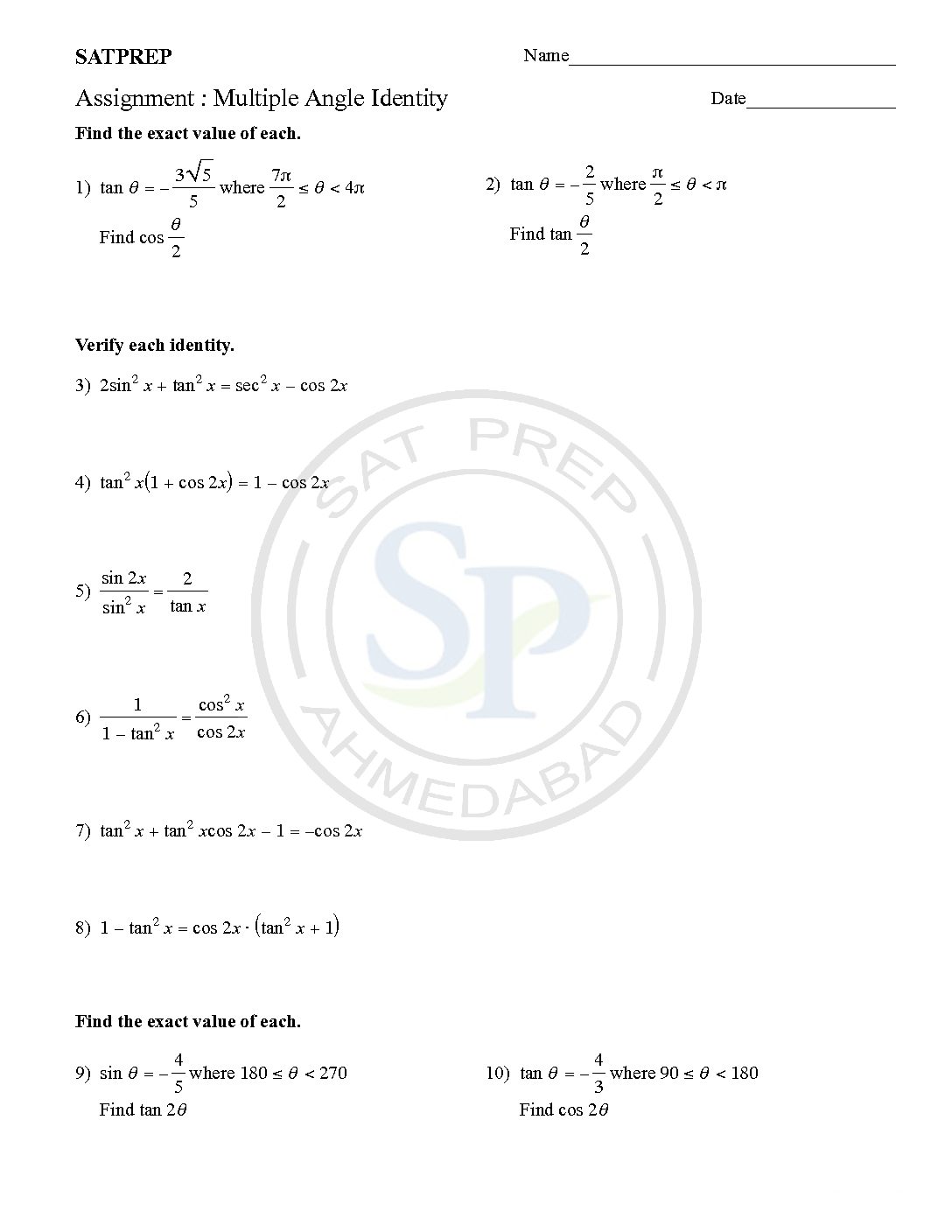
Multiple angle identity
Multiple angles identity are nothing but the trigonometric identity of multiple angles. Use for Proof of the double-angle and half-angle formulas. Solving Trigonometric Equations and Identities using Double–Angle and Half- Angle Formulas, examples and step by step solutions. Hence double angle formulae for sin 2A, cos 2A and tan 2A use for solving identity. Also to solve […]
Tangent and normal : Implicit
