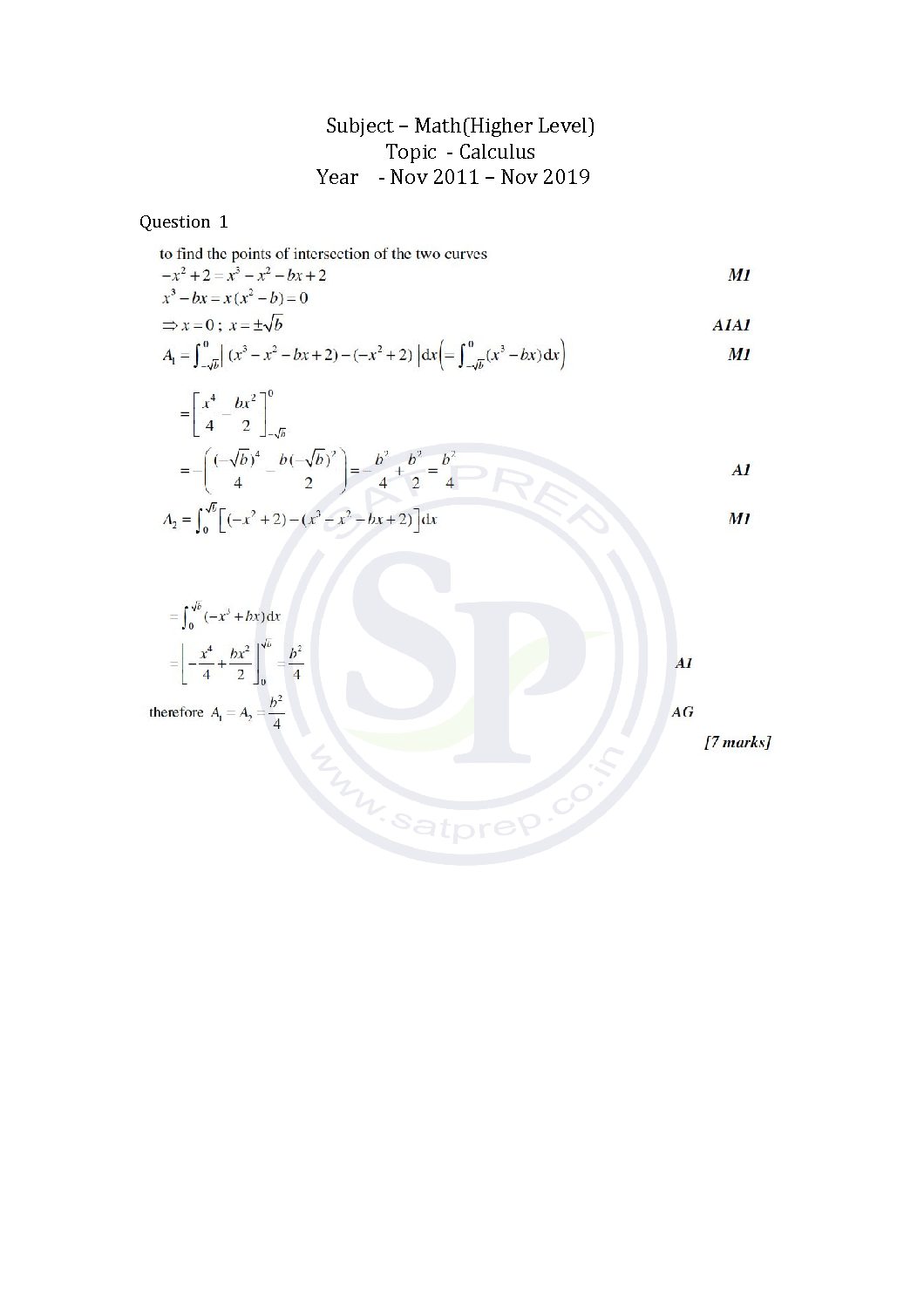
This post is about the solutions of questions of calculus from Math HL Paper -1 past paper. In this post questions are from different paper from Nov 2011 to Nov 2019. By this post students will come to know variety of questions asked in previous year papers. www.ibo.org
You are browsing archives for
Tag: Calculus
Definite integration
A Definite Integral has start and end values. In other words there is an interval [a, b]. Hence , definite integral gives particular solution. Definite Integration
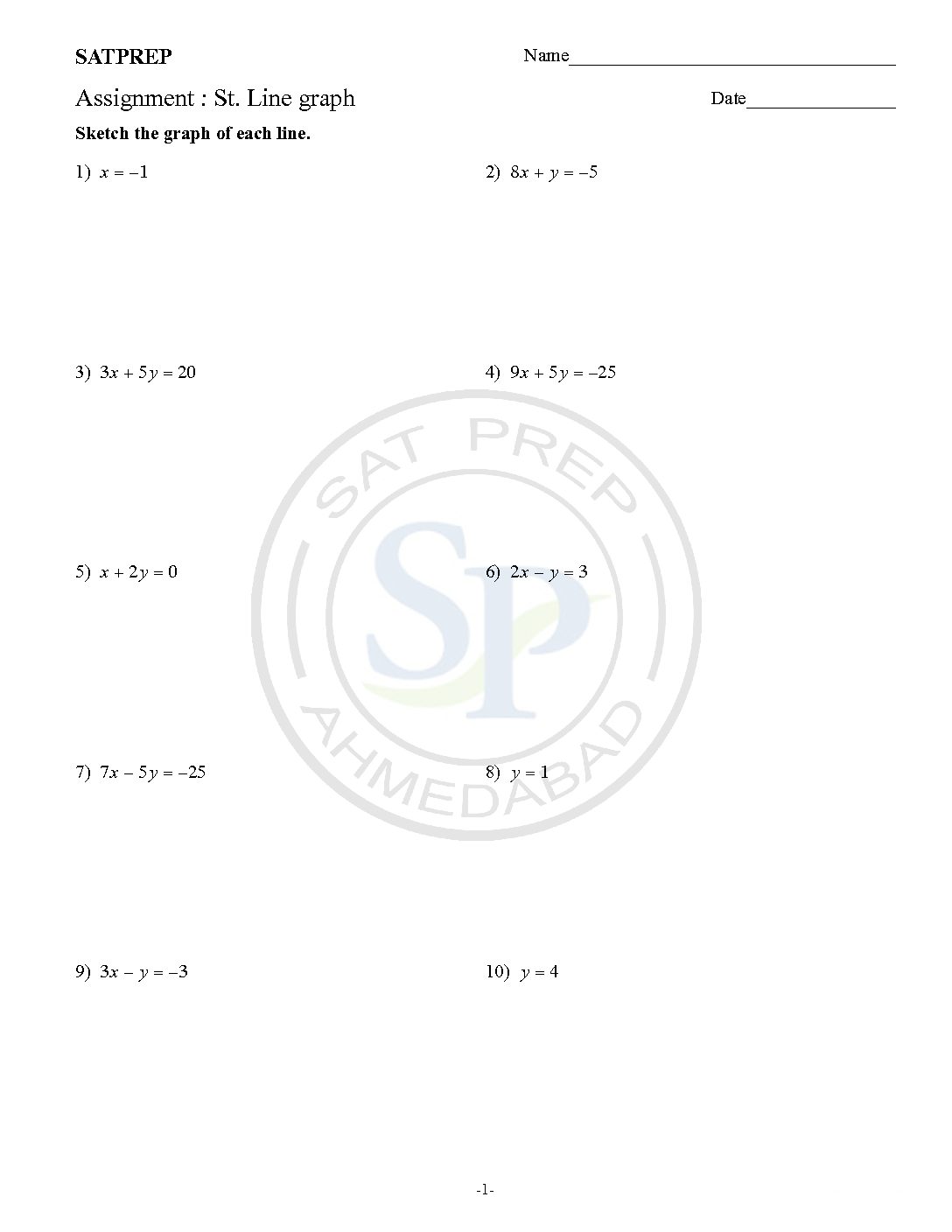
St. Line Graph
