This post about Slope of lines Eq. of line is part of coordinate geometry. coordinate geometry
You are browsing archives for
Category: Cambridge Maths AS
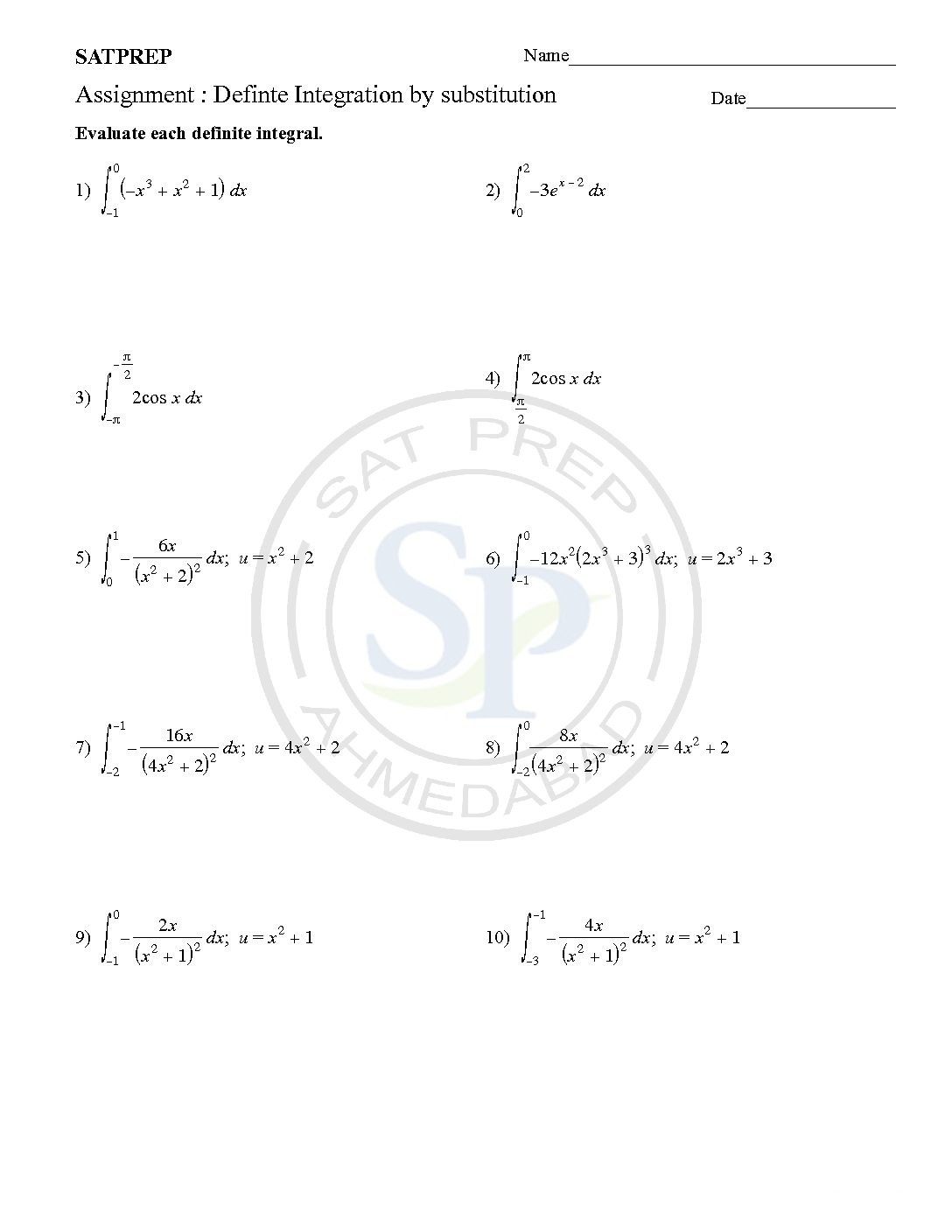
Definite integration
A Definite Integral has start and end values. In other words there is an interval [a, b]. Hence , definite integral gives particular solution. Definite Integration
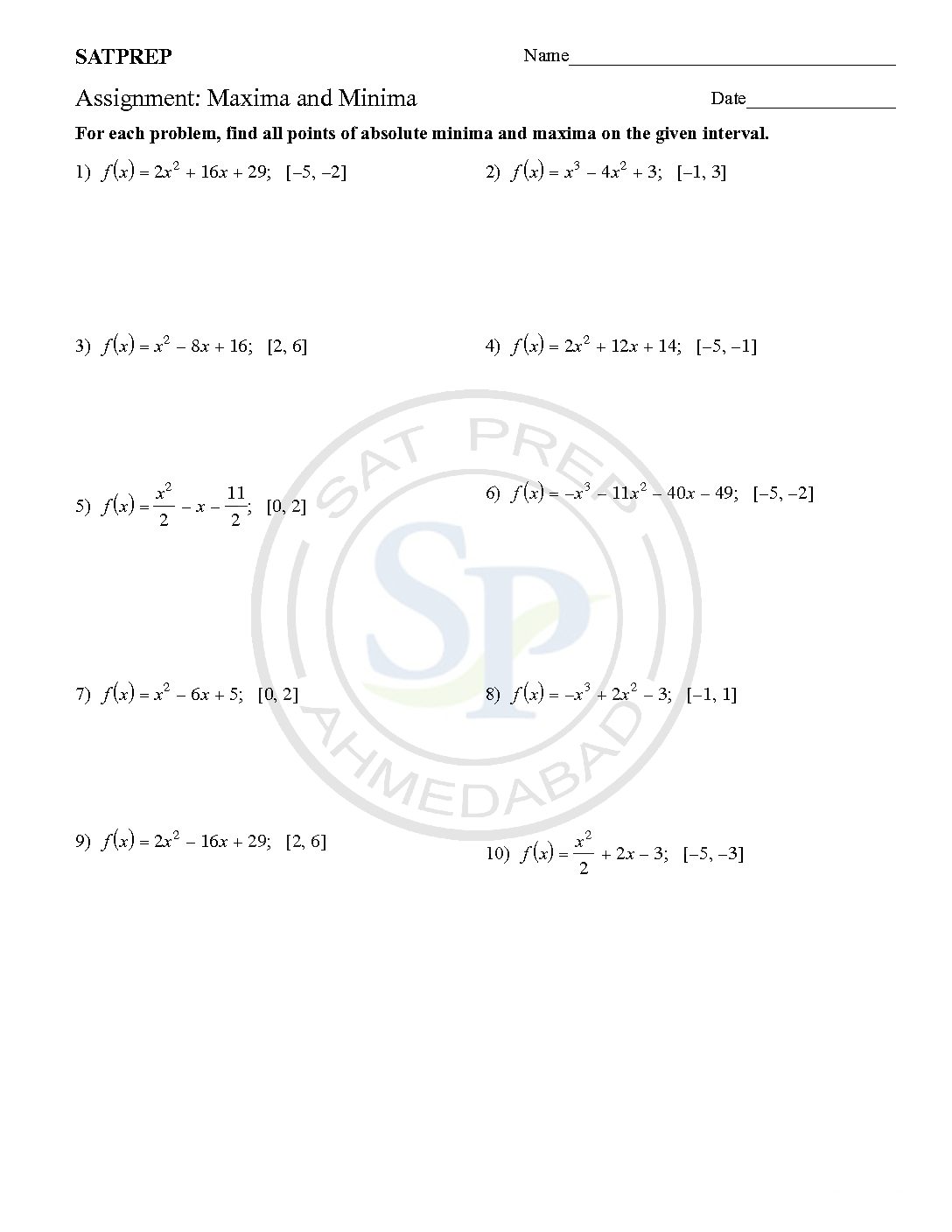