Tangent and Normal Lines for implicit curves are a line that touches the implicit curve at one point and has the same slope as the curve at that point. A normal to a curve is a line perpendicular to a tangent to the curve. tangent and normal
Trapezoidal Rule-2
trapezium rules is a way of estimating the area under a curve. so the trapezium rule gives a method of estimating integrals. Due to this we get approximate answer . Also we can get area using integration. trapezium rule
Trapezoidal Rule
The trapezium rules is a way of estimating the area under a curve. so the trapezium rule gives a method of estimating integrals. Due to this we get approximate answer . Also we can get area using integration. trapezium Rule
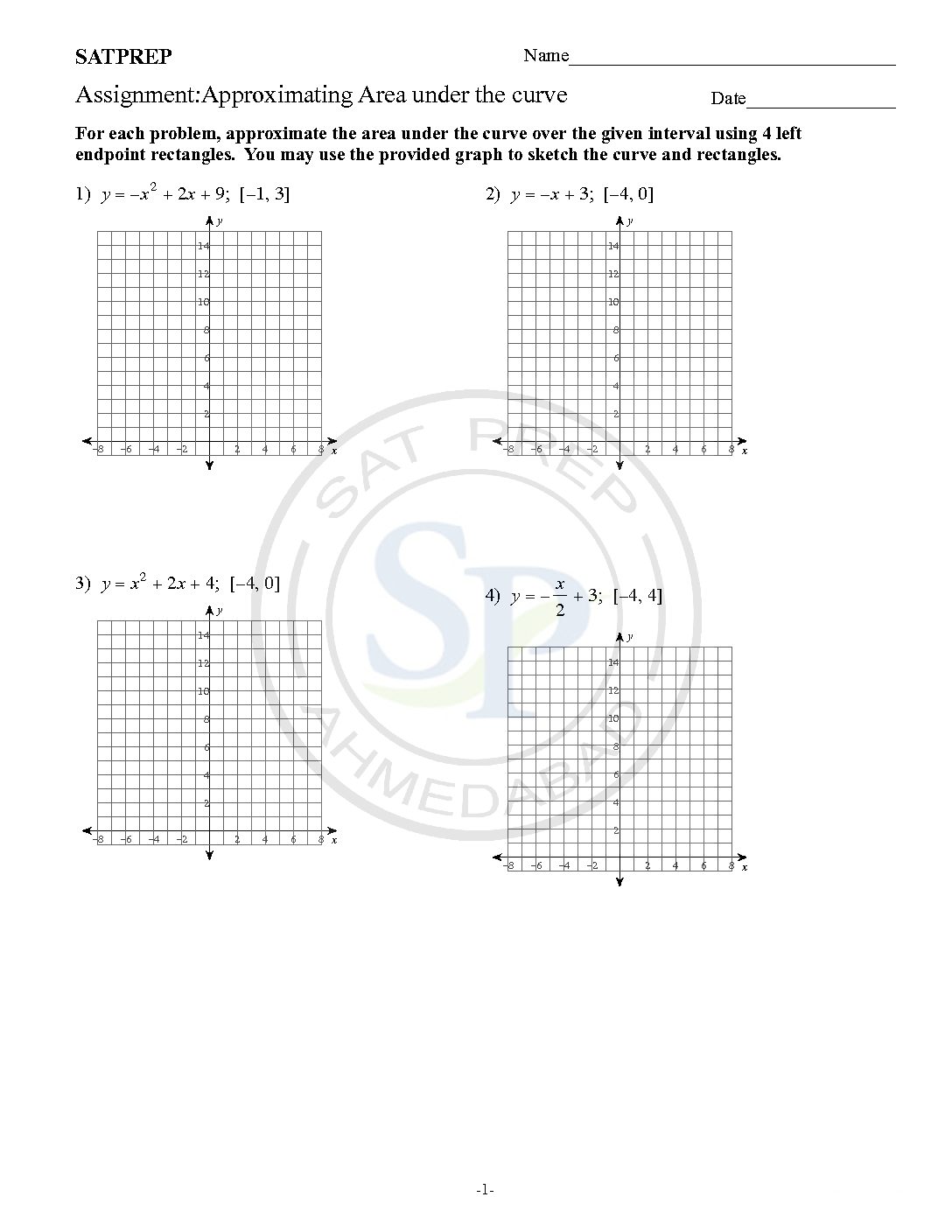
Approximating area under the curve
Approximate area of under a curve. Compute left, right, and midpoint Hence Riemann sums use with n rectangles are computed. Due to the this it approximate area. Approximate area under
