Differentiable functions of one variable is a function whose derivative exists at each point in its domain. Also function is differentiable at a point if it has a derivative there. Therefore function also continuous in given domain. Differentiable_function
You are browsing archives for
Tag: AP Calculus
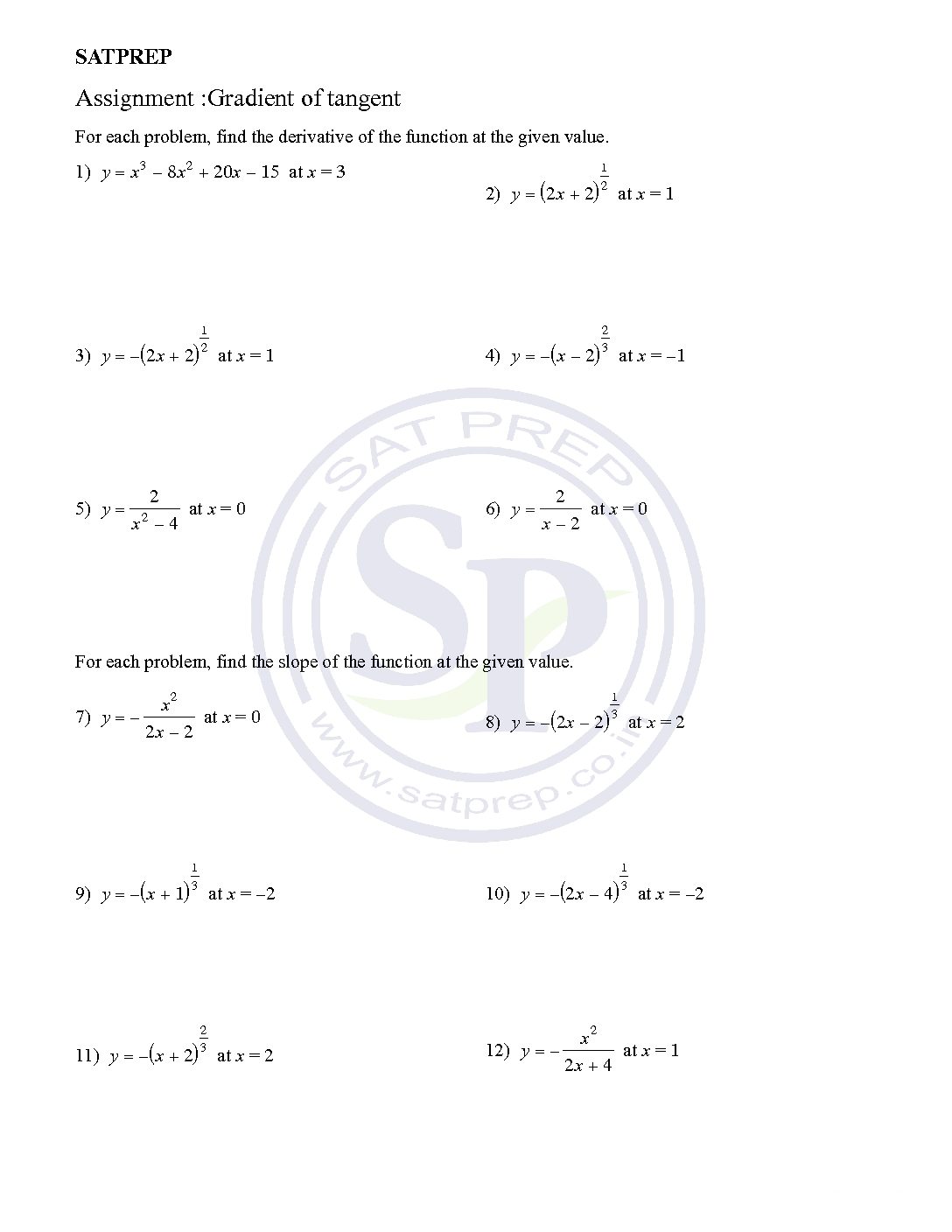
Gradient of tangent
At a given point on a curve, the gradient of the curve is equal to the gradient of the tangent to the curve. The derivative (or gradient function) describes