You are browsing archives for
Tag: A-Level
Topic wise A-Level Math Past Paper Comp...
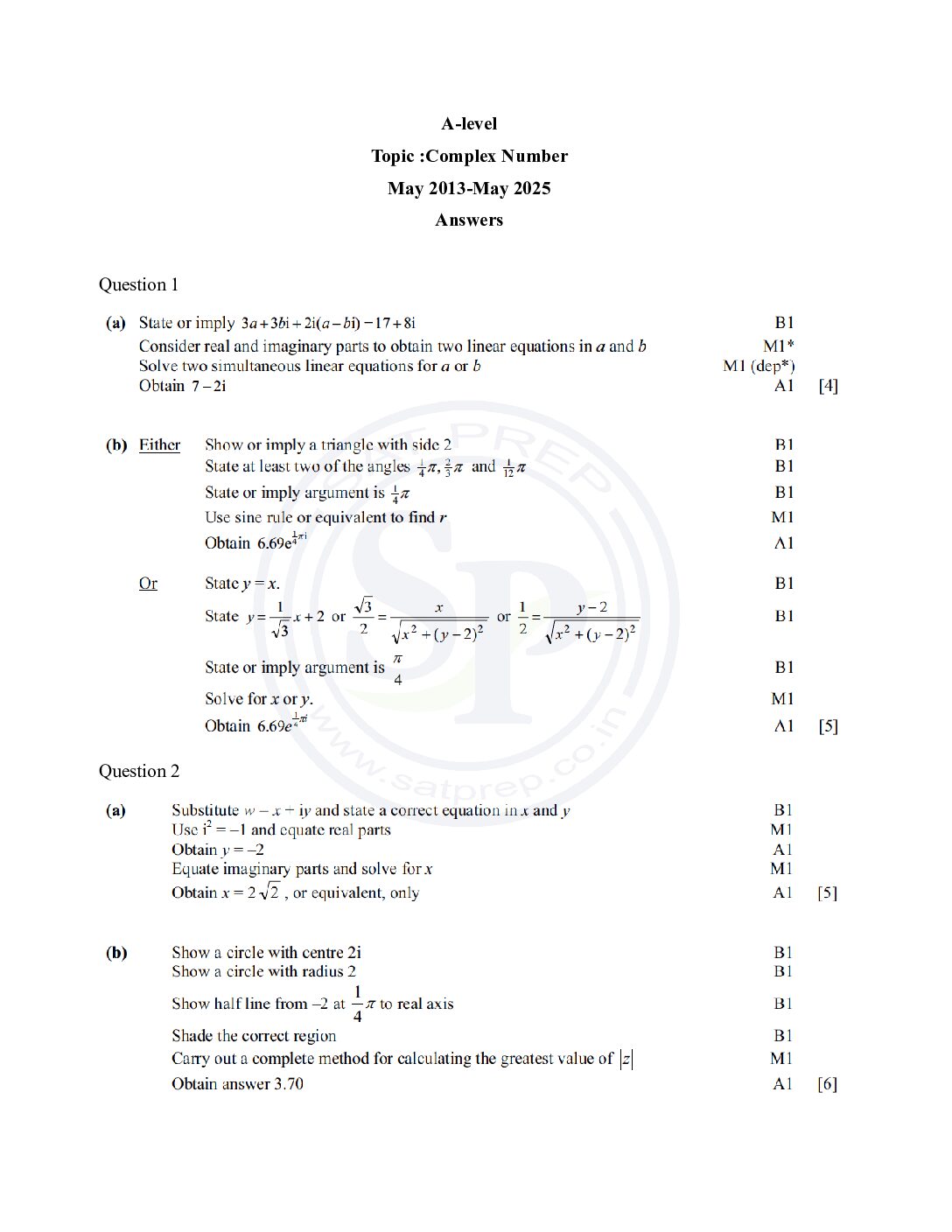
This post is about question of complex number from A-level Math past paper. In this post questions are from different paper from May 2013 to May 2025. By this post students will come to know variety of questions asked in previous year papers. The questions type in this post is calculator www.cie.org.uk
Topic wise A-Level Math Past Paper Cal...