Polynomial with complex root
nth degree polynomial with real coefficients has precisely n complex roots . Hence when all root cannot be real. Complex root with Polynomial
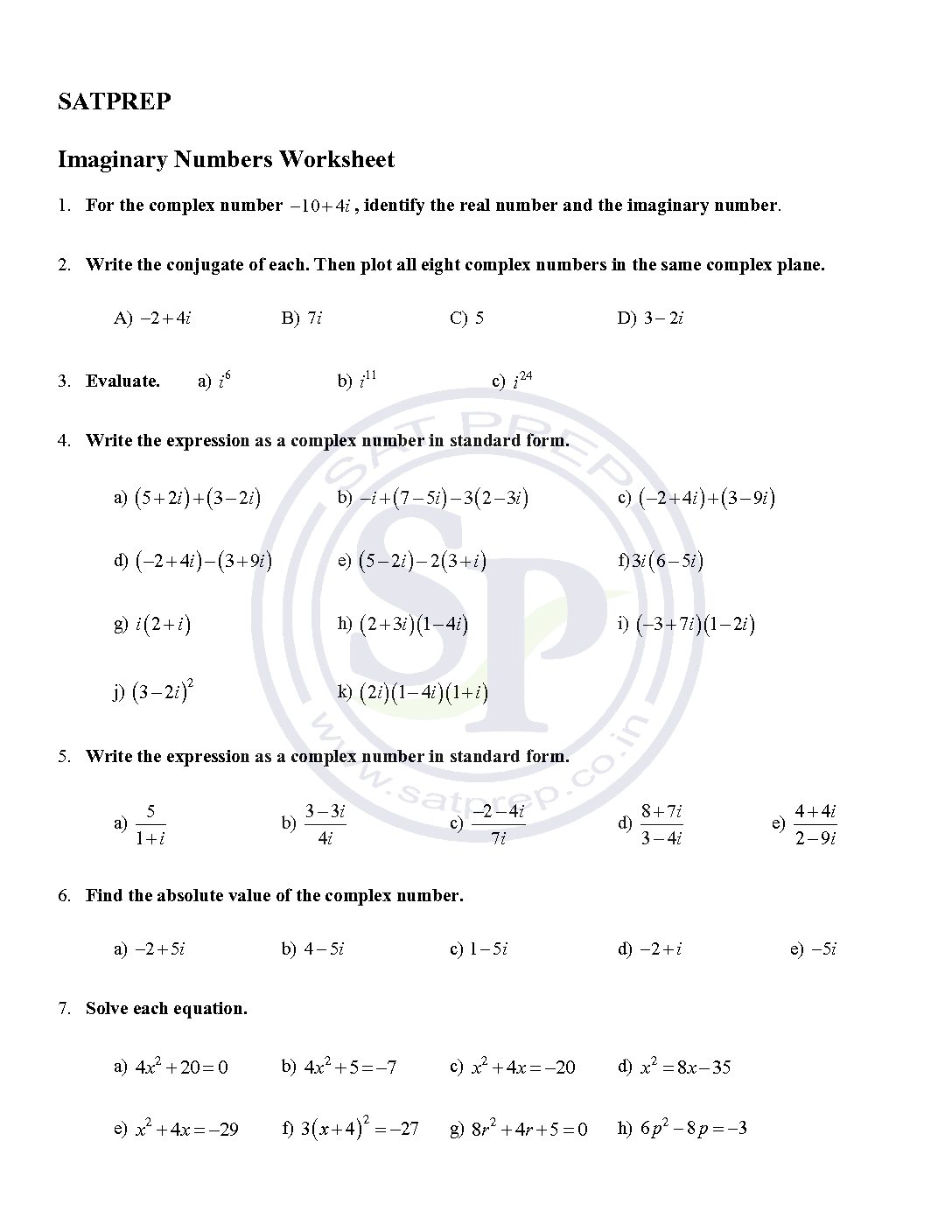
Arithmetics of complex no
imaginary number is any number of the form a + bi where a and b are real numbers. Addition and Subtraction of complex numbers is to add or subtract real parts and the imaginary parts. complex no
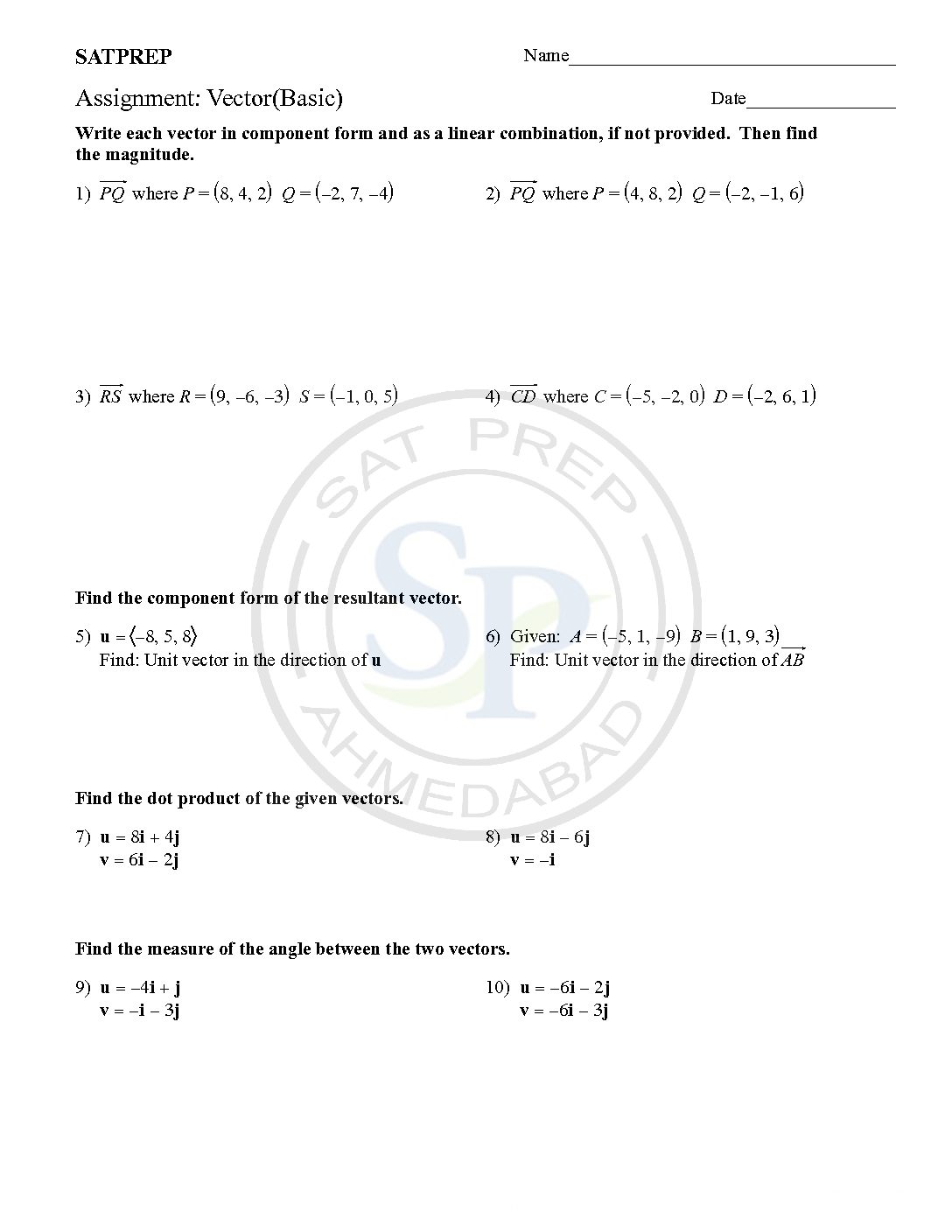
Vector and Scalar product.