Straight line graphs. The graph of each of equations is a straight line: If an equation can be rearranged into the form y = mx +c, then its graph will be a straight line. ax +by= c can be rearranged as (which can be re-written as y = mx+c). Therefore vertical lines have equations have slope undefined form x =k . Hence graph depend on […]
Area Under the Curve
This post about Area under a Curve. The area between the graph of y = f ( x ) and the x -axis is given by the definite integral. This formula gives a positive result for a graph above the x -axis, and a negative result for a graph below the x -axis. Because of enclosed region by limit. Hence , we use definite integration. Similarly for volume […]
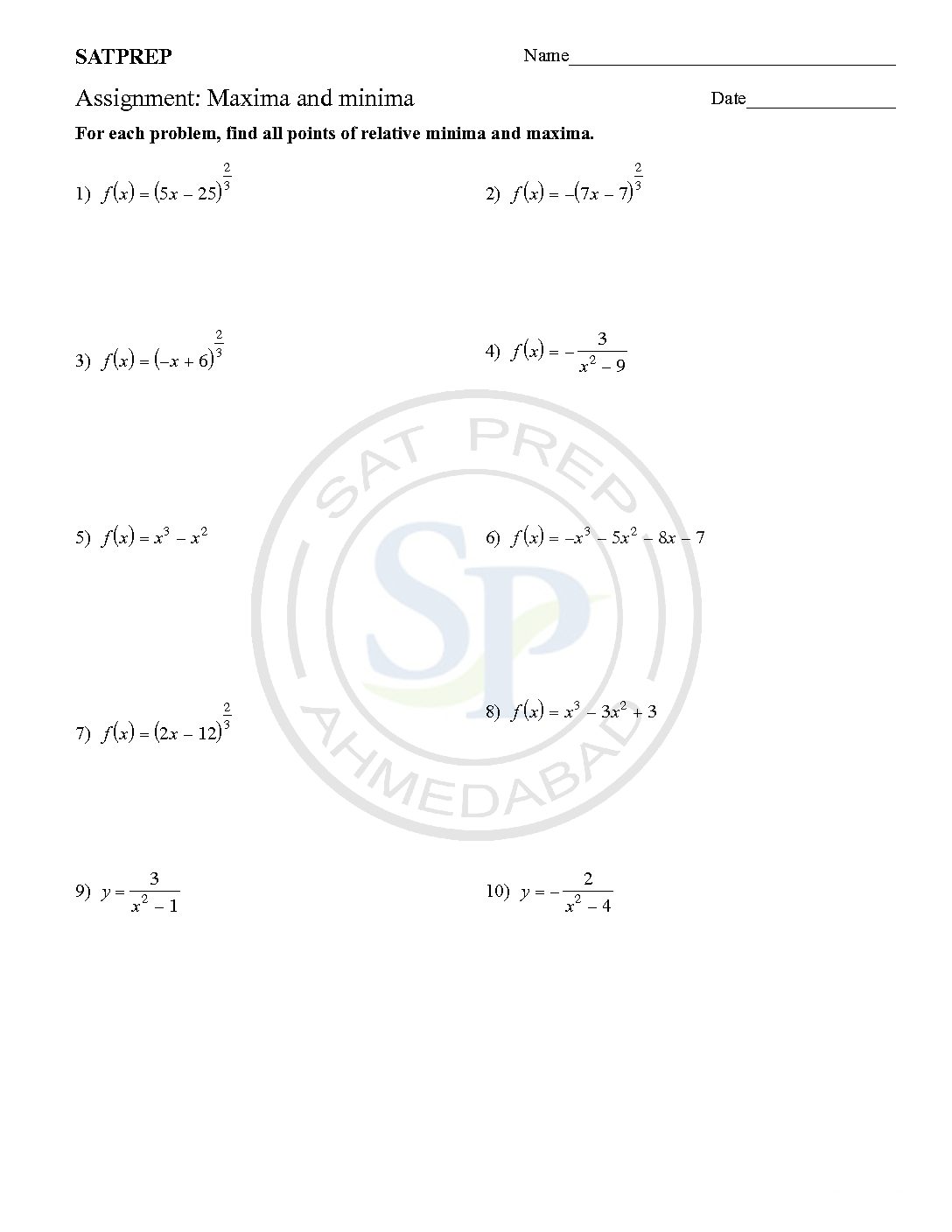
Maxima and Minima
Maximum and minimum of Points of Inflection. The value f ‘(x) is the gradient at any point but often we want to find the Turning or Stationary Point (Maximum and Minimum points) or Point of Inflection These happen where the gradient is zero, f ‘(x) = 0. Critical Points include Turning points and Points where f ‘ (x) does […]
Equation of Tangent and Normal