This post is about solution of question of calculus from AS-level Math past paper. In this post questions are from different paper from May 2013 to Nov 2017. By this post students will come to know variety of questions asked in previous year papers. The questions type in this post is calculator . www.cie.org.uk
Topic wise A-Level Math Past Paper Ca...
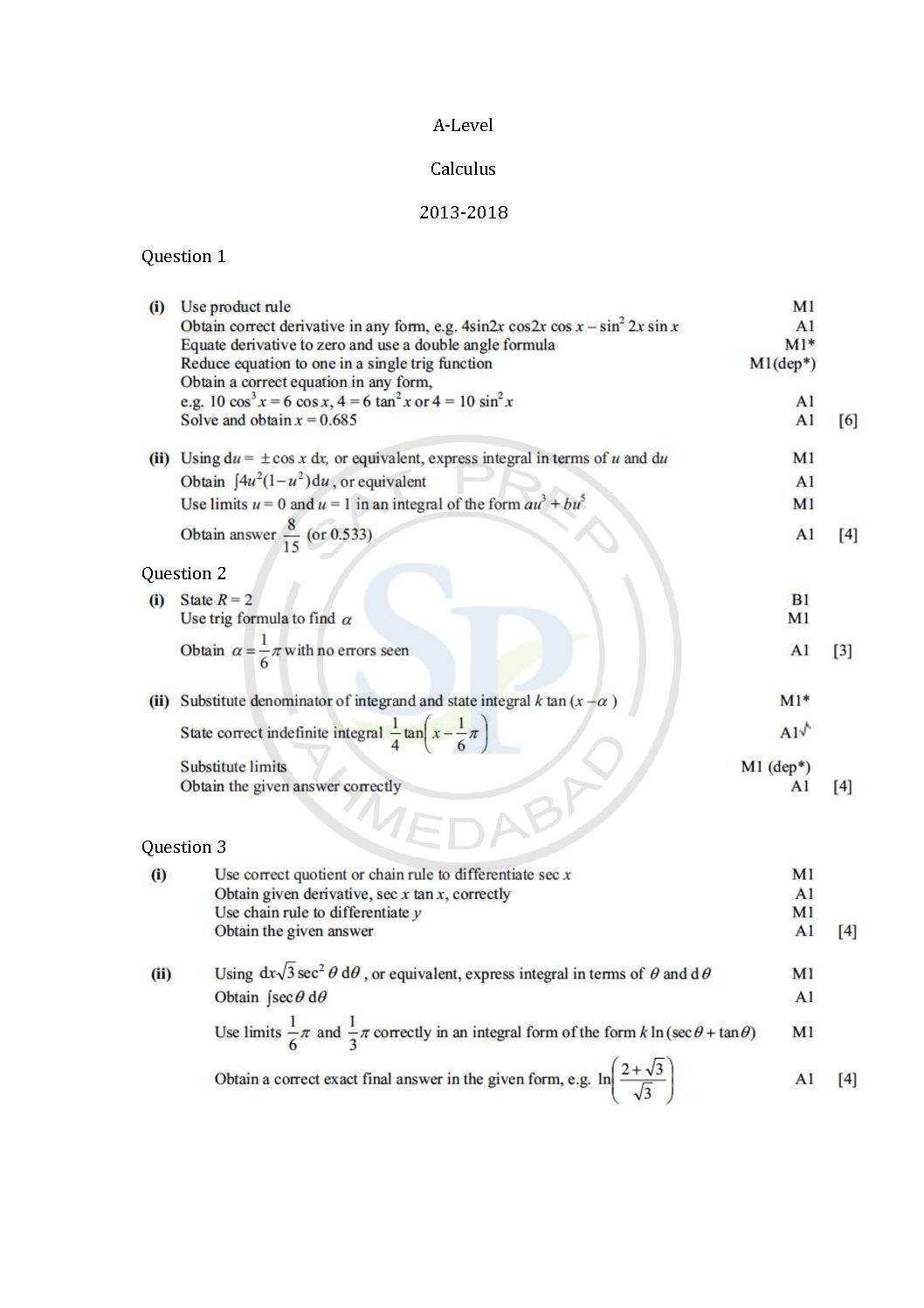
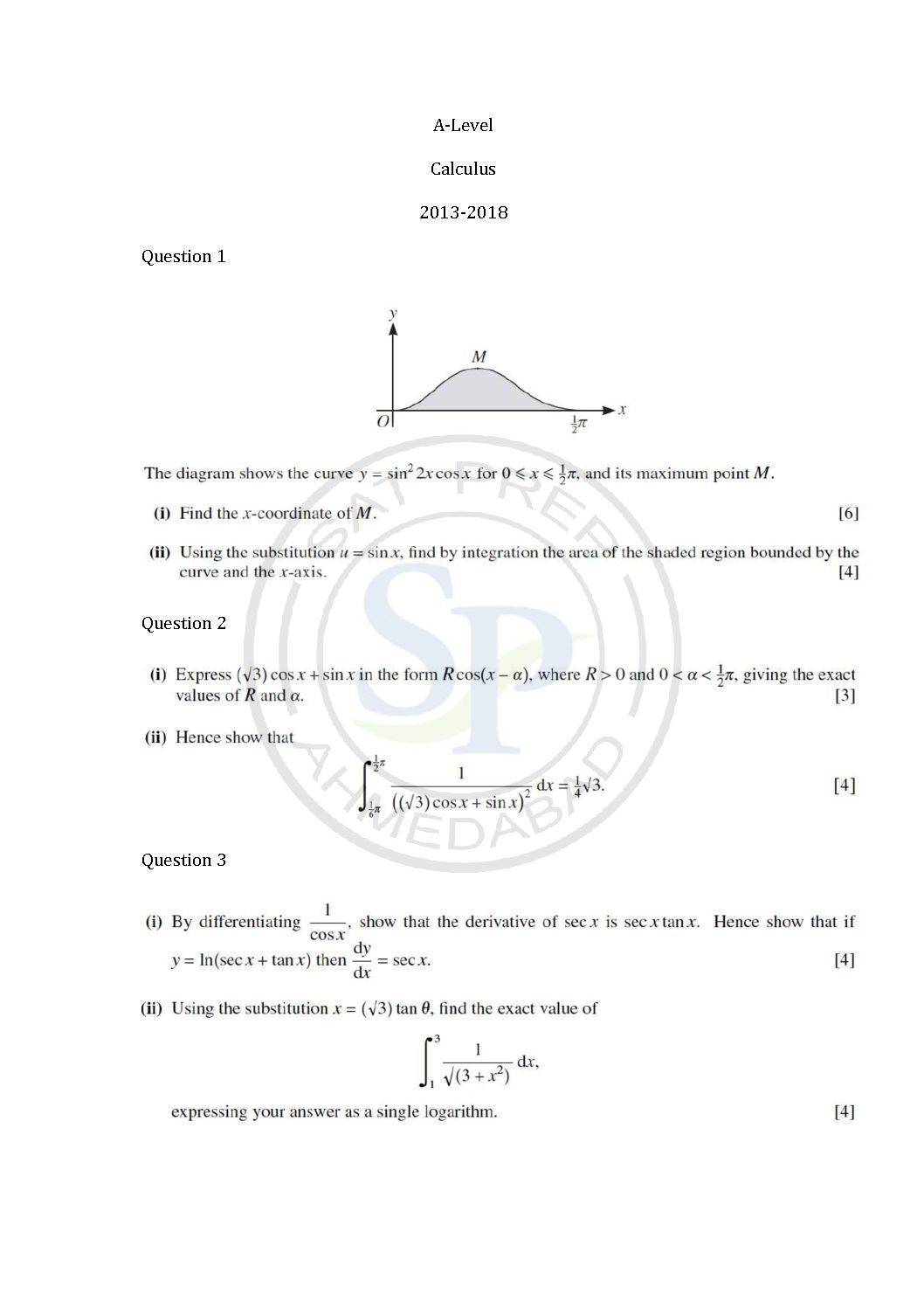
This post is about question of calculus from A-level Math past paper. In this post questions