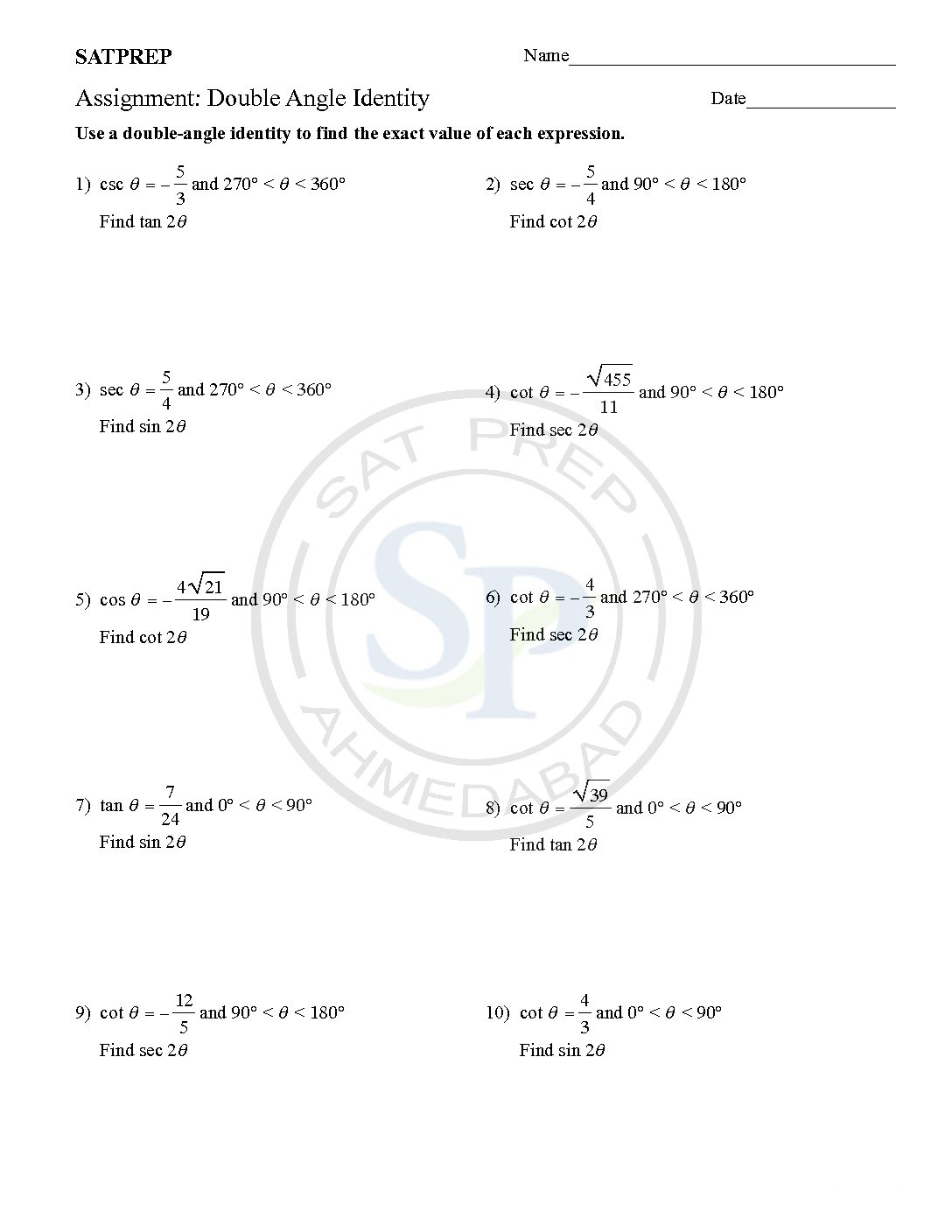
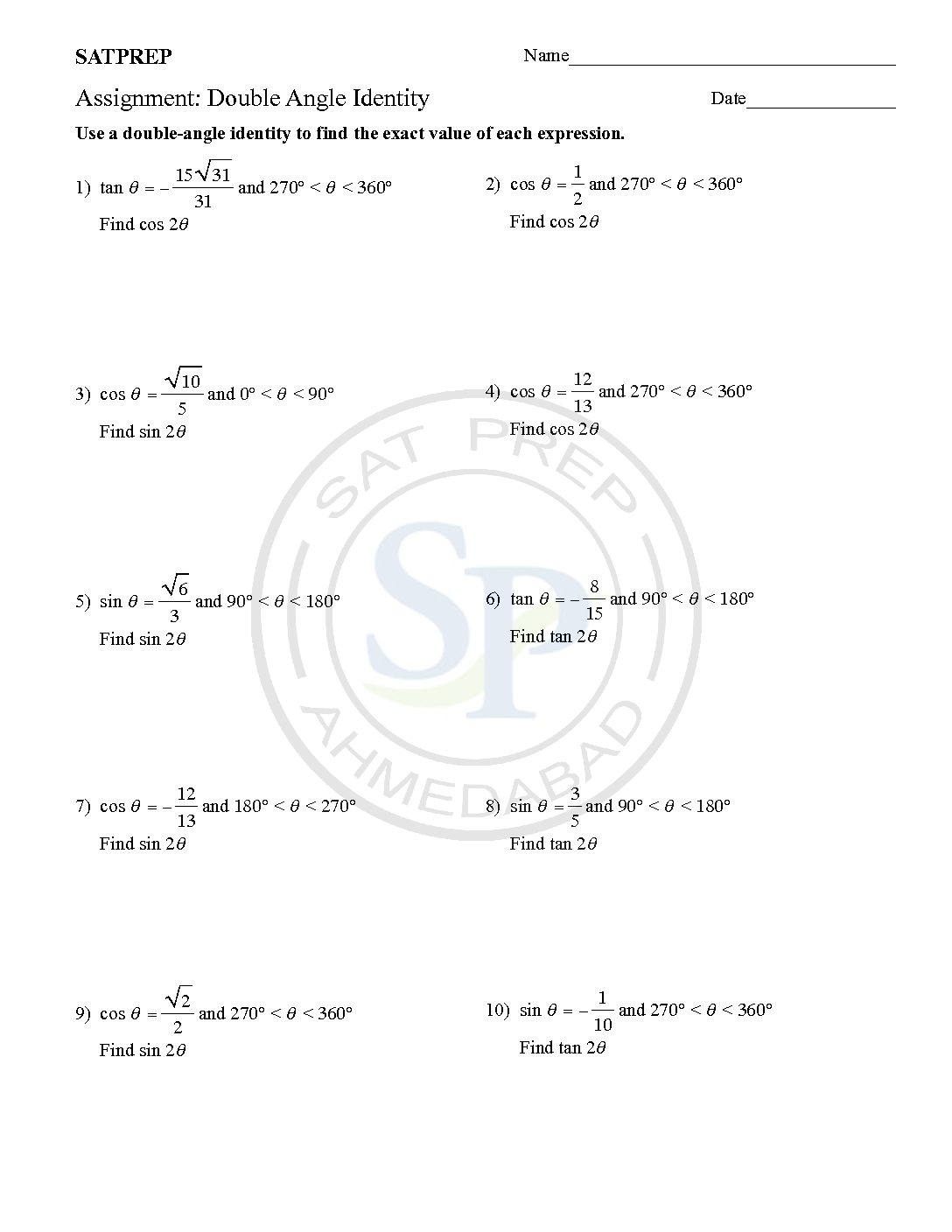
Double angle equations are allowing the expression of trigonometric functions of angles equal to 2u in terms of u. The double angle formulas can simplify the functions and gives ease to perform more complex calculations. The double angle formulas are useful for finding the values of unknown trigonometric functions. Therefore in double angle equation we need to consider two rotation. […]
You are browsing archives for
Tag: IBDP
Normal Distribution
A standard Normal Distribution graph is “Bell Curve”.The standard normal distribution has two parameters: mean and standard deviation. Hence it use for continuous random variable as well as it use for continuous values. Due to continuous values we use area under the curve for calculating probability. Normal
A Double angles identity
A Double angles identity is written2θ, for example, as sin 2θ, cos 2α, or tan 2x, where 2θ, 2α, and 2x. The angle measures and the assumption is that you mean sin(2θ), cos(2α), or tan(2x). Because tangent is equal to the ratio of sine and cosine . Therefor its identity comes from their double-angle identities. double angle identity
