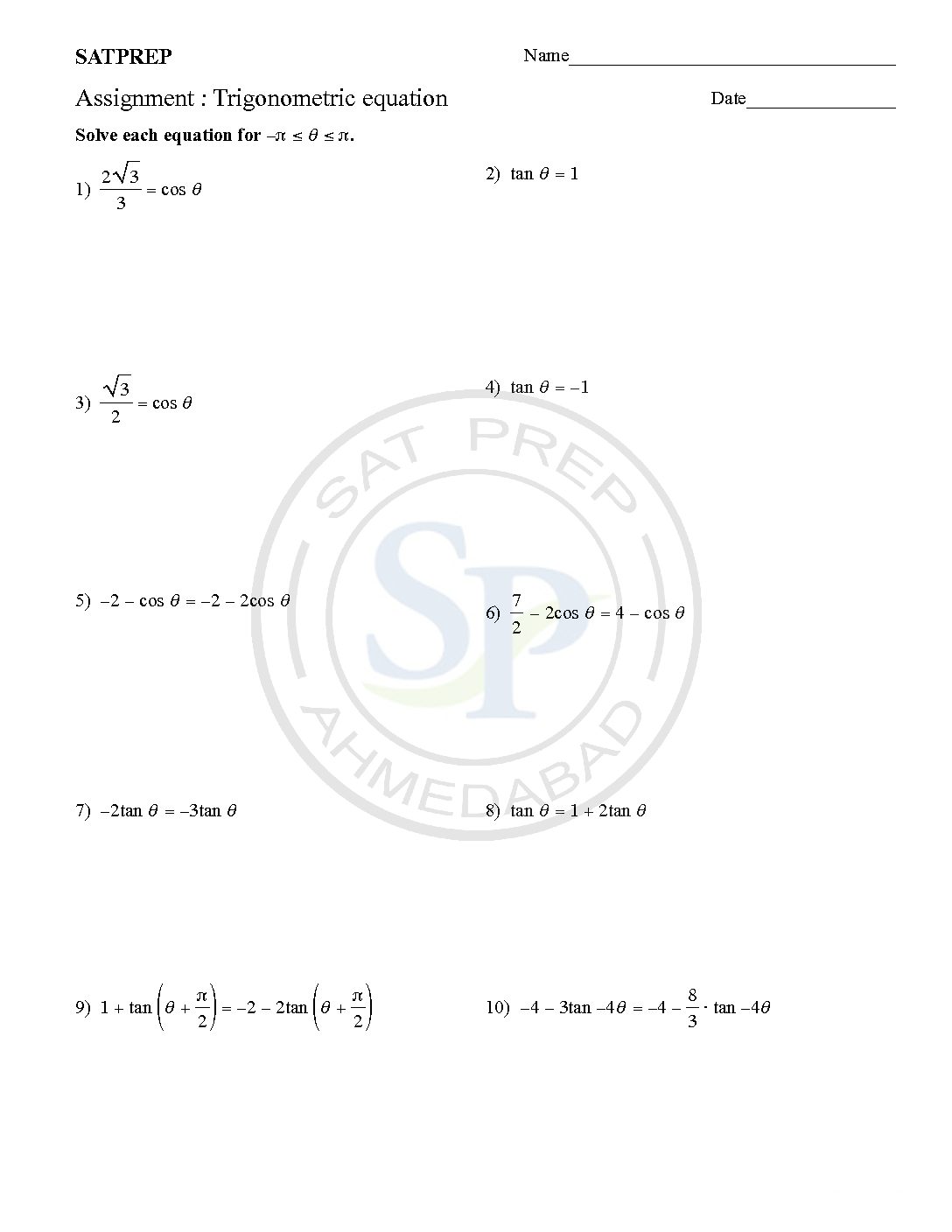
Solving trig equations use both the reference angles and trigonometric identities The general method of solving an equation is to convert it into the form of one ratio only. Then, using these results, hence, we can obtain solutions. Trigonometric equation
You are browsing archives for
Category: Cambridge Maths AS
Binomial distributions
This post is about binomial distributions. The Binomial distribution has two parameters like n and p. Due to n and p it is binomial. these n and p are n and p is the discrete probability distribution of the number of successes in a sequence of n independent experiment. Also we use probability of failure. Binomial
Normal Distribution