Maxima and minima
Maximum and Minima of Points of Inflection. The value f ‘(x) is the gradient at any point but often we want to find the Turning or Stationary Point (Maximum and Minimum points) or Point of Inflection These happen where the gradient is zero, f ‘(x) = 0. Critical Points include Turning points and Points where f ‘ (x) does not exist. […]
Rules of derivative
Rule for derivatives. Rules for derivatives. Sum rule: The derivative of the sum or difference of two functions is the sum or difference of their derivatives. (u + v)’ = u’ + v’ Constant multiple: The derivative of a constant times a function is the constant times the derivative of the function. (ku)’ = ku’ Rules of derivative
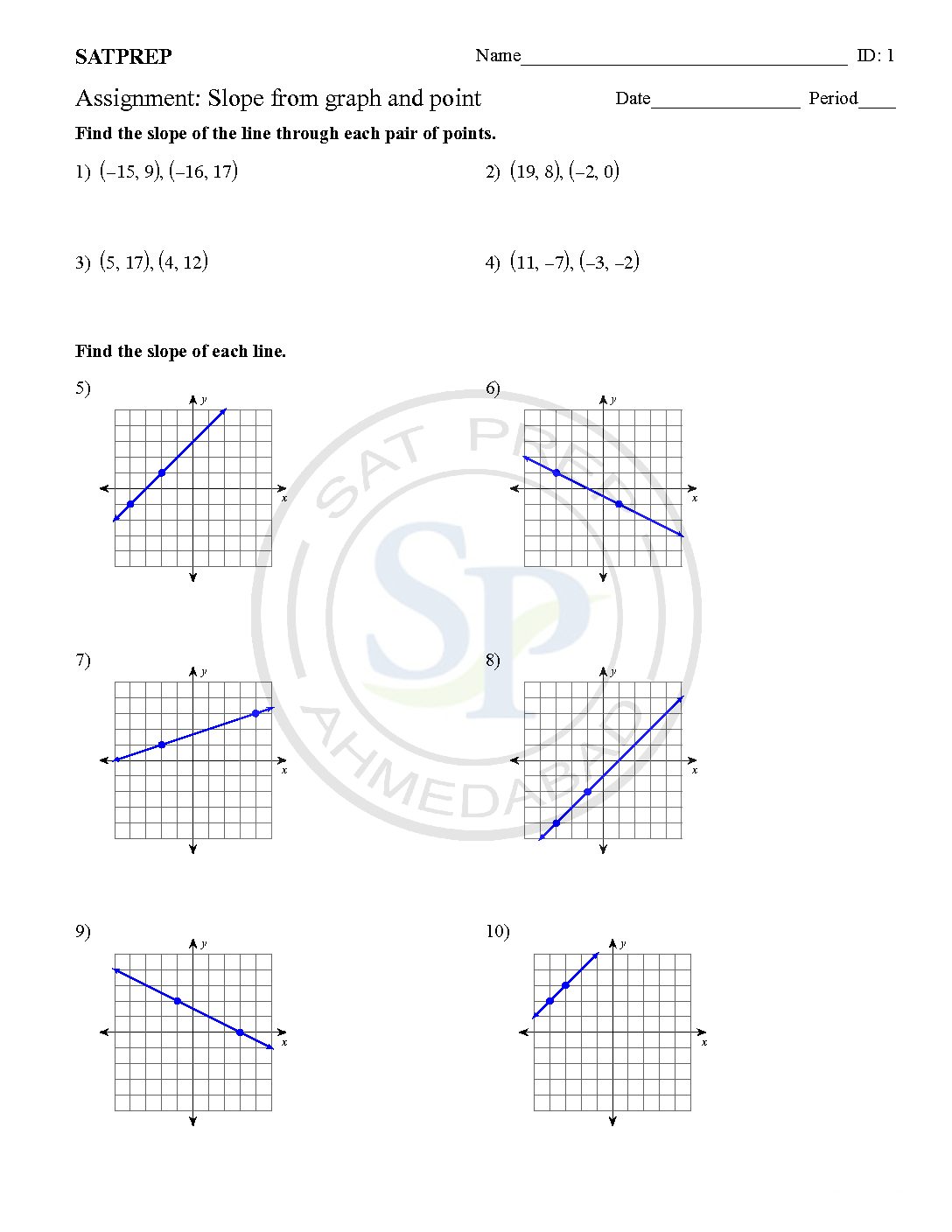
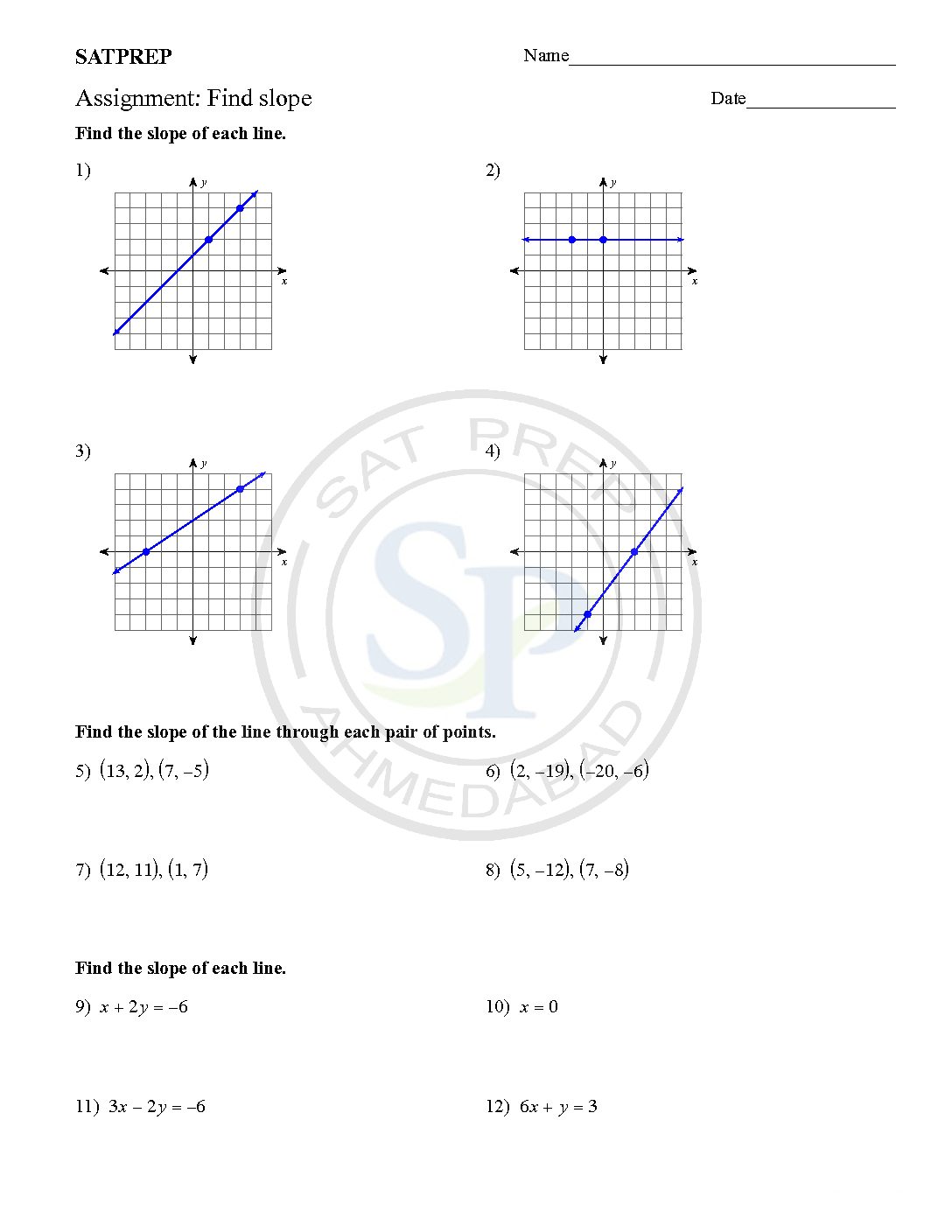
Find slope
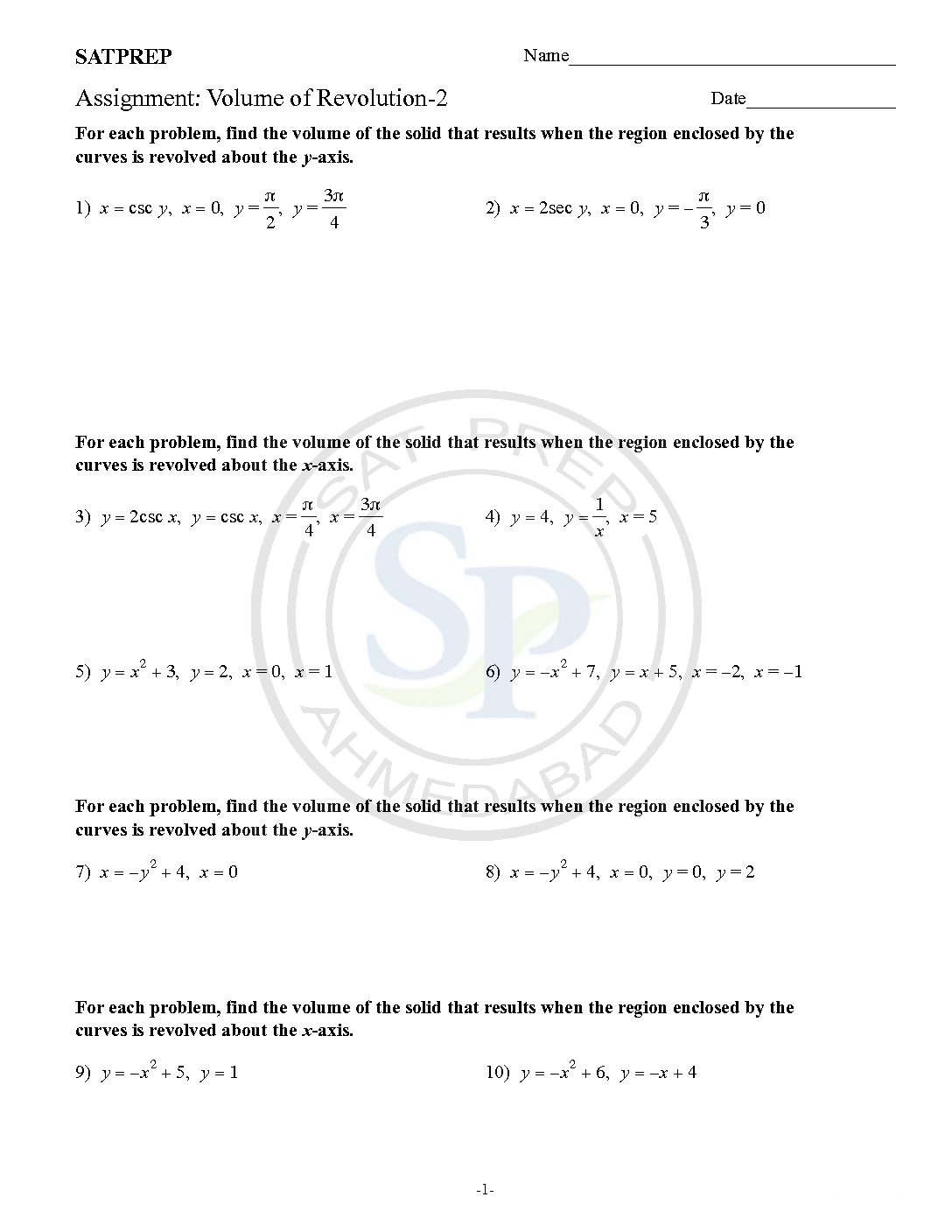