Double Angle trigonometric Identity
A Double angles identity is written2θ, for example, as sin 2θ, cos 2α, or tan 2x, where 2θ, 2α, and 2x. The angle measures and the assumption is that you mean sin(2θ), cos(2α), or tan(2x). Because tangent is equal to the ratio of sine and cosine . Therefor its identity comes from their double-angle identities. Double angle
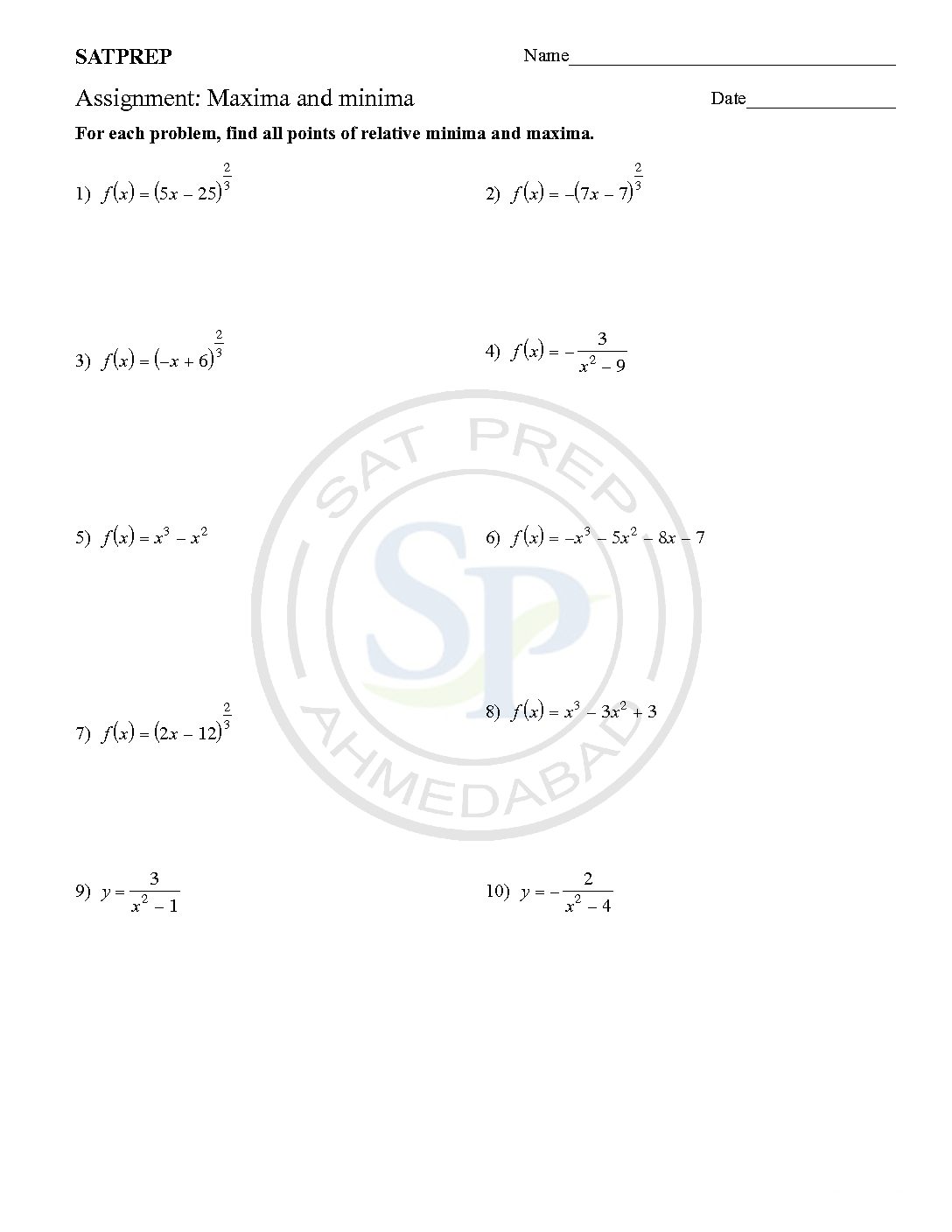
Maxima and Minima
Maximum and minimum of Points of Inflection. The value f ‘(x) is the gradient at any point but often we want to find the Turning or Stationary Point (Maximum and Minimum points) or Point of Inflection These happen where the gradient is zero, f ‘(x) = 0. Critical Points include Turning points and Points where f ‘ (x) does […]
Derivative of implicit and inverse trigo...
In calculus, a methods of implicit differentiation, Makes use of the chain rule to differentiate implicitly defined functions. To differentiate an implicit function y ( x ), defined by an equation R ( x, y) = 0, it is not generally possible to solve it explicitly for y and then differentiate. The derivatives of inverse trig functions we’ll need the formula from the last section […]
Trigonometric Equation
Solving trigonometric equations use both the reference angles and trigonometric identities The general method of solving an equation is to convert it into the form of one ratio only. Then, using these results, hence, we can obtain solutions. Trigonometric Equation
Integration of Polynomials
In integration the power of polynomials increase like quadratic become cubic etc. As well as get integration constant . It always give general solution due to integration constant. Integration
Integration by Parts
By parts apply for integration when different functions are in product form . As well as one derivative of another. By parts
Integration (Basic)
Integration is summation of function. Integration is a way of adding functions to find the sum of functions, also we find equation of curve. As well as Applications are area under the curve and volume. It can be used to find areas, volumes, central points and many useful things. it help you practice by showing you […]