vector has magnitude and direction. It start from one point to another point. The length of vector is called magnitude. The scalar product of two vectors is multiply and obtain a scalar quantity. It represent on ‘dot’. Another name is dot product. Vector and scalar product
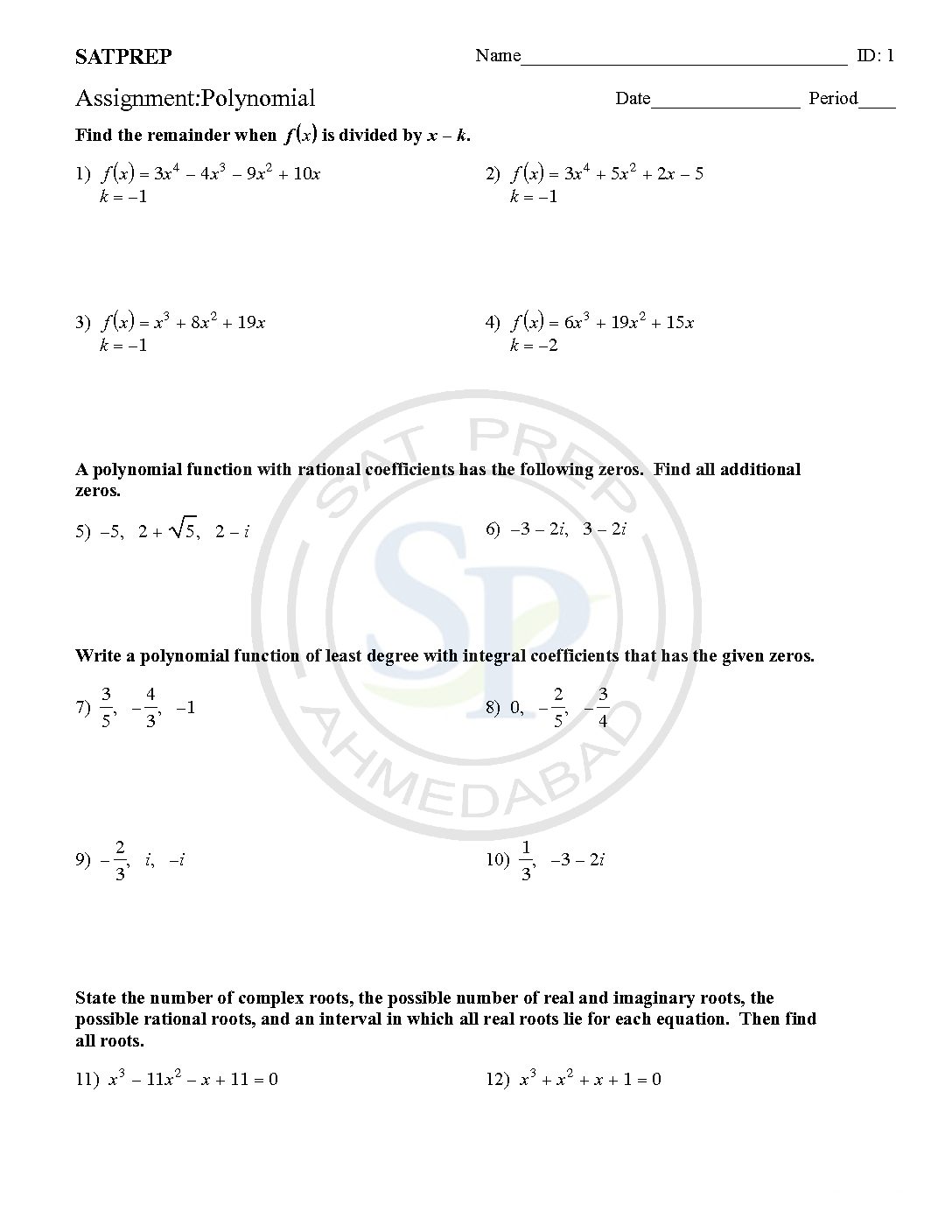
Polynomial
The polynomials are an expression involving a sum of powers in one or more variables multiplied by coefficients and constant. Polynomial linear , quadratic etc as per value of n=1, n = 2 etc . We can graph the polynomial for finding solution. Another polynomial is also use for curve as well as st. line. As […]