Rule for derivatives. Rules for derivatives. Sum rule: The derivative of the sum or difference of two functions is the sum or difference of their derivatives. (u + v)’ = u’ + v’ Constant multiple: The derivative of a constant times a function is the constant times the derivative of the function. (ku)’ = ku’ Rules of derivative
You are browsing archives for
Category: Calculus
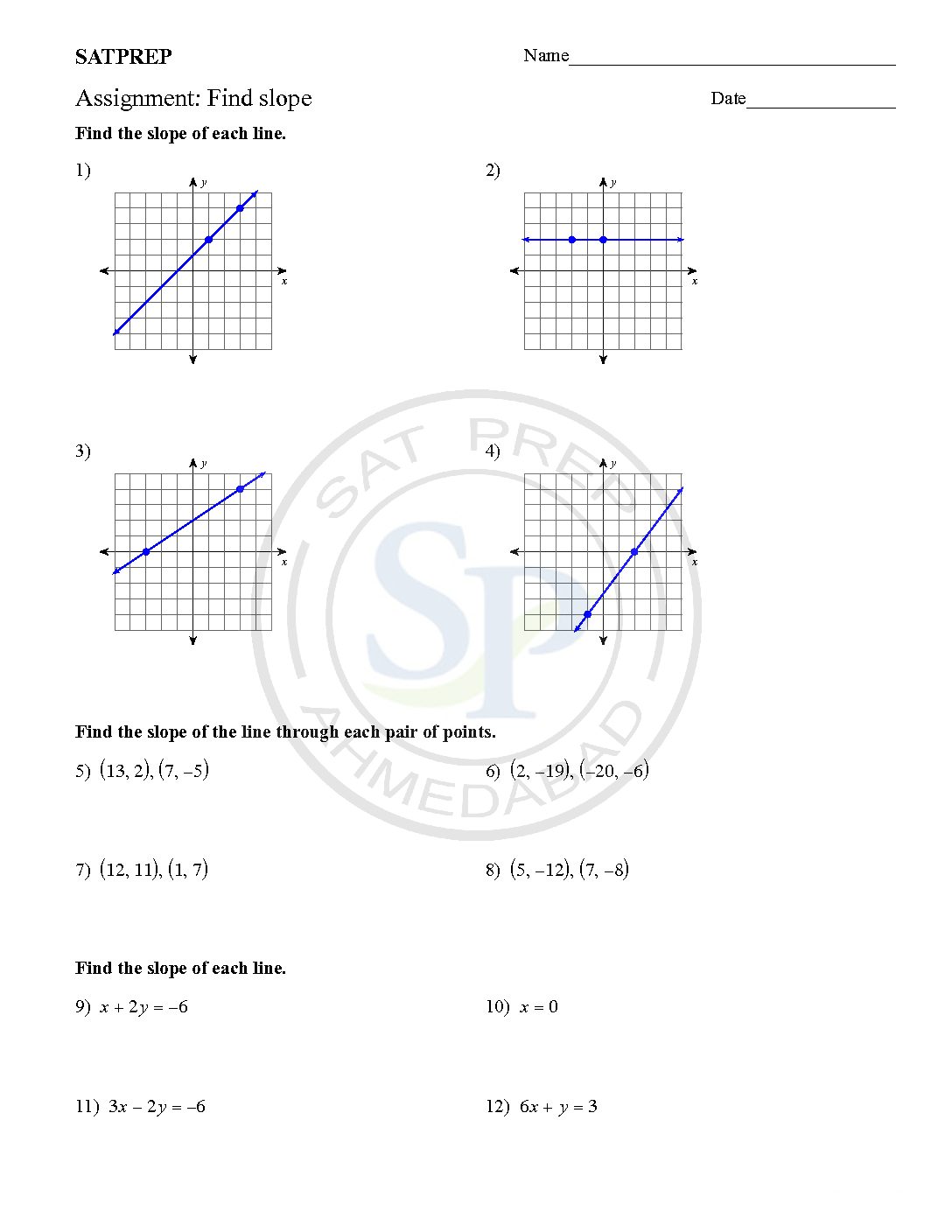
Find slope
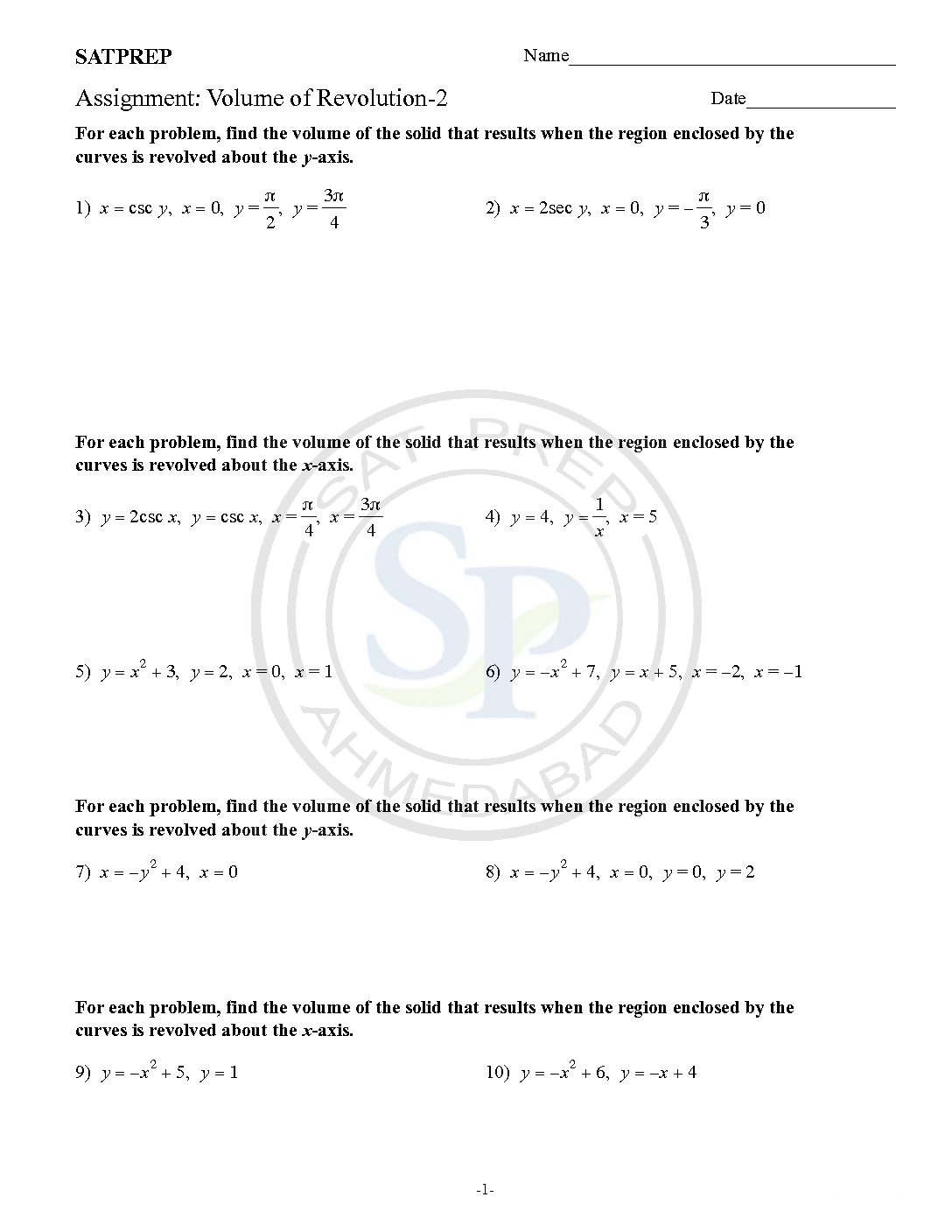
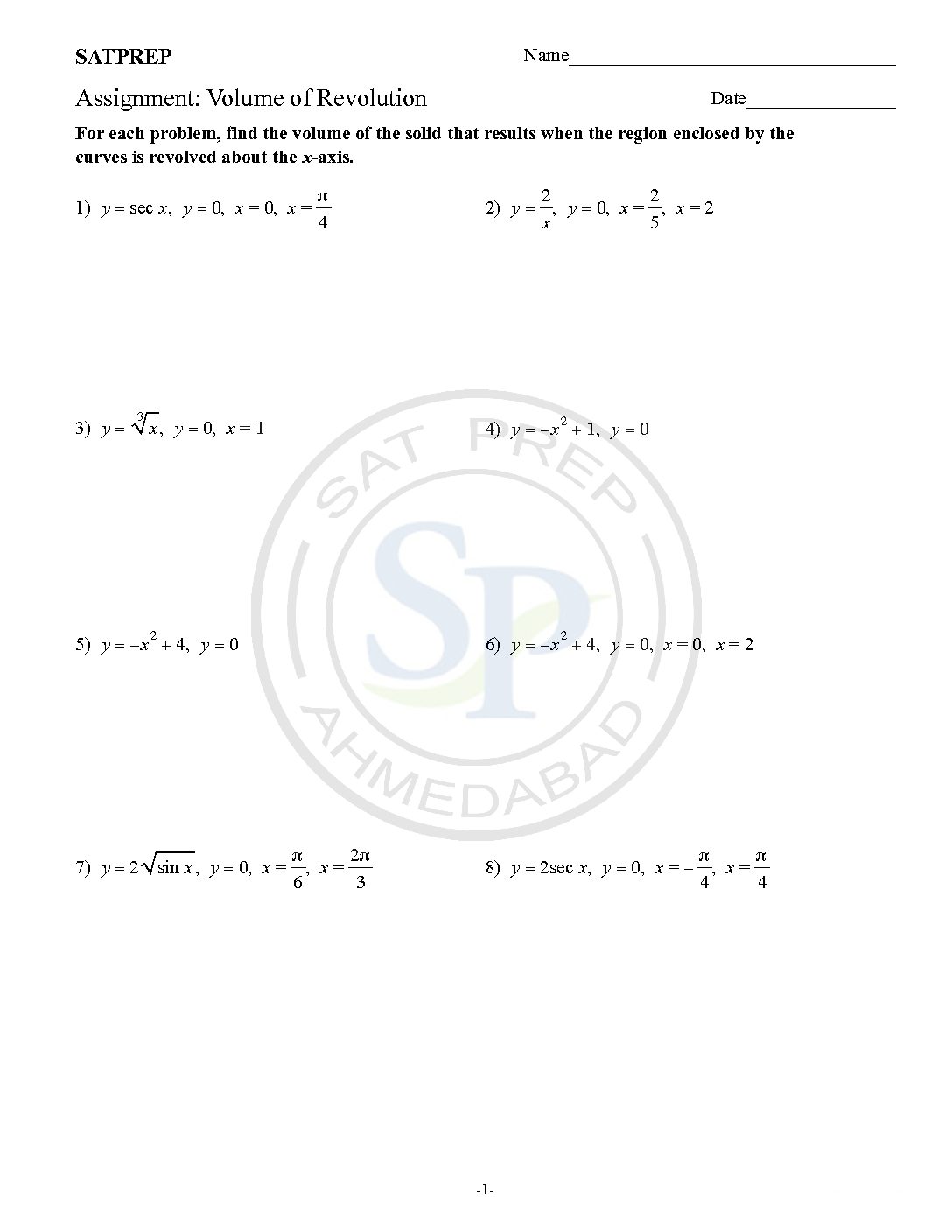
Volume of revolution of solid
Volume of revolution. To get a solid of revolution we start out with a function, y=f (x), on an interval [a,b]. We then rotate this curve about a given axis to get the surface of the solid of revolution. For purposes of this discussion let’s rotate the curve about the x -axis, although it could be any vertical […]
Volume of revolution of solid