are from different paper from May 2013 to Nov 2017. By this post students will come to know variety of questions asked in previous year papers. The questions type in this post is calculator . www.cie.org.uk
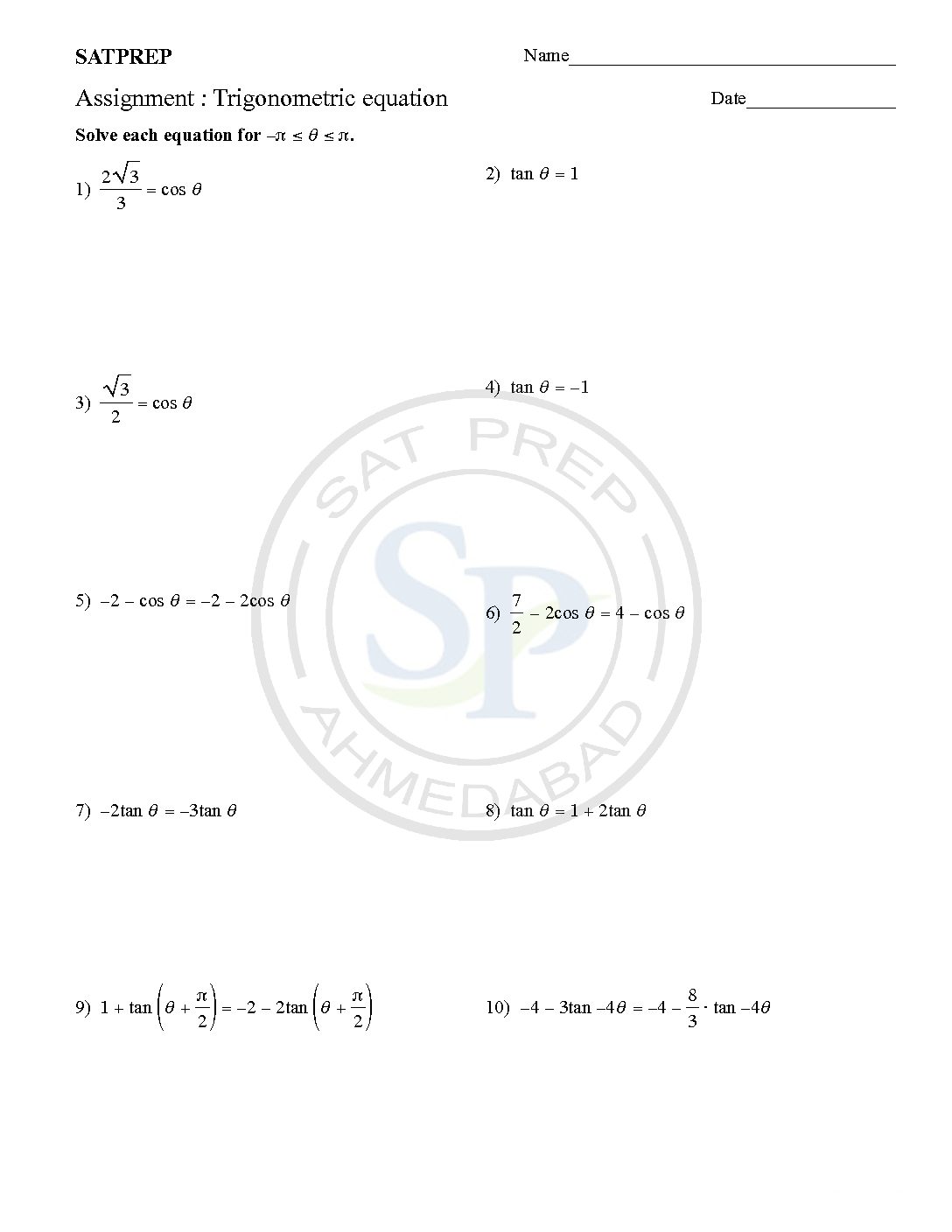
Trigonometric Equation
Solving trig equations use both the reference angles and trigonometric identities The general method of solving an equation is to convert it into the form of one ratio only. Then, using these results, hence, we can obtain solutions. Trigonometric equation