Volume of revolution of solid
Volume of revolution. To get a solid of revolution we start out with a function, y=f (x), on an interval [a,b]. We then rotate this curve about a given axis to get the surface of the solid of revolution. For purposes of this discussion let’s rotate the curve about the x -axis, although it could be any vertical […]
Volume of revolution of solid
Volume with Rings. To get a solid of revolution we start out with a function, y=f (x), on an interval [a,b]. We then rotate this curve about a given axis to get the surface of the solid of revolution. For purposes of this discussion let’s rotate the curve about the x -axis, although it could be any vertical or […]
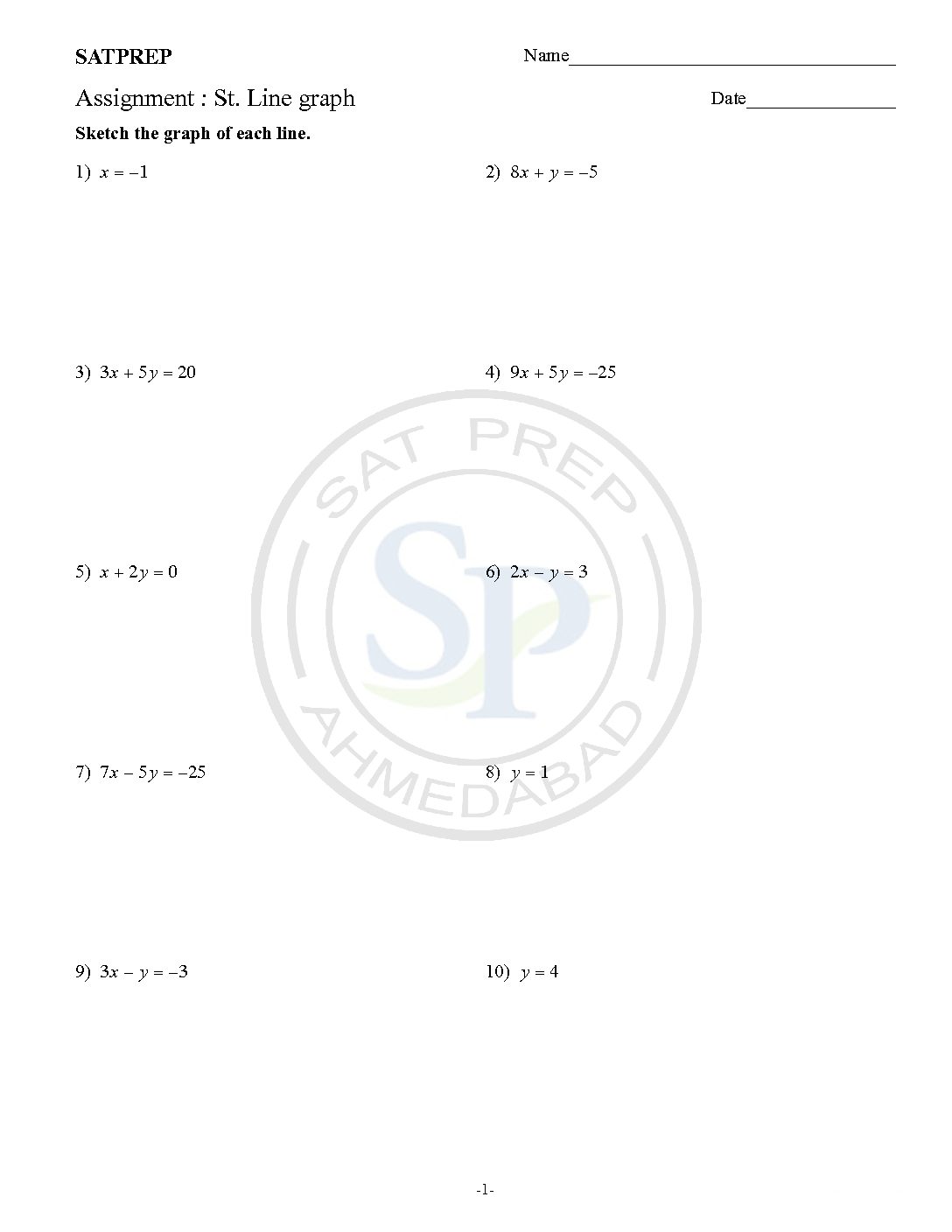
St. Line Graph
Straight line graphs. The graph of each of equations is a straight line: If an equation can be rearranged