A graphical representation of a normal distributions are sometimes called a bell curve because of its flared shape. The precise shape can vary according to the distribution of the population but the peak is always in the middle and the curve is always symmetrical. In a normal distribution, the mean, mode and median are all the same. The Normal distribution has two […]
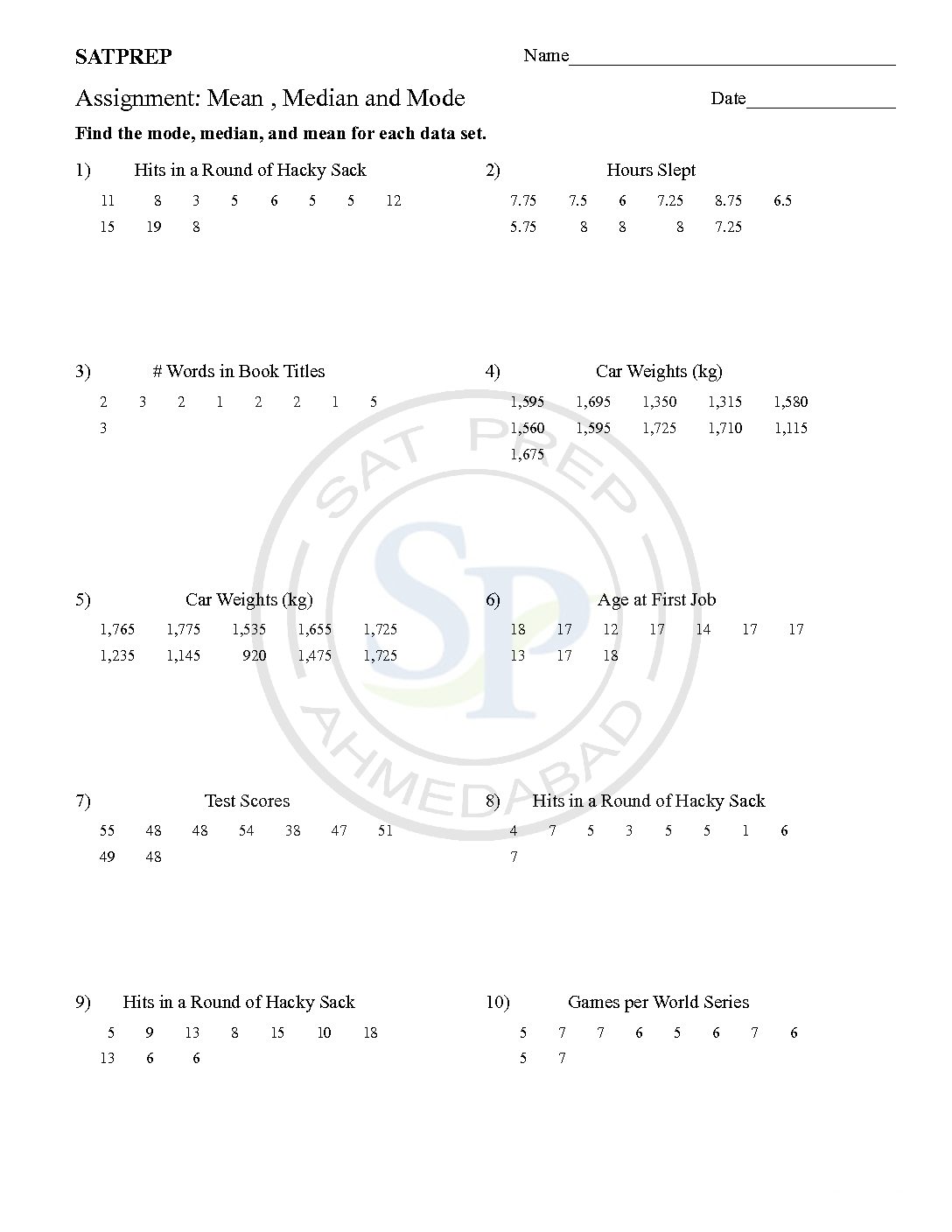
Mean , Median and Mode
Maxima and minima
A high point of curve is called a maxima. A low point is called a minima. In the Curve only one global maxima or minima exists , while more than one local maximum or minimum. Due to curve turn on these point are called local. Hence these point also called stationary points. Maxima and minima
Equation of curve