Vector and vector equation of line
The vector is direction one point to another point. The vector equation of a line is r = a + tb. In this equation, “a” represents position vector and “b” represents a direction vector of the line. Moreover “r” represents the vector of any general point on the line and “t” is constant. Hence it is similar to equation of line vector
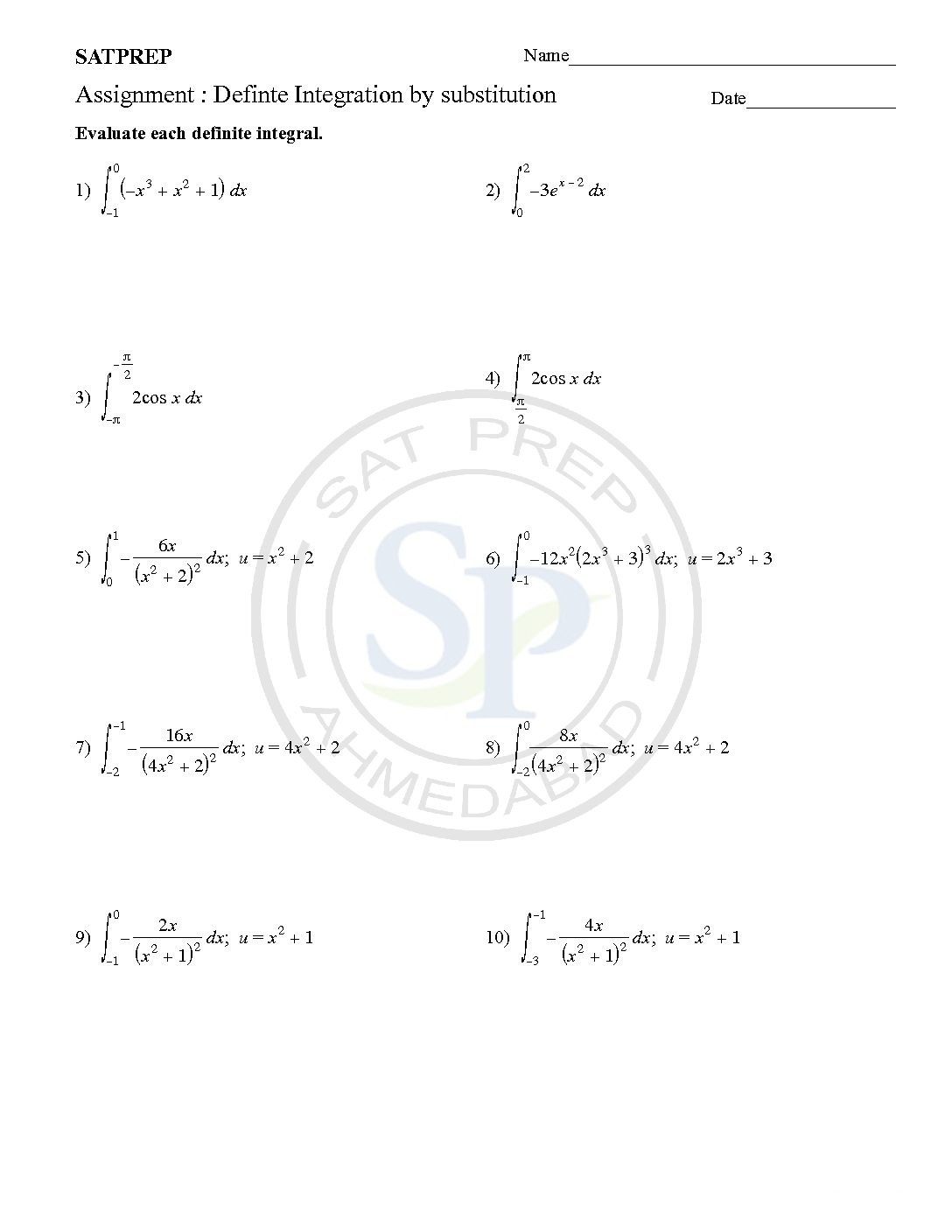
Definite integration
A Definite Integral has start and end values. In other words there is an interval [a, b]. Hence , definite integral gives particular solution. Definite Integration
