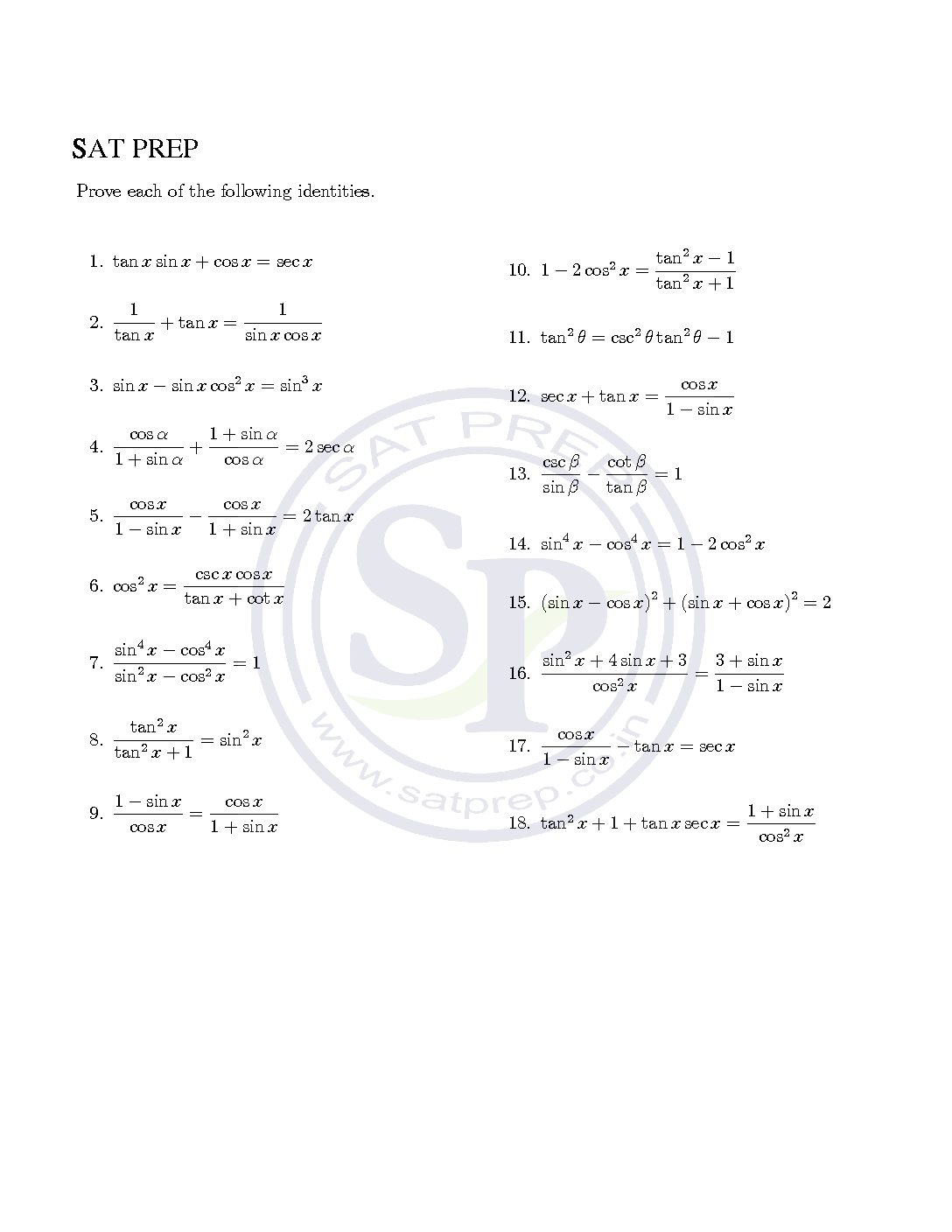
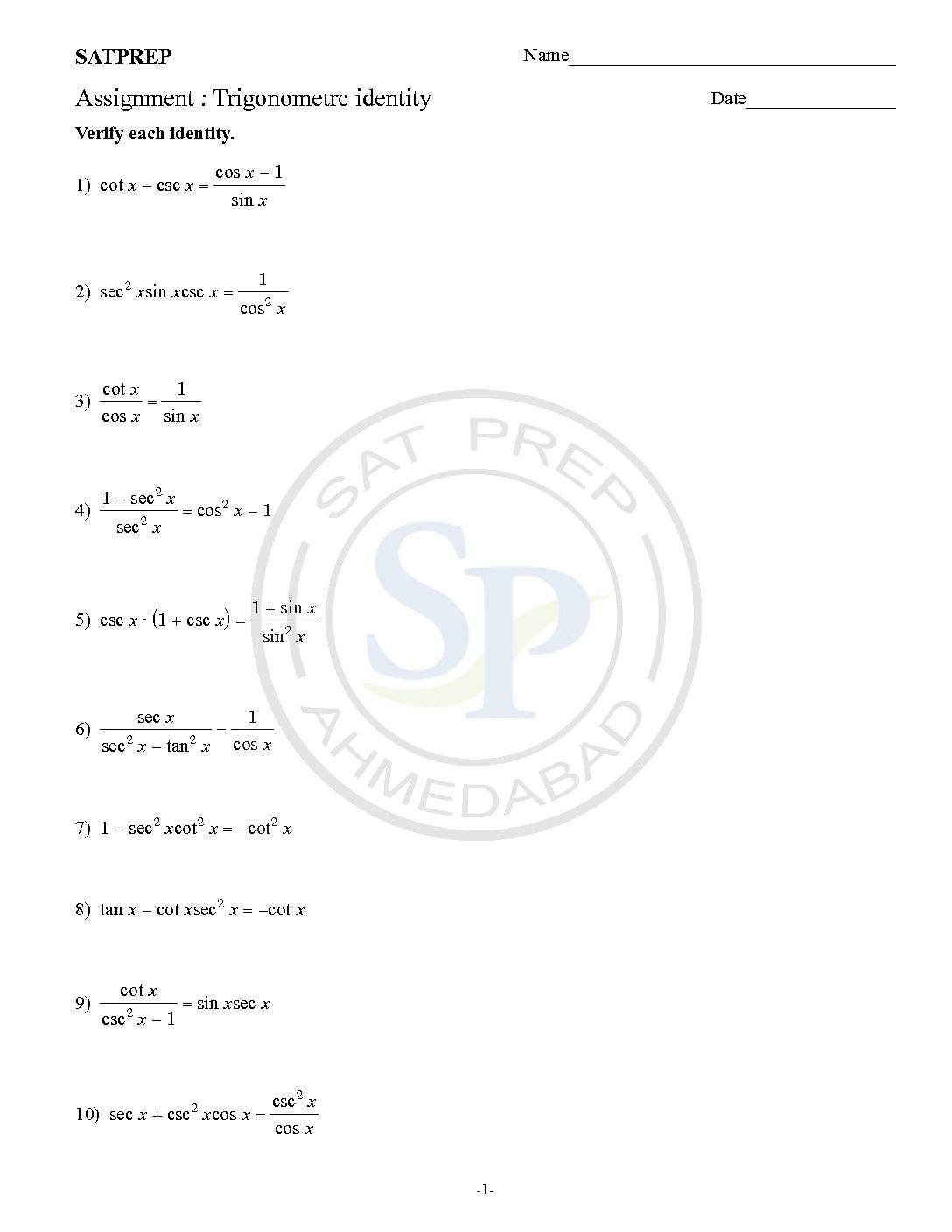
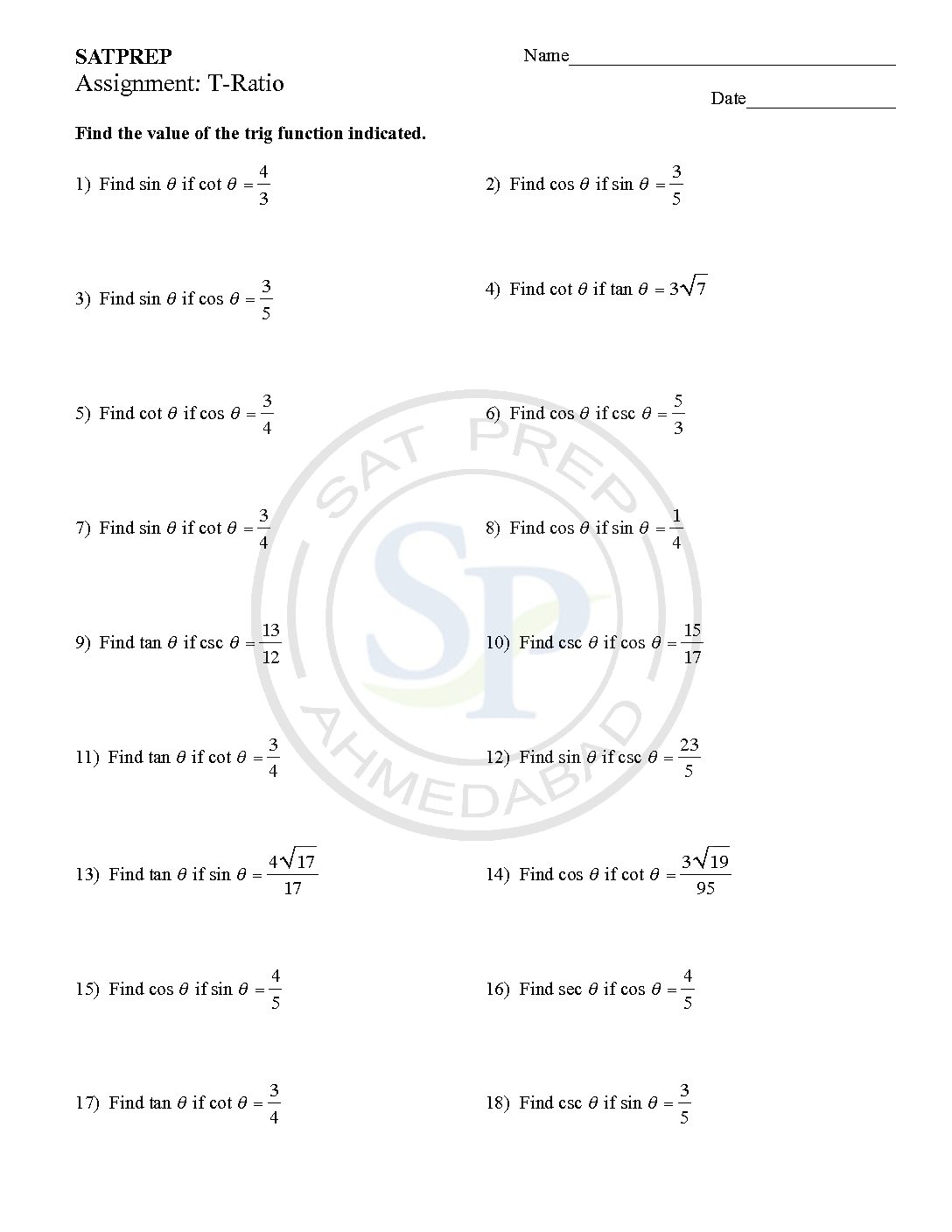
Worksheet of trigonometric identities . To prove that the left side is equal to the right side. Hence we have to use all six ratio their reciprocal. Also we have to use trigonometric relationship. As well as we use algebraic identity. Trigonometric identity
You are browsing archives for
Tag: Trigonometric
Trigonometric Equation
Transformed trigonometric equation adjusting their amplitude, period, phase shift, and vertical shift. Hence we have to find solution accordingly. Also we need to use GDC. Trigonometric equation
Mathematical Induction with Trigonometri...
Principle of Mathematical Induction, is a way to prove a statement is true by first making an assumption or hypothesis. There are only three steps for a Proof by Mathematical Induction before we can draw our conclusion. Once P(k+1) has been proved to be true, the statement is true for all values of the variable, by Principle of Mathematical […]
Integration by trigonometric substitutio...