Equations of curve evaluate by doing integration of derivative curve. The gradient and a point the curve passes through are given as.. Gradient: dy/dx = 6sqrt(x) Point the curve passes through: (4,1) I need to find the equation of the curve. Therefore integration is process of finding equation of the curve. Equation of curve
Binomial Theorem
When a binomial is raised to whole number powers, the coefficients of the terms in the expansion form a pattern. Each expansion has one more term than the power on the binomial. The sum of the exponents in each term in the expansion is the same as the power on the binomial. www.kutasoftware.com
Equation of line
Equation of line
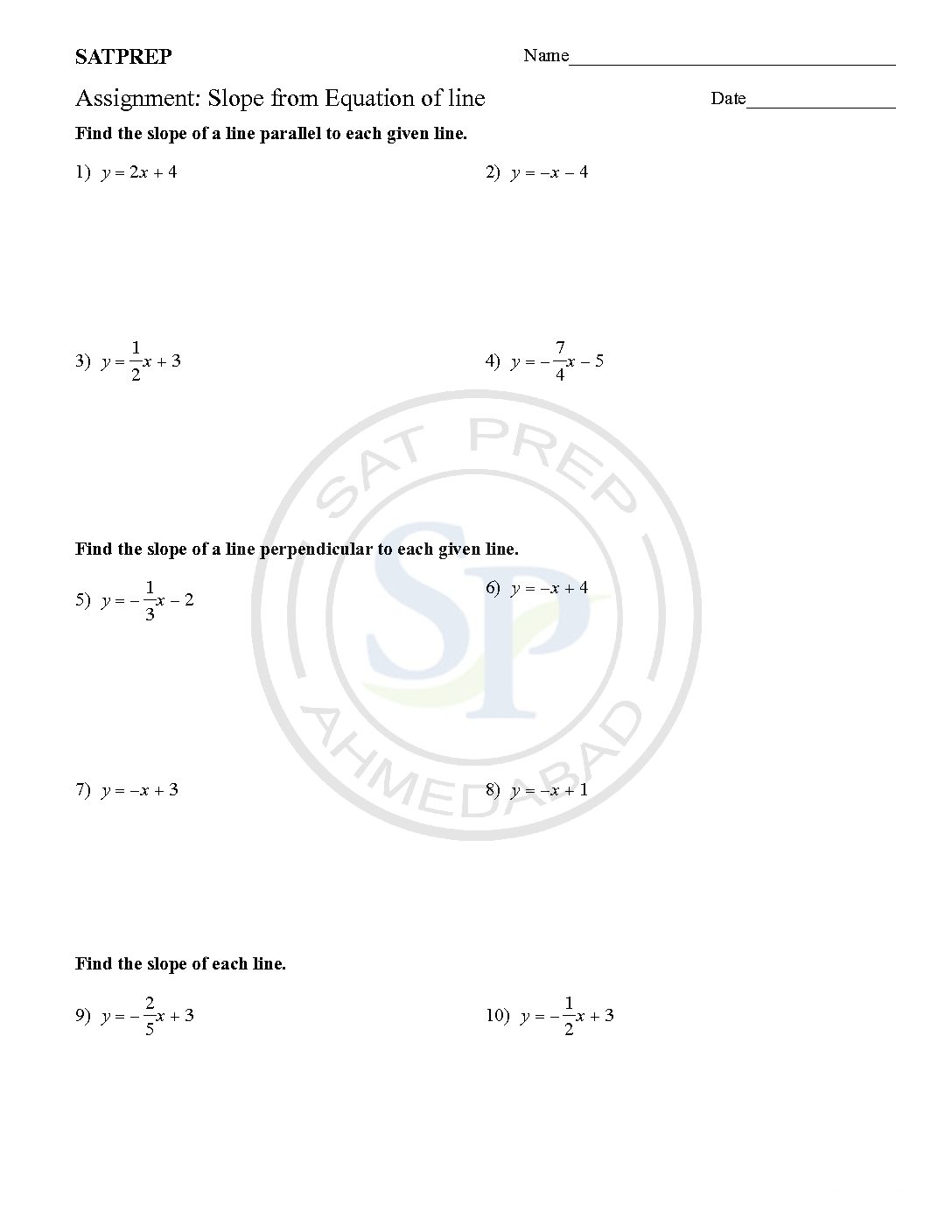
Slope from line
This post about slope of equation of lines . Eq. of line is part of coordinate geometry. coordinate geometry