into the form y = mx +c, then its graph will be a straight line. ax +by= c can be rearranged as (which can be re-written as y = mx+c). Therefore vertical lines have equations have slope undefined form x =k . Hence graph depend on […]
Binomial Theorem
Binomial theorems is another ways of expansion of two terms. Another way it is generalised form of expansion. Due to expansion of two term it is binomial. “What are the binomial coefficients?” . It shows how to calculate the coefficients in the expansion of (a + b) n. The symbol for a binomial coefficient nCr. As well as pascal […]
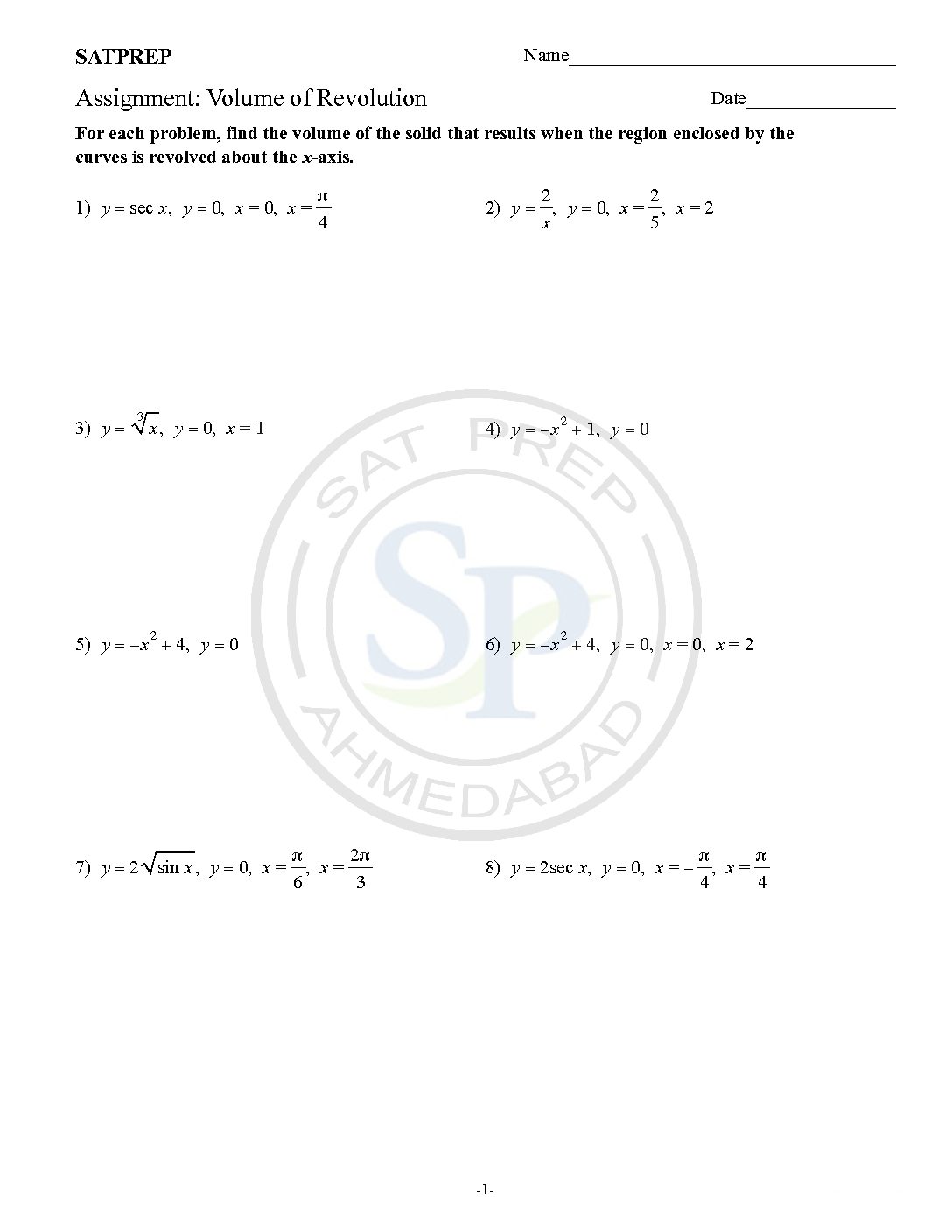
Volume of revolution
To get a solid of revolution we start out with a function, y=f (x), on an interval [a,b]. We then rotate this curve about a given axis to get the surface of the solid of revolution Volume of Revolution