the gradient of a curve at any point on the curve. Similarly, it also describes the gradient of a tangent to a curve at any point […]
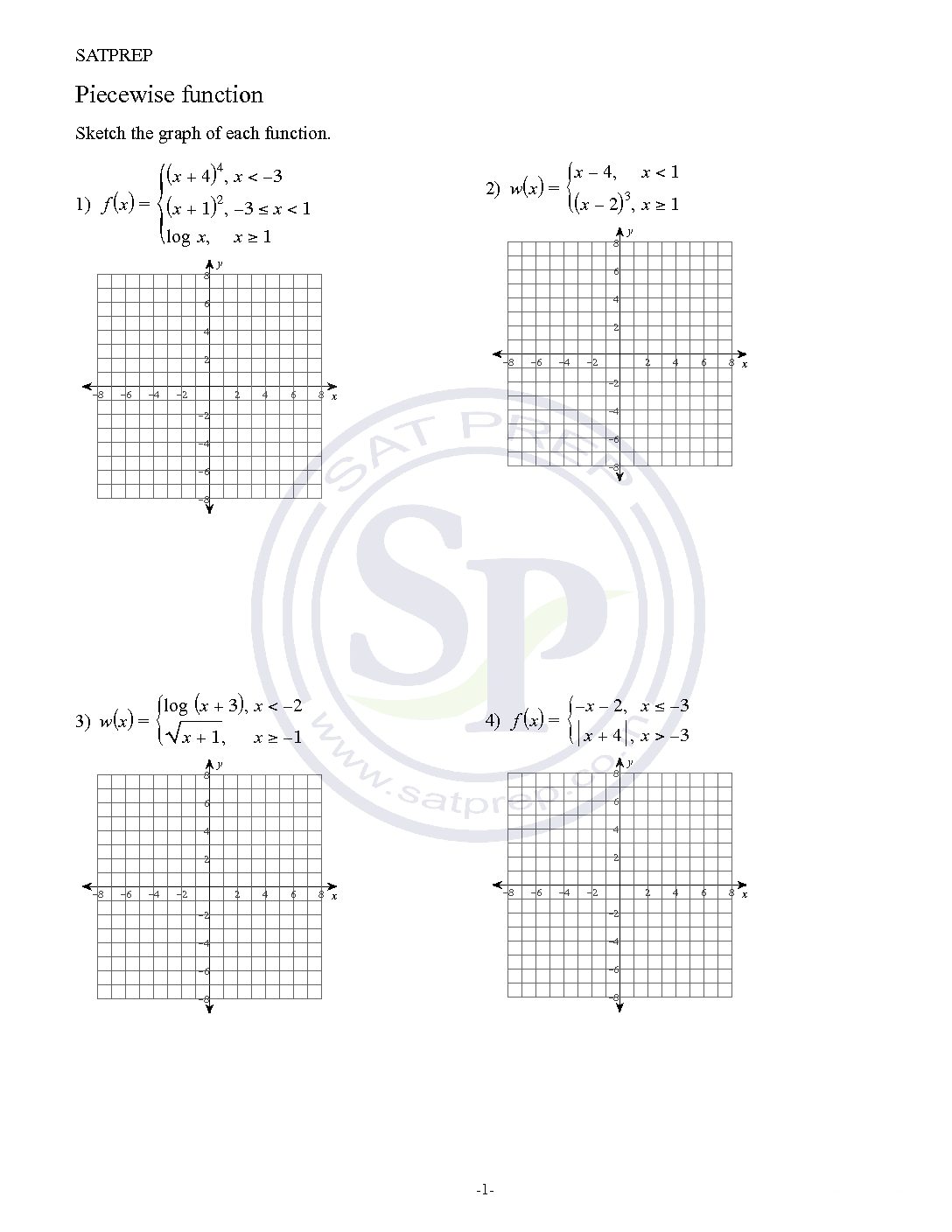
Piecewise Function
Functions that behave differently based on the input (x) value. Piecewise Function. A function made up of 3 pieces as well as two pieces. Hence in some case piecewise function give discontinuous graph. Piecewise
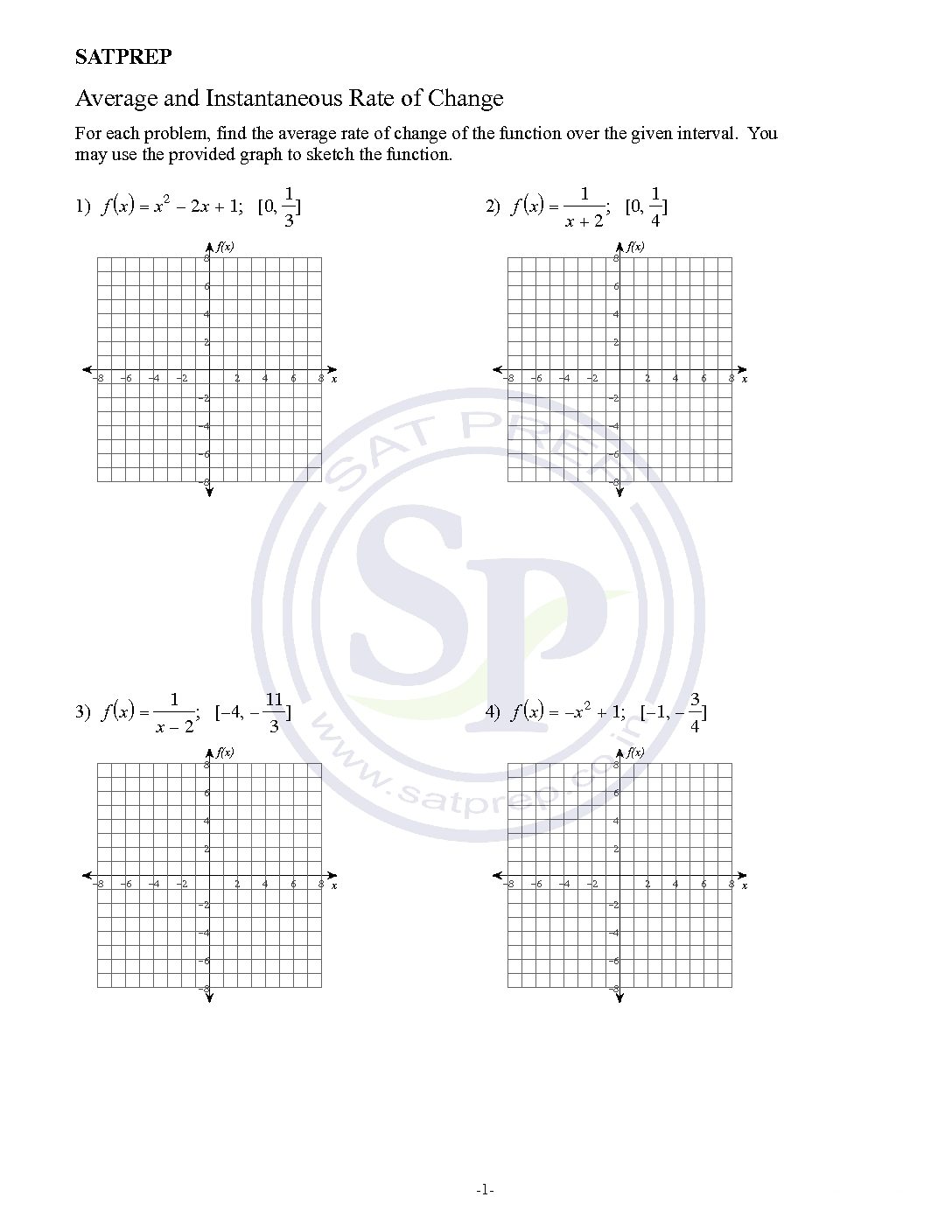
Average and Instantaneous rate of change