This post is about worksheet of Integration by trigonometric substitution. It also one of most important concept of integral calculus . The function ƒ(φ(t))φ′(t) is also integrable on [a,b] Integration by substitution
Integration by substitution
This post is about worksheet of integration by trigonometric substitution. It also one of most important concept of integral calculus . The function ƒ(φ(t))φ′(t) is also integrable on [a,b] Integration by trigonometric substitutions
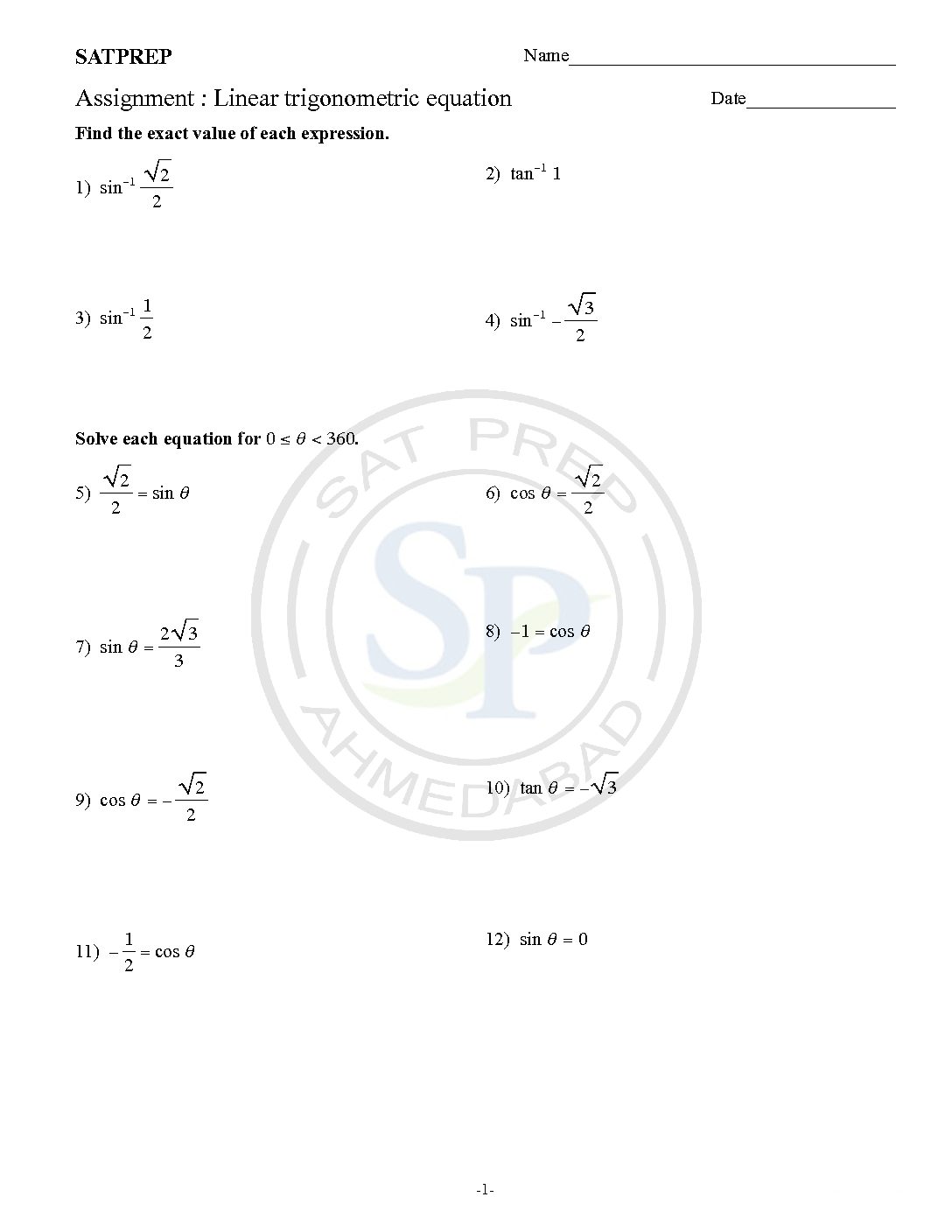
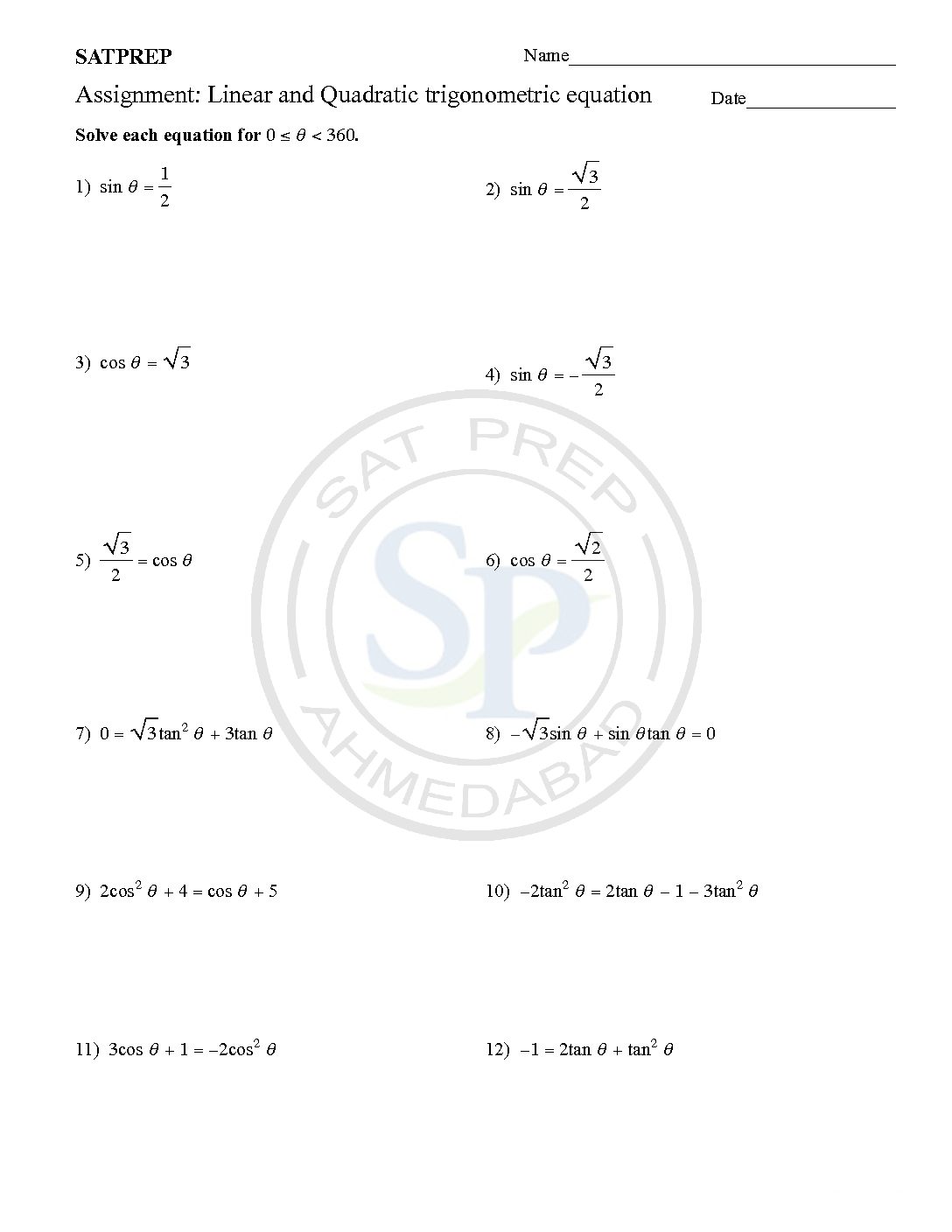
Linear trigonometric equation