Volume with Rings. To get a solid of revolution we start out with a function, y=f (x), on an interval [a,b]. We then rotate this curve about a given axis to get the surface of the solid of revolution. For purposes of this discussion let’s rotate the curve about the x -axis, although it could be any vertical or […]
Kinematics
Kinematic is the branch of classical mechanics. describes the motion of points, objects and systems of groups of objects, without reference to the causes of motion. The symbol a stands for the acceleration of the object. And the symbol v stands for the instantaneous velocity of the object. The derivative of displacement with time is velocity […]
Volume of revolution
To get a solid of revolution we start out with a function, y=f (x), on an interval [a,b]. We then rotate this curve about a given axis to get the surface of the solid of revolution Volume of Revolution
Equation of Tangent and Normal
Tangents to a curve are a line that touches the curve at one point and has the same slope as the curve at that point. A normal to a curve is a line perpendicular to a tangent to the curve. Tangent and Normal
Product to Sum
Product‐Sum and Sum‐Product Identities. The process of converting products into sums can make a difference . Integrate \( \int \! \sin 3x \cos 4x \, \mathrm{d}x.\) This problem may seem tough at first, but after using the product-to-sum trigonometric formula, this integral very quickly changes into a standard form . Converting a sum of trig functions into a product. Write as and then […]
Integration by trigonometric substitutio...
This post is about worksheet of Integration by trigonometric substitution. It also one of most important concept of integral calculus . The function ƒ(φ(t))φ′(t) is also integrable on [a,b] Integration by substitution
Volume
To get a solid of revolution we start out with a function, y=f (x), on an interval [a,b]. We then rotate this curve about a given axis to get the surface of the solid of revolution. volume of revolution