Average rate of change of a function f(x) on an interval [a,b] is the slope of the secant line . The instantaneous rate of change of f(x) at x=a is the slope of the tangent line. Therefore the slope of the line measures the average rate of change of the function and can be found from any two points on […]
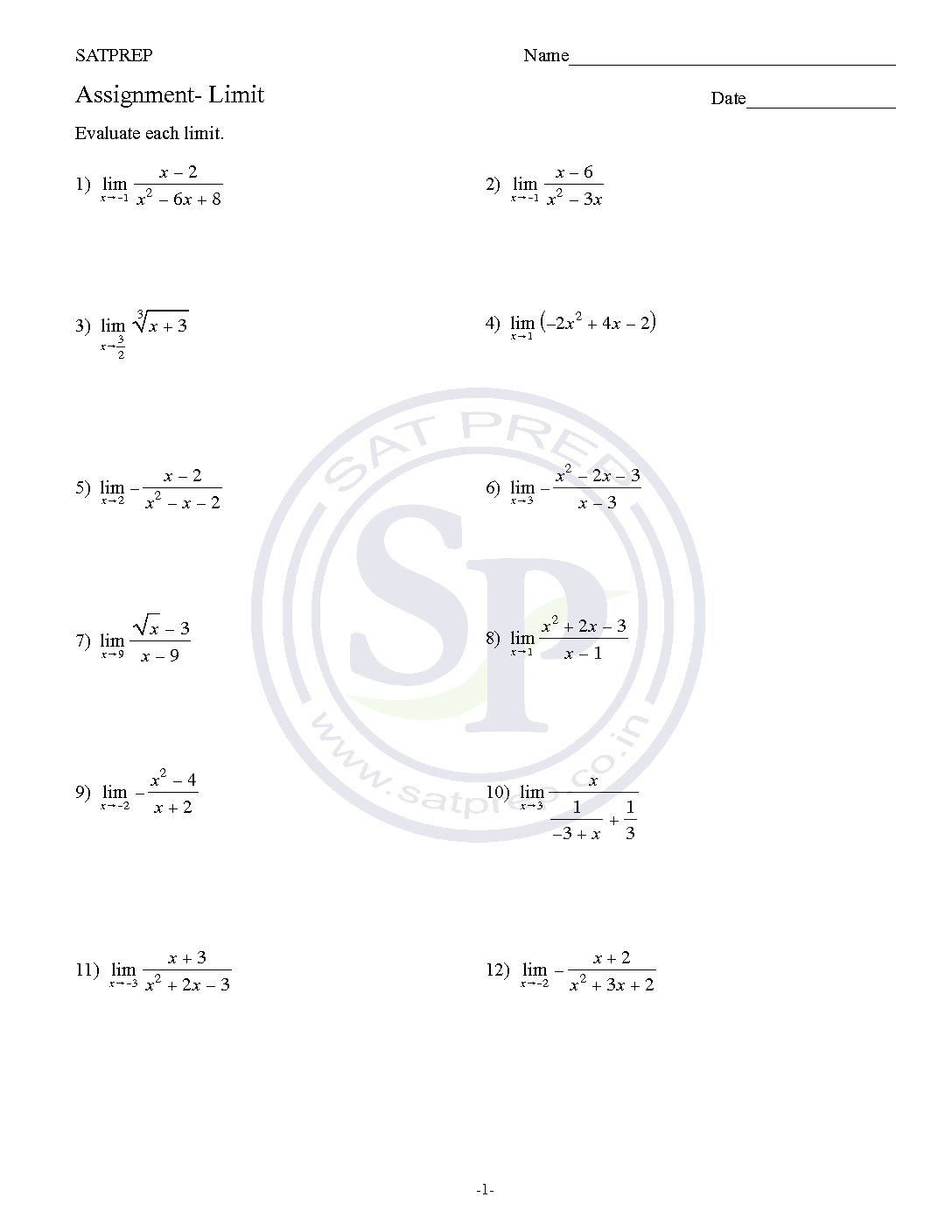
Limits
limit is the value that a function (or sequence) “approaches” as the input (or index) “approaches” some value. Limits describe how a function behaves near a point, instead of at that point. Limit