Linear Trigonometric equations are either linear or quadratic in nature. To find the angle value(s) that satisfy the given equation. Because it is linear trigonometric eq. hence it has two roots. Linear trigonometric eq
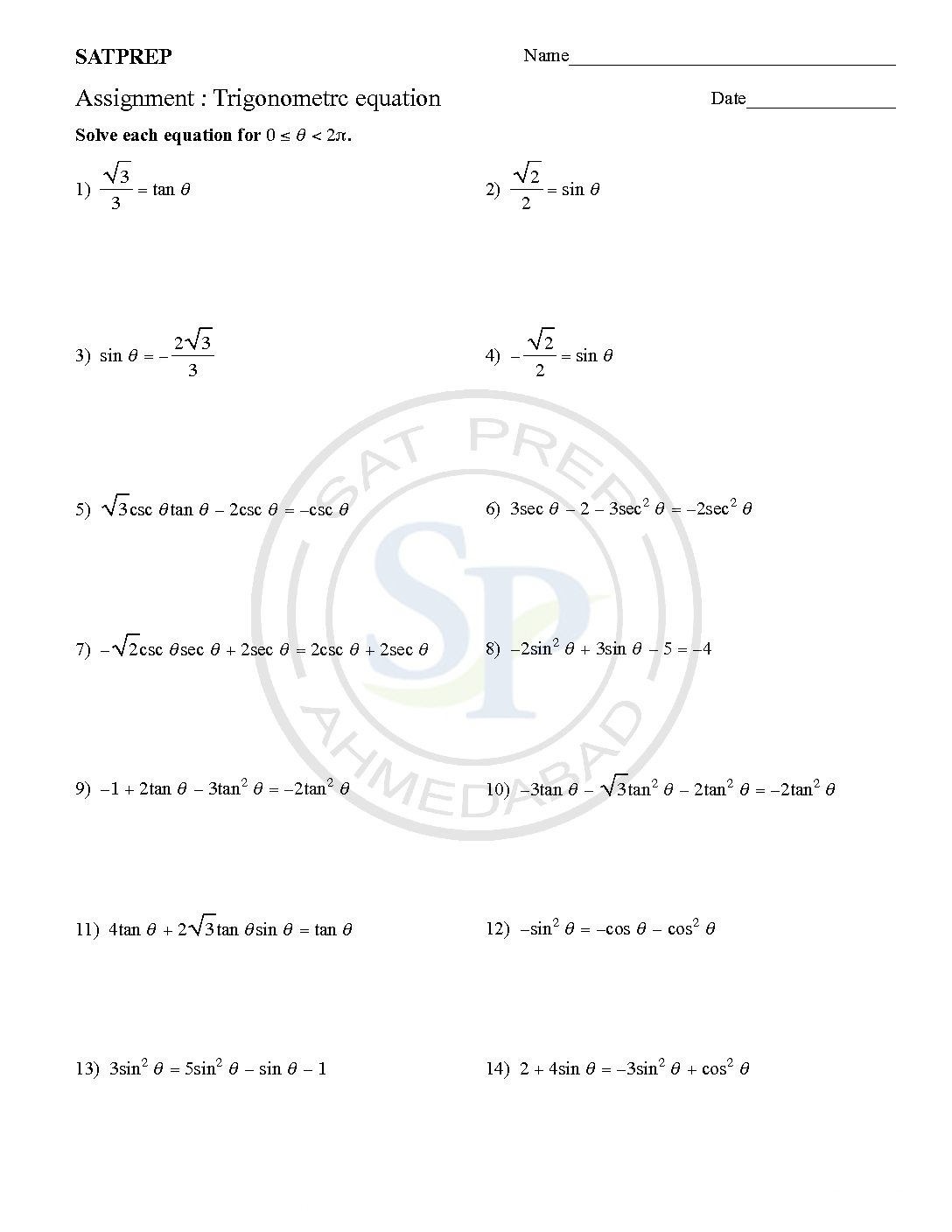
Trigonometric Equation (Radian)
Trigonometric Equation involve one or more trigonometric ratios of unknown angles. Due to difference unit of angle , hence it gives angle in different form. Similarly it give value in radian. Trigonometric equation
Trigonometric Equation(Degree)
Trigonometric Equations involve one or more trigonometric ratios of unknown angles. Due to difference unit of angle , hence it gives angle in two different form. Similarly it give value in degree. Trigonometric Equation
Trigonometric identity
Trig identity is equations that are true for Right Angled Triangles. D1: sin 2A+ cos 2A=1 D2: 1+ tan 2A= sec 2A D3: 1+ cot 2A= csc 2A Hence trigonometric identities are prove by above D1,D2 and D3. Similarly also using reciprocal identity. Trigonometric Identity
Trigonometric ratio
The ratios of the sides of a right triangle are called trigonometric ratios. Sine, Cosine and Tangent are main ratio while rest three reciprocal. Hence Sine and Cosine are the trigonometric ratios, whose values are less that 1 for an acute angle. Because they are periodic. Trigonometric ratio