Tangents to a curve are a line that touches the curve at one point and has the same slope as the curve at that point. A normal to a curve is a line perpendicular to a tangent to the curve. Tangent and Normal
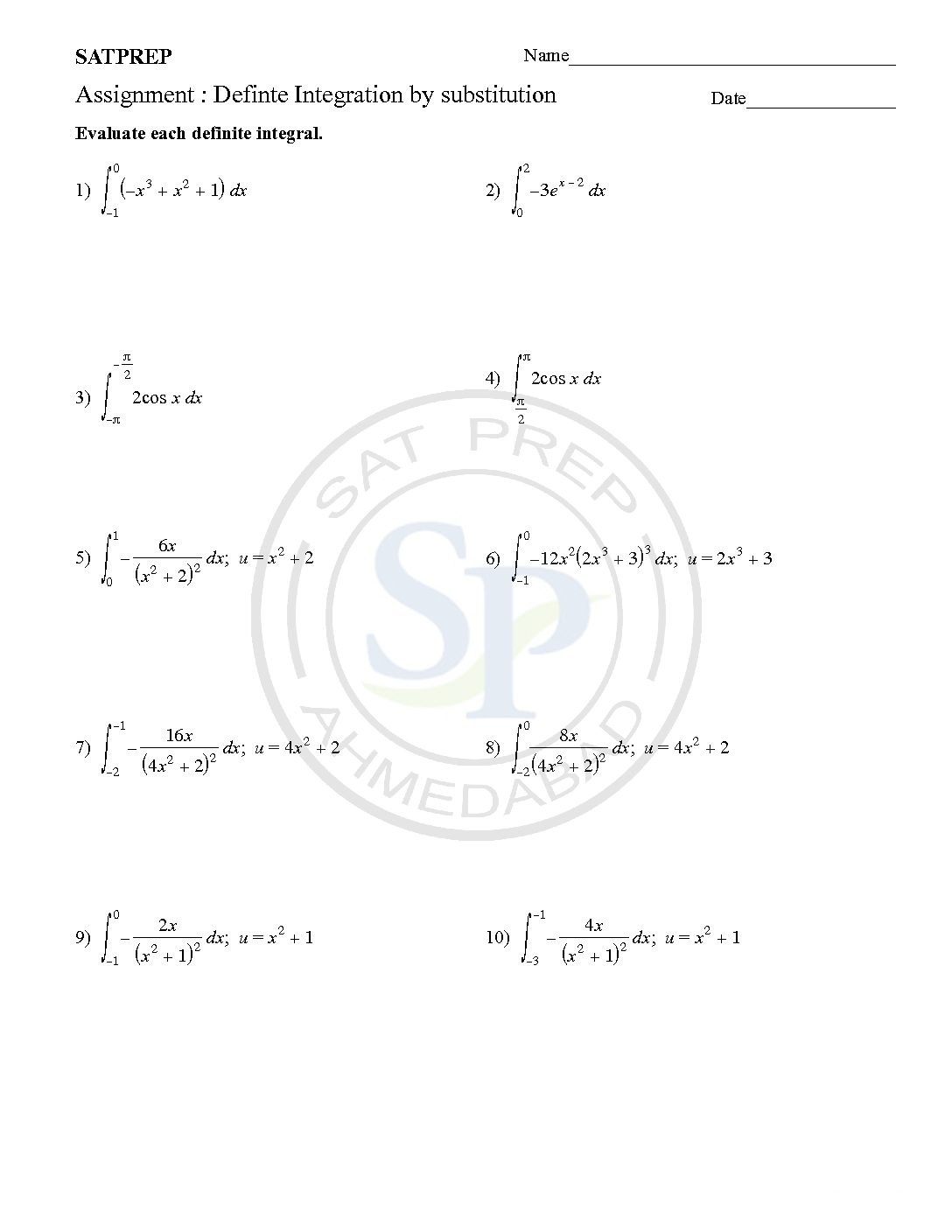
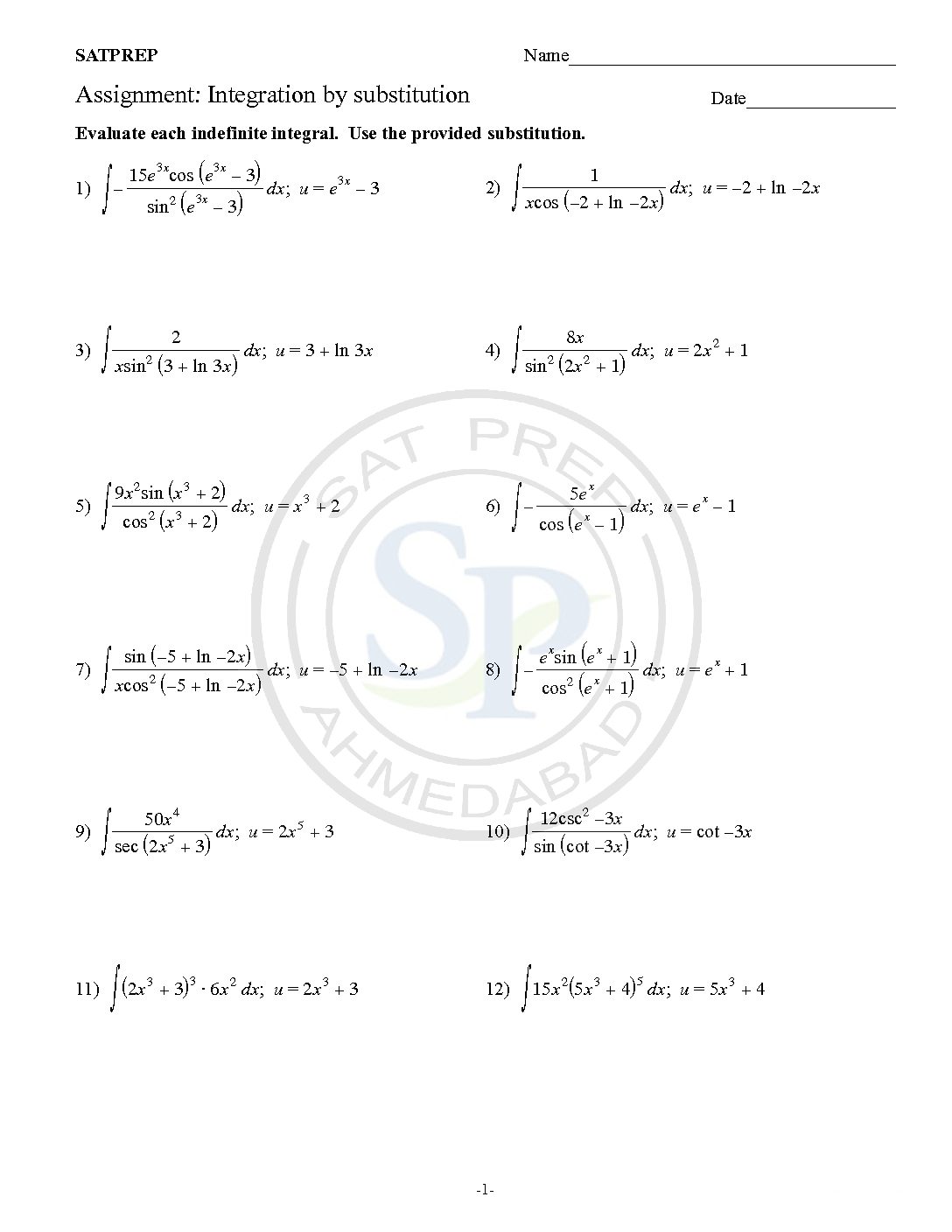
Integration by Substitution-5
This post is about worksheet of integration by substitutions. It also one of most important concept of integral calculus . The function ƒ(φ(t))φ′(t) is also integrable on [a,b] Integration by substitution
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
FTC(Fundamental theorem calculus). If we define an area function, F (x), as the area under the curve y=f (t) from t=0 to t=x, then the area function in this case is F (x)=c∗x. We would like to be able to evaluate more integrals with a process like this, The fundamental theorem of calculus tells us that if f is […]
Calculus
This formula sheet help the students for preparing precalculus and calculus. Further this sheet also help in academic math. This can also be use in Pre-calculus. Calculus
AP Calculus formula sheet
This formula sheet help the students for preparing AP calculus. Further this sheet also help for Optional Calculus of IBDP Math(HL) AP Calculus