Differentiation formulae
The Basic Differentiation rules. This include the constant rule, power rule. also include sum rule, difference rule , Product Rule and Quotient Rule. Consequently rule these rule applicable on two different functions. Differentiation rule
Parametric and Polar Equation
Parametric and Polar Equations , a function with two variables, x and y. In some cases, though it is useful to introduce a third variable, called a parameter, and express x and y in terms of the parameter. Polar equations ,work. Coordinates in polar equations are of the form (r,θ), where r represents radius and θ represents angle. Hence both are same type […]
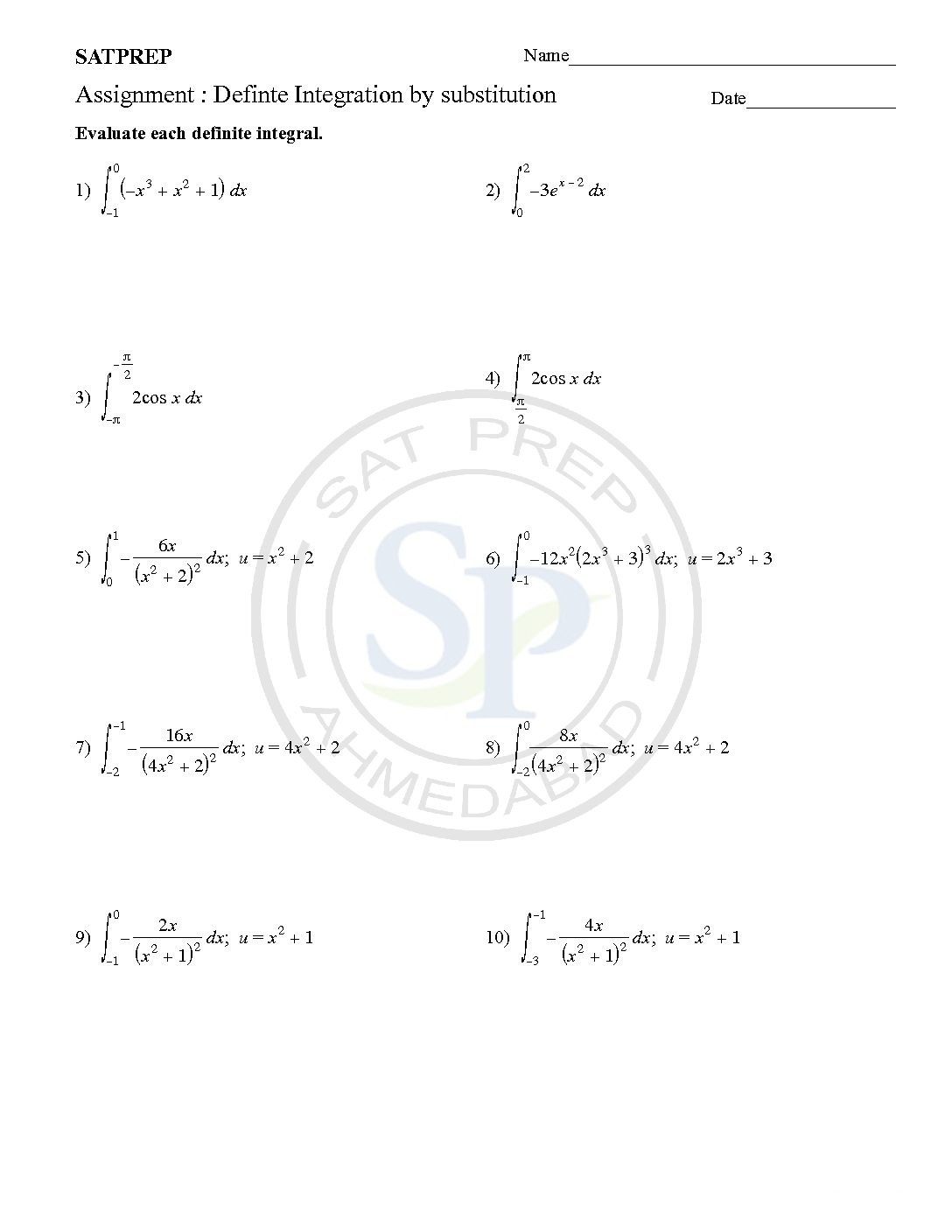
Definite integration
A Definite Integral has start and end values. In other words there is an interval [a, b]. Hence , definite integral gives particular solution. Definite Integration
Equation of Tangent and Normal
A tangent to a curves are a line that touches the curve at one point and has the same