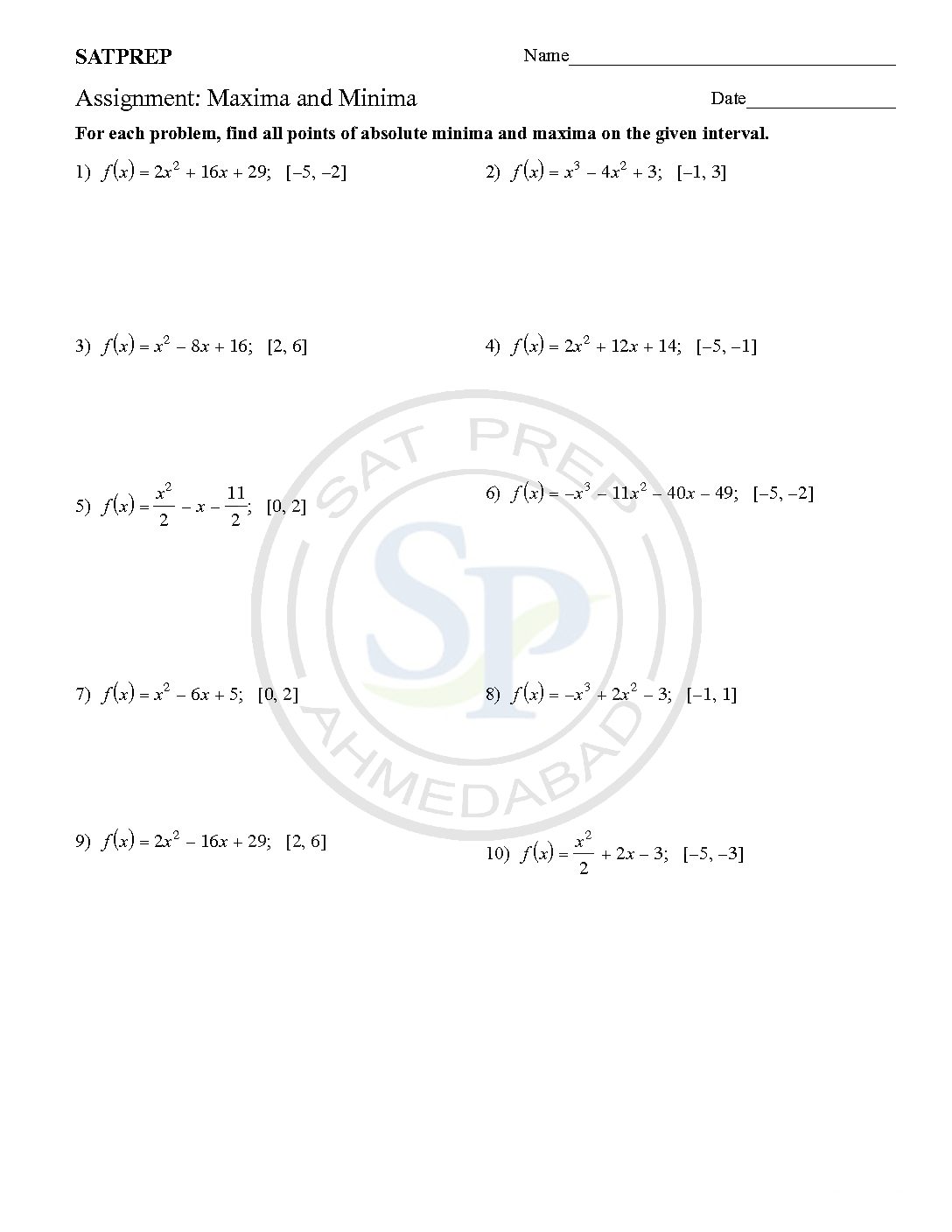
Maxima and minima
Maximum and Minima of Points of Inflection. The value f ‘(x) is the gradient at any point but often we want to find the Turning or Stationary Point (Maximum and Minimum points) or Point of Inflection These happen where the gradient is zero, f ‘(x) = 0. Critical Points include Turning points and Points where f ‘ (x) does not exist. […]
Equation of Tangent and Normal
A tangent to a curves are a line that touches the curve at one point and has the same slope as the curve at that point. A normal to a curve is a line perpendicular to a tangent to the curve. Tangent and normal
Rules of derivative
Rule for derivatives. Rules for derivatives. Sum rule: The derivative of the sum or difference of two functions is the sum or difference of their derivatives. (u + v)’ = u’ + v’ Constant multiple: The derivative of a constant times a function is the constant times the derivative of the function. (ku)’ = ku’ Rules of derivative