slope as the curve at that point. A normal to a curve is a line perpendicular to a tangent to the curve. Tangent and normal
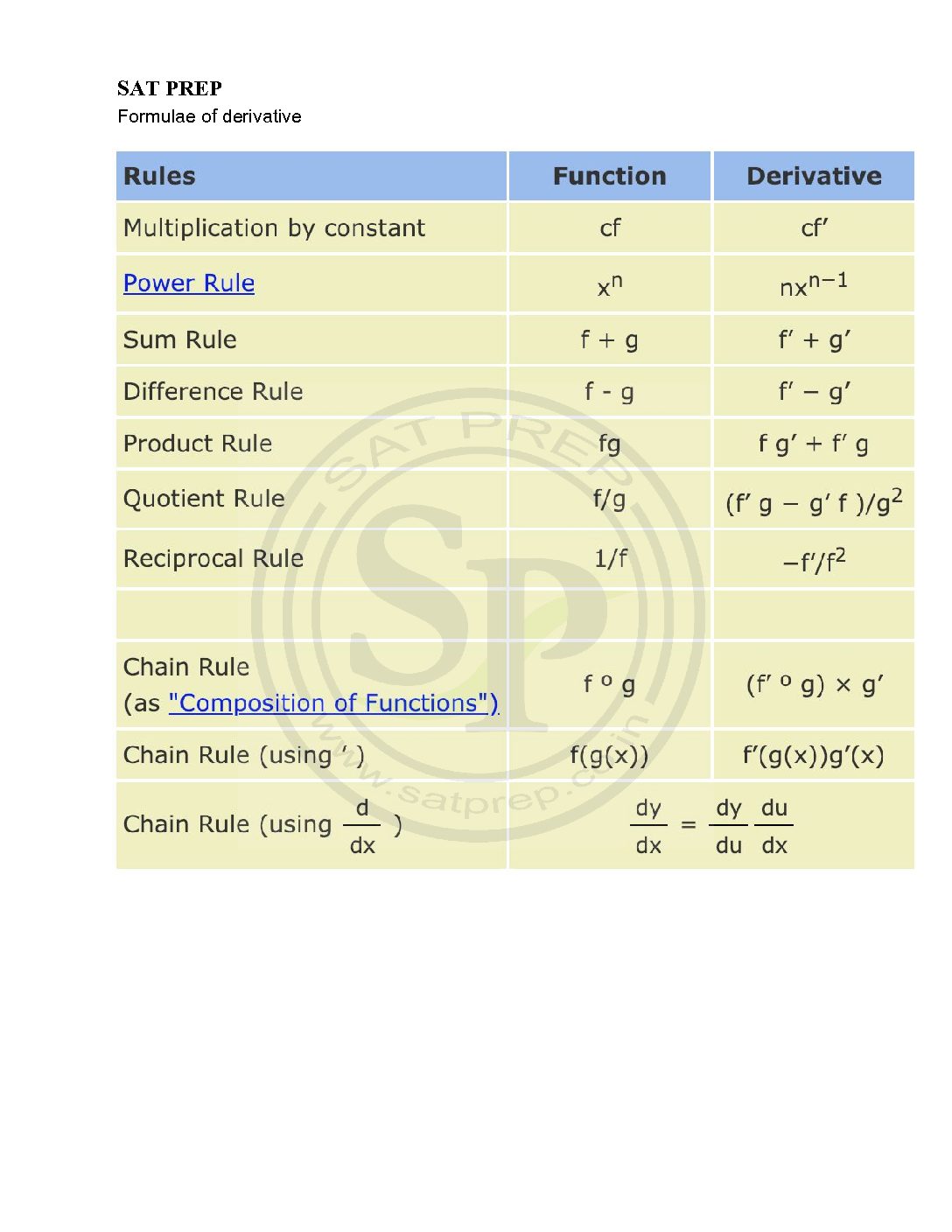
Rules of derivative
Rule for derivatives. Rules for derivatives. Sum rule: The derivative of the sum or difference of two functions is the sum or difference of their derivatives. (u + v)’ = u’ + v’ Constant multiple: The derivative of a constant times a function is the constant times the derivative of the function. (ku)’ = ku’ Rules of derivative